Summary
1. Glutamate–NMDA receptor excitotoxicity and oxidative stress are two common mechanisms associated with most neurodegenerative diseases. We hypothesize that the vital state of neurons is regulated in part by two key transcription factors, CREB and NF-κB. To test this hypothesis we used hippocampal–entorhinal cortex slice cultures.
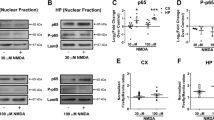
2. Glutamate neurotoxicity and oxidative stress neurotoxicity, using hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) are both associated with a decrease in CREB DNA binding and an increase in NF-κB DNA binding.
3. Agents that modulate CREB and NF-κB DNA-binding activity alter neurotoxicity. Rolipram, a phosphodiesterase IV inhibitor, increased CREB DNA binding activity and decreased toxicity, whereas TNFα, increased NF-κB DNA-binding activity and increased neurotoxicity to both glutamate and H2O2. Ethanol decreased CREB and increased NF-κB DNA-binding activity and increased neurotoxicity to both glutamate and H2O2.
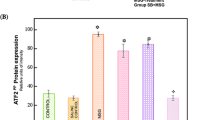
4. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a transcriptionally regulated trophic factor whose expression follows sensitivity to toxicity suggesting it is one of the transcriptionally regulated factors that contributes to neuronal vitality secondary to the balance of CREB–NF-κB-activated transcription. Together these studies suggest that neurotoxicity through glutamate–NMDA receptors or oxidative stress is dependent upon CREB and NF-κB DNA transcription that regulates vitality of neurons.













Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bison, S., and Crews, F. (2003). Alcohol withdrawal increases neuropeptide Y immunoreactivity in rat brain. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 27:1173–1183.
Buntinx, M., Stinissen, P., Steels, P., Ameloot, M., and Raus, J. (2002). Immune-mediated oligodendrocyte injury in multiple sclerosis: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 22:391–424.
Carlezon, W. A., Jr., Duman, R. S., and Nestler, E. J. (2005). The many faces of CREB. Trends Neurosci. 28:436–445.
Chandler, L. J., Sumners, C., and Crews, F. T. (1993). Ethanol inhibits NMDA receptor-mediated excitotoxicity in rat primary neuronal cultures. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 17:54–60.
Chao, C. C., Molitor, T. W., and Hu, S. (1993). Neuroprotective role of IL-4 against activated microglia. J. Immunol. 151:1473–1481.
Cheng, B., Christakos, S., and Mattson, M. P. (1994). Tumor necrosis factors protect neurons against metabolic-excitotoxic insults and promote maintenance of calcium homeostasis. Neuron. 12:139–153.
Cicchetti, F., Brownell, A. L., Williams, K., Chen, Y. I., Livni, E., and Isacson, O. (2002). Neuroinflammation of the nigrostriatal pathway during progressive 6-OHDA dopamine degeneration in rats monitored by immunohistochemistry and PET imaging. Eur. J. Neurosci. 15:991–998.
Crews, F. T., Waage, H. G., Wilkie, M. B., and Lauder, J. M. (1999). Ethanol pretreatment enhances NMDA excitotoxicity in biogenic amine neurons: Protection by brain derived neurotrophic factor. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 23:1834–1842.
Crews, F. T., Collins, M. A., Dlugos, C., Littleton, J., Wilkins, L., Neafsey, E. J., Pentney, R., Snell, L. D., Tabakoff, B., Zou, J., and Noronha, A. (2004). Alcohol-induced neurodegeneration: When, where and why? Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 28:350–364.
Datta, K., Babbar, P., Srivastava, T., Sinha, S., and Chattopadhyay, P. (2002). p53 dependent apoptosis in glioma cell lines in response to hydrogen peroxide induced oxidative stress. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 34:148–157.
Emch, G. S., Hermann, G. E., and Rogers, R. C. (2000), TNF-alpha activates solitary nucleus neurons responsive to gastric distension. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 279:G582–G586.
Emch, G. S., Hermann, G. E., and Rogers, R. C. (2001). TNF-alpha-induced c-Fos generation in the nucleus of the solitary tract is blocked by NBQX and MK-801. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 281:R1394–1400.
Finkbeiner, S., Tavazoie, S. F., Maloratsky, A., Jacobs, K. M., Harris, K. M., and Greenberg, M. E. (1997). CREB: A major mediator of neuronal neurotrophin responses. Neuron. 19:1031–1047.
Flohe, L., Brigelius-Flohe, R., Saliou, C., Traber, M. G., and Packer, L. (1997). Redox regulation of NF-kappa B activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 22:1115–1126.
Fukuchi, M., Tabuchi, A., and Tsuda, M. (2005). Transcriptional regulation of neuronal genes and its effect on neural functions: Cumulative mRNA expression of PACAP and BDNF genes controlled by calcium and cAMP signals in neurons. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 98:212–218.
Ghosh, S., May, M. J., and Kopp, E. B. (1998). NF-kappa B and Rel proteins: Evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 16:225–260.
Grilli, M., and Memo, M. (1999). Possible role of NF-kappaB and p53 in the glutamate-induced pro-apoptotic neuronal pathway. Cell Death Differ. 6:22–27.
