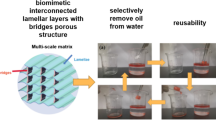
Abstract
Absorption is one of the most important methods for oil spill cleanup. An ideal absorbent is expected to possess advantages of low cost, green, high absorption capacity and excellent reusability. In this paper, a facile and environmentally-friendly top-down approach was developed for the preparation of the highly mesoporous and compressible sugarcane aerogel. Individualization of cellulose microfibrils within the sugarcane cell wall structure without introducing mechanical disintegration was realized, prepared by oxidation of delignified sugarcane at the neutral condition with TEMPO/NaClO/NaClO2 system. The results proved that the cellulose nanofibers in the cell wall maintains their natural alignment structure. The high fibril orientation and ordered arrangement of the network-like microstructure can be processed into anisotropic aerogels with high porosity (98.8%) and high compressive strength (0.53 MPa at 80% strain). The increased porosity and partial cellulose fibrillation result in specific surface areas of 32.94 m2/g. Subsequent hydrophobic coating with methyltrimethoxysilane, the hydrophobic and oleophilic sugarcane aerogel (water contact angle as high as 145.73°) was capable of adsorbing a wide range of organic solvents and oils (22.8 ~ 40.2 g/g). Moreover, the porous aerogel maintained a high oil-absorption capacity after absorbing and squeezing multiple times. This new sugarcane aerogel offers potential possibilities for the subsequent in high efficiency oil–water separation applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability material
The datasets used or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Al-Majed AA, Adebayo AR, Hossain ME (2012) A sustainable approach to controlling oil spills. J Environ Manage 113:213–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.07.034
Atlas RM (1995) Bioremediation of petroleum pollutants. Int Biodeterior 35:317–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/0964-8305(95)90041-1
Bansal S, von Arnim V, Stegmaier T, Planck H (2011) Effect of fibrous filter properties on the oil-in-water-emulsion separation and filtration performance. J Hazard Mater 190:45–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.01.134
Barrett EP, Joyner LG, Halenda PP (1951) The determination of pore volume and area distributions in porous substances. I. Computations from nitrogen isotherms. J Am Chem Soc 73:373–380. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01145a126
Borrega M, Gibson LJ (2015) Mechanics of balsa (Ochroma pyramidale) wood. Mech Mater 84:75–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmat.2015.01.014
Burgert I, Fratzl P (2009) Plants control the properties and actuation of their organs through the orientation of cellulose fibrils in their cell walls. Integr Comp Biol 49:69–79. https://doi.org/10.1093/icb/icp026
Burgert I, Cabane E, Zollfrank C, Berglund L (2015) Bio-inspired functional wood-based materials–hybrids and replicates. Int Mater Rev 60:431–450. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743280415Y.0000000009
Chen B, Ma Q, Tan C, Lim TT, Huang L, Zhang H (2015) Carbon-based sorbents with three-dimensional architectures for water remediation. Small 11:3319–3336. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201403729
Chen M, Zhang X, Zhang A, Liu C, Sun R (2016) Direct preparation of green and renewable aerogel materials from crude bagasse. Cellulose 23:1325–1334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0814-9
Chen C, Wang Y, Wu Q, Wan Z, Li D, Jin Y (2020) Highly strong and flexible composite hydrogel reinforced by aligned wood cellulose skeleton via alkali treatment for muscle-like sensors. Chem Eng J 400:125876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125876
De France KJ, Hoare T, Cranston ED (2017) Review of hydrogels and aerogels containing nanocellulose. Chem Mater 29:4609–4631. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b00531
Deschamps G, Caruel H, Borredon M-E, Albasi C, Riba J-P, Bonnin C, Vignoles C (2003) Oil removal from water by sorption on hydrophobic cotton fibers. 2. Study of sorption properties in dynamic mode. Environ Sci Technol 37:5034–5039. https://doi.org/10.1021/es020249b
Dilamian M, Noroozi B (2021) Rice straw agri-waste for water pollutant adsorption: Relevant mesoporous super hydrophobic cellulose aerogel. Carbohyd Polym 251:117016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117016
Doshi B, Sillanpää M, Kalliola S (2018) A review of bio-based materials for oil spill treatment. Water Res 135:262–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.02.034
Elanthikkal S, Gopalakrishnapanicker U, Varghese S, Guthrie JT (2010) Cellulose microfibres produced from banana plant wastes: isolation and characterization. Carbohydr Polym 80:852–859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.12.043
Foo K, Lee L, Hameed B (2013) Preparation of activated carbon from sugarcane bagasse by microwave assisted activation for the remediation of semi-aerobic landfill leachate. Bioresour Technol 134:166–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.01.139
French AD, Santiago Cintrón M (2013) Cellulose polymorphy, crystallite size, and the Segal Crystallinity Index. Cellulose 20:583–588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9833-y
Fu Q, Ansari F, Zhou Q, Berglund LA (2018) Wood nanotechnology for strong, mesoporous, and hydrophobic biocomposites for selective separation of oil/water mixtures. ACS Nano 12:2222–2230
Garemark J, Yang X, Sheng X, Cheung O, Sun L, Berglund LA, Li Y (2020) Top-down approach making anisotropic cellulose aerogels as universal substrates for multifunctionalization. ACS Nano 14:7111–7120. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c01888
Gary T, Burns RB et al (1992) High-temperature chemistry of the conversion of siloxanes to silicon carbide. Chem Mater 4:1313–1323. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm00024a035
Genç N, Dogan EC (2015) Adsorption kinetics of the antibiotic ciprofloxacin on bentonite, activated carbon, zeolite, and pumice. Desalination Water Treat 53:785–793. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.842504
Guan H, Cheng Z, Wang X (2018) Highly compressible wood sponges with a spring-like lamellar structure as effective and reusable oil absorbents. ACS Nano 12:10365–10373. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b05763
Guo Z, Long B, Gao S, Luo J, Wang L et al (2021) Carbon nanofiber based superhydrophobic foam composite for high performance oil/water separation. J Hazard Mater 402:123838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123838
Håkansson KM, Fall AB, Lundell F, Yu S, Krywka C et al (2014) Hydrodynamic alignment and assembly of nanofibrils resulting in strong cellulose filaments. Nat Commun 5:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5018
Han X, Wang Z, Ding L, Chen L, Wang F, Pu J, Jiang S (2021) Water molecule-induced hydrogen bonding between cellulose nanofibers toward highly strong and tough materials from wood aerogel. Chin Chem Lett 32:3105–3108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2021.03.044
Hashim SNAS, Zakaria S, Jaafar SNS, Hua CC Purification of empty fruit bunch (EFB) and kenaf soda lignin with acidified water. In: AIP Conference Proceedings, 2014. vol 1. American Institute of Physics, pp 129–135. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4895184
Hong H-J, Ban G, Kim HS, Jeong HS, Park MS (2021) Fabrication of cylindrical 3D cellulose nanofibril (CNF) aerogel for continuous removal of copper (Cu2+) from wastewater. Chemosphere 278:130288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130288
Jiang F, Hsieh Y-L (2013) Chemically and mechanically isolated nanocellulose and their self-assembled structures. Carbohydr Polym 95:32–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.02.022
Jiang F, Hsieh Y-L (2014) Super water absorbing and shape memory nanocellulose aerogels from TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibrils via cyclic freezing–thawing. J Mater Chem A 2:350–359. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ta13629a
Jing Z, Hao W, He X, Fan J, Zhang Y, Miao J, Jin F (2016) A novel hydrothermal method to convert incineration ash into pollucite for the immobilization of a simulant radioactive cesium. J Hazard Mater 306:220–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.12.024
Kang W, Cui Y, Qin L, Yang Y, Zhao Z, Wang X, Liu X (2020) A novel robust adsorbent for efficient oil/water separation: magnetic carbon nanospheres/graphene composite aerogel. J Hazard Mater 392:122499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122499
Karatum O, Steiner SA III, Griffin JS, Shi W, Plata DL (2016) Flexible, mechanically durable aerogel composites for oil capture and recovery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:215–224. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b08439
Kaya GG, Deveci H (2020) Synergistic effects of silica aerogels/xerogels on properties of polymer composites: a review. Ind Eng Chem Res 89:13–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2020.05.019
Kim S, Kim K, Jun G, Hwang W (2020) Wood-nanotechnology-based membrane for the efficient purification of oil-in-water emulsions. ACS Nano 14:17233–17240
Lee W (2000) Cellular solids, structure and properties. Mater Sci Technol 16:233. https://doi.org/10.1016/0921-5093(90)90295-e
Lewis A, Trudel BK, Belore RC, Mullin JV (2010) Large-scale dispersant leaching and effectiveness experiments with oils on calm water. Mar Pollut Bull 60:244–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2009.09.019