Hara, T., Hamada, J., Yano, S., Morioka, M., Kai, Y., and Ushio, Y. (2003). CREB is required for acquisition of ischemic tolerance in gerbil hippocampal CA1 region. J. Neurochem. 86:805–814.
Hardingham, G. E., and Bading, H. (2002). Coupling of extrasynaptic NMDA receptors to a CREB shut-off pathway is developmentally regulated. Biochim. Biophys Acta. 1600:148–153.
Hayakawa, M., Miyashita, H., Sakamoto, I., Kitagawa, M., Tanaka, H., Yasuda, H., Karin, M., Kikugawa, K. (2003). Evidence that reactive oxygen species do not mediate NF-kappaB activation. EMBO J. 22:3356–3366.
Heese, K., Fiebich, B. L., Bauer, J., and Otten, U. (1997). Nerve growth factor (NGF) expression in rat microglia is induced by adenosine A2a-receptors. Neurosci. Lett. 231:83–86.
Hermann, G. E., Rogers, R. C., Bresnahan, J. C., and Beattie, M. S. (2001). Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces cFOS and strongly potentiates glutamate-mediated cell death in the rat spinal cord. Neurobiol. Dis. 8:590–599.
Hinoi, E., Balcar, V. J., Kuramoto, N., Nakamichi, N., and Yoneda, Y. (2002). Nuclear transcription factors in the hippocampus. Prog. Neurobiol. 68:145–165.
Hu, B. R., Fux, C. M., Martone, M. E., Zivin, J. A., and Ellisman, M. H. (1999). Persistent phosphorylation of cyclic AMP responsive element-binding protein and activating transcription factor-2 transcription factors following transient cerebral ischemia in rat brain. Neuroscience 89:437–452.
Huang, E. J., and Reichardt, L. F. (2001). Neurotrophins: Roles in neuronal development and function. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24:677–736.
Hunot, S., and Hirsch, E. C. (2003). Neuroinflammatory processes in Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol. 53(Suppl 3):S49–S58; discussion S58–S60.
Jean, D., Harbison, M., McConkey, D. J., Ronai, Z., and Bar-Eli, M. (1998). CREB and its associated proteins act as survival factors for human melanoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 273:24884–24890.
Kaltschmidt, B., Baeuerle, P. A., and Kaltschmidt, C. (1993). Potential involvement of the transcription factor NF-kappa B in neurological disorders. Mol. Aspects Med. 14:171–190.
Lee, B., Butcher, G. Q., Hoyt, K. R., Impey, S., and Obrietan, K. (2005a). Activity-dependent neuroprotection and cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB): Kinase coupling, stimulus intensity, and temporal regulation of CREB phosphorylation at serine 133. J. Neurosci. 25:1137–1148.
Lee, C. S., Kim, Y. J., Ko, H. H., and Han, E. S. (2005b). Synergistic effects of hydrogen peroxide and ethanol on cell viability loss in PC12 cells by increase in mitochondrial permeability transition. Biochem. Pharmacol. 70:317–325.
Lee, Y., Aono, M., Laskowitz, D., Warner, D. S., and Pearlstein, R. D. (2004). Apolipoprotein E protects against oxidative stress in mixed neuronal-glial cell cultures by reducing glutamate toxicity. Neurochem. Int. 44:107–118.
Lonze, B. E., and Ginty, D. D. (2002). Function and regulation of CREB family transcription factors in the nervous system. Neuron. 35:605–623.
Mabuchi, T., Kitagawa, K., Kuwabara, K., Takasawa, K., Ohtsuki, T., Xia, Z., Storm, D., Yanagihara, T., Hori, M., and Matsumoto, M., (2001). Phosphorylation of cAMP response element-binding protein in hippocampal neurons as a protective response after exposure to glutamate in vitro and ischemia in vivo. J. Neurosci. 21:9204–9213.
MacKenzie, S. J., and Houslay, M. D. (2000). Action of rolipram on specific PDE4 cAMP phosphodiesterase isoforms and on the phosphorylation of cAMP-response-element-binding protein (CREB) and p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase in U937 monocytic cells. Biochem. J. 347:571–578.
Mantamadiotis, T., Lemberger, T., Bleckmann, S. C., Kern, H., Kretz, O., Martin Villalba, A., Tronche, F., Kellendonk, C., Gau, D., Kapfhammer, J., Otto, C., Schmid, W., Schutz, G. (2002). Disruption of CREB function in brain leads to neurodegeneration. Nat. Genet. 31:47–54.
Mattson, M. P., and Camandola, S. (2001). NF-kappaB in neuronal plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders. J. Clin. Invest. 107:247–254.
Meffert, M. K., and Baltimore, D. (2005). Physiological functions for brain NF-kappaB. Trends Neurosci. 28:37–43.
Meffert, M. K., Chang, J. M., Wiltgen, B. J., Fanselow, M. S., and Baltimore, D. (2003). NF-kappa B functions in synaptic signaling and behavior. Nat. Neurosci. 6:1072–1078.