Li Y-Q, Samad YA, Polychronopoulou K, Liao K (2015) Lightweight and highly conductive aerogel-like carbon from sugarcane with superior mechanical and EMI shielding properties. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 3:1419–1427. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b00340
Li P, Cai Q, Lin W, Chen B, Zhang B (2016) Offshore oil spill response practices and emerging challenges. Mar Pollut Bull 110:6–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.06.020
Li Y, Wang B, Sui X, Xu H, Zhang L, Zhong Y, Mao Z (2017) Facile synthesis of microfibrillated cellulose/organosilicon/polydopamine composite sponges with flame retardant properties. Cellulose 24:3815–3823. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1373-z
Li Y, Zhu L, Wang B, Mao Z, Xu H et al (2018b) Fabrication of thermoresponsive polymer-functionalized cellulose sponges: flexible porous materials for stimuli-responsive catalytic systems. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:27831–27839. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b12060
Li F, Bhushan B, Pan Y, Zhao X (2019a) Bioinspired superoleophobic/superhydrophilic functionalized cotton for efficient separation of immiscible oil-water mixtures and oil-water emulsions. J Colloid Interface Sci 548:123–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.04.031
Li Y, Zhu L, Grishkewich N, Tam KC, Yuan J, Mao Z, Sui X (2019b) CO2-responsive cellulose nanofibers aerogels for switchable oil–water separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:9367–9373. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b22159
Li K, Luo Q, Xu J, Li K, Zhang W et al (2020a) A novel freeze-drying-free strategy to fabricate a biobased tough aerogel for separation of oil/water mixtures. J Agric Food Chem 68:3779–3785. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b07629
Li K, Wang S, Chen H, Yang X, Berglund LA, Zhou Q (2020b) Self-densification of highly mesoporous wood structure into a strong and transparent film. Adv Mater 32:2003653. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202003653
Li T, Song J, Zhao X, Yang Z, Pastel G et al. (2018a) Anisotropic, lightweight, strong, and super thermally insulating nanowood with naturally aligned nanocellulose. Sci Adv 4: eaar3724. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aar3724.
Liao Q, Su X, Zhu W, Hua W, Qian Z, Liu L, Yao J (2016) Flexible and durable cellulose aerogels for highly effective oil/water separation. RSC Adv 6:63773–63781. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra12356b
Lin J, Shang Y, Ding B, Yang J, Yu J, Al-Deyab SS (2012) Nanoporous polystyrene fibers for oil spill cleanup. Mar Pollut Bull 64:347–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.11.002
Liu P, Yu H, Hui F, Villena MA, Li X, Lanza M, Zhang Z (2020) Fabrication of 3D silica with outstanding organic molecule separation and self-cleaning performance. Appl Surf Sci 511:145537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.145537
Liu D, Jiang P, Xu X, Wu J, Lu Y et al (2022) MOFs decorated sugarcane catalytic filter for water purification. Chem Eng J 431:133992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.133992
Long S, Feng Y, Liu Y, Zheng L, Gan L et al (2021) Renewable and robust biomass carbon aerogel derived from deep eutectic solvents modified cellulose nanofiber under a low carbonization temperature for oil-water separation. Sep Purif Technol 254:117577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117577
Lou H, Zhu D, Yuan L, Lin H, Lin X, Qiu X (2015) Fabrication and properties of low crystallinity nanofibrillar cellulose and a nanofibrillar cellulose–graphene oxide composite. RSC Adv 5:67568–67573. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra13181b
Lu Y, Wang H, Lu Y (2019) An architectural exfoliated-graphene carbon aerogel with superhydrophobicity and efficient selectivity. Mater Des 184:108134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2019.108134
Meng Y, Liu T, Yu S, Cheng Y, Lu J, Wang H (2020) A lignin-based carbon aerogel enhanced by graphene oxide and application in oil/water separation. Fuel 278:118376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118376
Mo L, Pang H, Tan Y, Zhang S, Li J (2019) 3D multi-wall perforated nanocellulose-based polyethylenimine aerogels for ultrahigh efficient and reversible removal of Cu (II) ions from water. Chem Eng J 378:122157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122157
Muttin F (2008) Structural analysis of oil-spill containment booms in coastal and estuary waters. Appl Ocean Res 30:107–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apor.2008.07.001
Navi P, Heger F (2004) Combined densification and thermo-hydro-mechanical processing of wood. MRS Bull 29:332–336. https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs2004.100
Nguyen ST, Feng J, Le NT, Le AT, Hoang N, Tan VB, Duong HM (2013) Cellulose aerogel from paper waste for crude oil spill cleaning. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:18386–18391. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie4032567
Obataya E, Chen S (2018) Shape recovery and anomalous swelling of steam-compressed wood by swimming ring-like expansion of cell lumina. Wood Sci Technol 52:1009–1023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-018-1018-x
Orakwue EO, Asokbunyarat V, Rene ER, Lens PN, Annachhatre A (2016) Adsorption of Iron (II) from acid mine drainage contaminated groundwater using coal fly ash, coal bottom ash, and bentonite clay. Water Air Soil Pollut 227:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2772-8
Othman MBH, Ahmad Z, Akil HM, Zakaria MR, Ullah F (2015) The effects of the SiOSi segment presence in BAPP/BPDA polyimide system on morphology and hardness properties for opto-electronic application. Mater Des 82:98–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.05.054
Pääkkö M, Vapaavuori J, Silvennoinen R, Kosonen H, Ankerfors M et al (2008) Long and entangled native cellulose I nanofibers allow flexible aerogels and hierarchically porous templates for functionalities. Soft Matter 4:2492–2499. https://doi.org/10.1039/b810371b
Park S, Baker JO, Himmel ME, Parilla PA, Johnson DK (2010) Cellulose crystallinity index: measurement techniques and their impact on interpreting cellulase performance. Biotechnol Biofuels 3:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1754-6834-3-10
Peng L, Yuan S, Yan G, Yu P, Luo Y (2014) Hydrophobic sponge for spilled oil absorption. J Appl Polym Sci 131. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.40886
Peng B, Yao Z, Wang X, Crombeen M, Sweeney DG, Tam KC (2020) Cellulose-based materials in wastewater treatment of petroleum industry. Green Energy Environ 5:37–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gee.2019.09.003
Ras R, Ikkala O, Korhonen JT, Kettunen M (2011) Hydrophobic nanocellulose aerogels as floating, sustainable, reusable, and recyclable oil absorbents. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3:1813. https://doi.org/10.1021/am200475b
Segal L, Creely JJ, Martin A Jr, Conrad C (1959) An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-ray diffractometer. Text Res J 29:786–794
Sehaqui H, Salajková M, Zhou Q, Berglund LA (2010) Mechanical performance tailoring of tough ultra-high porosity foams prepared from cellulose I nanofiber suspensions. Soft Matter 6:1824–1832. https://doi.org/10.1039/b927505c
Tang H, Butchosa N, Zhou Q (2015) A transparent, hazy, and strong macroscopic ribbon of oriented cellulose nanofibrils bearing poly (ethylene glycol). Adv Mater 27:2070–2076. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201404565
Thai QB, Nguyen ST, Ho DK, Du Tran T, Huynh DM et al (2020) Cellulose-based aerogels from sugarcane bagasse for oil spill-cleaning and heat insulation applications. Carbohydr Polym 228:115365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115365
Tu K, Puértolas B, Adobes-Vidal M, Wang Y, Sun J et al (2020) Green synthesis of hierarchical metal–organic framework/wood functional composites with superior mechanical properties. Adv Sci 7:1902897. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201902897
Wang X, Cui X, Zhang L (2012) Preparation and characterization of lignin-containing nanofibrillar cellulose. Proc Environ Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2012.10.017
Wang J, Zheng Y, Wang A (2013) Coated kapok fiber for removal of spilled oil. Mar Pollut Bull 69:91–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.01.007
Wang D, Yu H, Fan X, Gu J, Ye S, Yao J, Ni Q (2018) High aspect ratio carboxylated cellulose nanofibers cross-linked to robust aerogels for superabsorption–flocculants: paving way from nanoscale to macroscale. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:20755–20766. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b04211
Wang K, Liu X, Tan Y, Zhang W, Zhang S, Li J (2019a) Two-dimensional membrane and three-dimensional bulk aerogel materials via top-down wood nanotechnology for multibehavioral and reusable oil/water separation. Chem Eng J 371:769–780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.04.108
Wicklein B, Kocjan A, Salazar-Alvarez G, Carosio F, Camino G, Antonietti M, Bergström L (2015) Thermally insulating and fire-retardant lightweight anisotropic foams based on nanocellulose and graphene oxide. Nat Nanotechnol 10:277–283. https://doi.org/10.1038/NNANO.2014.248
Wu J, Wang N, Wang L, Dong H, Zhao Y, Jiang L (2012) Electrospun porous structure fibrous film with high oil adsorption capacity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:3207–3212. https://doi.org/10.1021/am300544d