Nakagawa, S., Kim, J. E., Lee, R., Chen, J., Fujioka, T., Malberg, J., Tsuji, S., Duman, R. S., (2002). Localization of phosphorylated cAMP response element-binding protein in immature neurons of adult hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 22:9868–9876.
Nanji, A. A., Jokelainen, K., Fotouhinia, M., Rahemtulla, A., Thomas, P., Tipoe, G. L., Su, G. L., Dannenberg, A. J., (2001). Increased severity of alcoholic liver injury in female rats: Role of oxidative stress, endotoxin, and chemokines. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 281:G1348–G1356.
Nawashiro, H., Martin, D., and Hallenbeck, J. M. (1997). Neuroprotective effects of TNF binding protein in focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 778:265–271.
Nestler, E. J. (2002). Common molecular and cellular substrates of addiction and memory. Neurobiol. Learn Mem. 78:637–647.
Noraberg, J., Kristensen, B. W., and Zimmer, J. (1999). Markers for neuronal degeneration in organotypic slice cultures. Brain Res. Brain Res. Protoc. 3:278–290.
O’Neill, L. A., and Kaltschmidt, C. (1997). NF-kappa B: A crucial transcription factor for glial and neuronal cell function. Trends Neurosci. 20:252–258.
Pandey, S. C., Chartoff, E. H., Carlezon, W. A. Jr., Zou, J., Zhang, H., Kreibich, A. S., Blendy, J. A., Crews, F. T., (2005). CREB gene transcription factors: Role in molecular mechanisms of alcohol and drug addiction. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 29:176–184.
Pizzi, M., Goffi, F., Boroni, F., Benarese, M., Perkins, S. E., Liou, H. C., and Spano, P. (2002). Opposing roles for NF-kappa B/Rel factors p65 and c-Rel in the modulation of neuron survival elicited by glutamate and interleukin-1beta. J. Biol. Chem. 277:20717–20723.
Riccio, A., Ahn, S., Davenport, C. M., Blendy, J. A., and Ginty, D. D. (1999). Mediation by a CREB family transcription factor of NGF-dependent survival of sympathetic neurons. Science 286:2358–2361.
Schneider, A., Martin-Villalba, A., Weih, F., Vogel, J., Wirth, T., and Schwaninger, M. (1999). NF-kappaB is activated and promotes cell death in focal cerebral ischemia. Nat. Med. 5:554–559.
Shieh, P. B., and Ghosh, A. (1999). Molecular mechanisms underlying activity-dependent regulation of BDNF expression. J. Neurobiol. 41:127–134.
Shrivastava, A., and Aggarwal, B. B. (1999). Antioxidants differentially regulate activation of nuclear factor-kappa B, activator protein-1, c-jun amino-terminal kinases, and apoptosis induced by tumor necrosis factor: Evidence that JNK and NF-kappa B activation are not linked to apoptosis. Antioxid. Redox Signal 1:181–191.
Silva, A. J., Kogan, J. H., Frankland, P. W., and Kida, S. (1998). CREB and memory. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 21:127–148.
Somers, J. P., DeLoia, J. A., and Zeleznik, A. J. (1999). Adenovirus-directed expression of a nonphosphorylatable mutant of CREB (cAMP response element-binding protein) adversely affects the survival, but not the differentiation, of rat granulosa cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 13:1364–1372.
Venters, H. D., Dantzer, R., and Kelley, K. W. (2000). Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces neuronal death by silencing survival signals generated by the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 917:210–220.
Venters, H. D., Tang, Q., Liu, Q., VanHoy, R. W., Dantzer, R., and Kelley, K. W. (1999). A new mechanism of neurodegeneration: A proinflammatory cytokine inhibits receptor signaling by a survival peptide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 96:9879–9884.
Walton, M., Woodgate, A. M., Muravlev, A., Xu, R., During, M. J., and Dragunow, M. (1999). CREB phosphorylation promotes nerve cell survival. J Neurochem. 73:1836–1842.
Walton, M. R., and Dragunow, I. (2000). Is CREB a key to neuronal survival? Trends Neurosci. 23:48–53.
Yamakawa, H., Ito, Y., Naganawa, T., Banno, Y., Nakashima, S., Yoshimura, S., Sawada, M., Nishimura, Y., Nozawa, Y., and Sakai, N., (2000). Activation of caspase-9 and -3 during H2O2-induced apoptosis of PC12 cells independent of ceramide formation. Neurol. Res. 22:556–564.
Zhang, P., Nelson, S., Summer, W. R., and Spitzer, J. A. (1997). Acute ethanol intoxication suppresses the pulmonary inflammatory response in rats challenged with intrapulmonary endotoxin. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 21:773–778.
Zou, J. Y., and Crews, F. T. (2005). TNF alpha potentiates glutamate neurotoxicity by inhibiting glutamate uptake in organotypic brain slice cultures: Neuroprotection by NF kappa B inhibition. Brain Res. 1034:11–24.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, J., Crews, F. CREB and NF-κB Transcription Factors Regulate Sensitivity to Excitotoxic and Oxidative Stress Induced Neuronal Cell Death. Cell Mol Neurobiol 26, 383–403 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-006-9045-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-006-9045-9