Xiao S, Gao R, Lu Y, Li J, Sun Q (2015a) Fabrication and characterization of nanofibrillated cellulose and its aerogels from natural pine needles. Carbohydr Polym 119:202–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.11.041
Xiao S, Gao R, Lu Y, Li J, Sun Q (2015b) Fabrication and characterization of nanofibrillated cellulose and its aerogels from natural pine needles. Carbohyd Polym 119:202–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.11.041
Yang X, Cranston ED (2014) Chemically cross-linked cellulose nanocrystal aerogels with shape recovery and superabsorbent properties. Chem Mater 26:6016–6025. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm502873c
Yang S, Chen L, Liu S, Hou W, Zhu J, Zhang Q, Zhao P (2020) Robust bifunctional compressed carbon foam for highly effective oil/water emulsion separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:44952–44960. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c11879
Yousefi H, Nishino T, Faezipour M, Ebrahimi G, Shakeri A (2011) Direct fabrication of all-cellulose nanocomposite from cellulose microfibers using ionic liquid-based nanowelding. Biomacromol 12:4080–4085. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm201147a
Zhang Z, Sèbe G, Rentsch D, Zimmermann T, Tingaut P (2014b) Ultralightweight and flexible silylated nanocellulose sponges for the selective removal of oil from water. Chem Mater 26:2659–2668. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm5004164
Zhang X, Wang H, Cai Z, Yan N, Liu M, Yu Y (2018) Highly compressible and hydrophobic anisotropic aerogels for selective oil/organic solvent absorption. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:332–340. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b03554
Zhang X, Zhang T, An X, Li M, Pei D, Zhang J, Li C (2022) Guiding cellular channels of artificial nanohybrid woods for anisotropic properties and solar-thermal evaporation. Chem Eng J 428:132060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.132060
Zhang, Zheng, Sèbe, Gilles, Rentsch et al. (2014a) Ultralightweight and Flexible Silylated NanocelluloseSponges for the Selective Removal of Oil from Water. Chemistry of Materials.
Zhanying Li, Lin S, Wenbin et al (2018) Excellent reusable chitosan/cellulose aerogel as an oil and organic solvent absorbent. Carbohyd Polym. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.03.027
Zheng Q, Cai Z, Gong S (2014) Green synthesis of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)–cellulose nanofibril (CNF) hybrid aerogels and their use as superabsorbents. J Mater Chem A 2:3110–3118. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA14642A
Zhou W, Li S, Liu Y, Xu Z, Wei S et al (2018) Dual superlyophobic copper foam with good durability and recyclability for high flux, high efficiency, and continuous oil–water separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:9841–9848. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b19853
Zhu H, Luo W, Ciesielski PN, Fang Z, Zhu J et al (2016) Wood-derived materials for green electronics, biological devices, and energy applications. Chem Rev 116:9305–9374. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00225
Acknowledgments
This work was financially sponsored by the Key R & D Plan of Zhejiang Province of China (Nos. 2020C04015 and 2021C03160), the Science and Technology Program of Zhejiang Province of China (No. LGF18C160002), the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province of China (No. LY19C160010) and the Science Foundation of Zhejiang Sci-Tech University (ZSTU) (No. 21202297-Y). Throughout the writing of this dissertation I have received a great deal of support and assistance. I would particularly like to acknowledge my teammate/group mate/team members for their wonderful collaboration and valuable guidance throughout my studies. They provided me with the tools that I needed to choose the right direction and successfully complete my dissertation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: XC, SY. Methodology: XC. Validation: SY. Formal analysis: XC, TC. Resources: MR, JC. Data Curation: MR, XC, YG. Writing—Original Draft: XC. Writing—Review & Editing: SY, YZ. Supervision: YZ, HS. Project administration: HS, YZ, YK. Funding acquisition: LL, HS, YZ.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Consent for publication
That the work described has not been published before and that it is not under consideration for publication elsewhere.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Yang, S., Chen, T. et al. Highly mesoporous and compressible sugarcane aerogel via top-down nanotechnology as effective and reusable oil absorbents. Cellulose 30, 1057–1072 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04949-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04949-0