Abstract
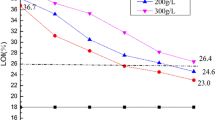
It is significant to treat cotton fabrics with flame retardant, which can effectively protect them from damage in the fire. A novel reactive flame retardant coating, ammonium salt of N,N-dimethylene-piperazine-(methylphosphonic acid) (ASNDP), was prepared and employed to enhance the anti-burning effect of pure cotton fabrics. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum were used to analyze the chemical composition of the synthesized ASNDP. The combustion behavior and anti-burning performance of coated cotton fabrics were fully investigated with using cone calorimetry test, limited oxygen index (LOI) test and vertical flammability test. The total heat release value of the sample coated with ASNDP (450 g/L) decreased to 3.7 ± 0.1 MJ/m2 and the LOI value of the sample with a weight gain of 17.4 ± 0.3% raised to 29.5 ± 0.1%. The thermal and thermo-oxidative stability of coated cotton fabrics were researched with thermogravimetric analysis. The integral procedural decomposition temperature (IPDT) value of coated cotton fabrics in nitrogen atmosphere increased from 610.1 to 1402.8 °C, which proved that ASNDP inhibited the thermal degradation of fiber unit by promoting the growth of the char layer. Besides, the morphological structure of uncoated and coated samples before and after combustion was characterized by scanning electron microscopy. It can be observed that the fiber skeleton of the coated cotton fabrics was evenly distributed and remained intact after combustion. The conclusion was that ASNDP endowed cotton fabrics with good flame retardancy, and effectively performed the flame-retardant effect in both gas phase and the condensed phase.
Graphic abstract
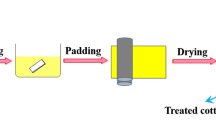
A novel phosphorus–nitrogen synergistic flame retardant containing multiple reactive groups was successfully synthesized and applied to improve the flame retardancy and thermal stability of pure cotton fabrics.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alongi J, Malucelli G (2015) Cotton flame retardancy: state of the art and future perspectives. RSC Adv 5:24239–24263. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA01176K
Alongi J, Ciobanu M, Malucelli G (2011) Novel flame retardant finishing systems for cotton fabrics based on phosphorus-containing compounds and silica derived from sol–gel processes. Carbohydr Polym 85:599–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.03.024
Barbalini M, Bartoli M, Tagliaferro A, Malucelli G (2020) Phytic acid and biochar: an effective all bio-sourced flame retardant formulation for cotton fabrics. Polymers 12:811. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040811
Carosio F, Fontaine G, Alongi J, Bourbigot S (2015) Starch-based layer by layer assembly: efficient and sustainable approach to cotton fire protection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:12158–12167. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b02507
Castellano A, Colleoni C, Iacono G, Mezzi A, Plutino MR, Malucelli G, Rosace G (2019) Synthesis and characterization of a phosphorous/nitrogen based sol–gel coating as a novel halogen- and formaldehyde-free flame retardant finishing for cotton fabric. Polym Degrad Stab 162:148–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2019.02.006
Cheng XW, Tang RC, Guan JP, Zhou SQ (2020) An eco-friendly and effective flame retardant coating for cotton fabric based on phytic acid doped silica sol approach. Prog Org Coat. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2020.105539
Dong CH, Lu Z, Wang P, Zhu P, Li XC, Sui SY, Zhang L, Liu J (2017) Flammability and thermal properties of cotton fabrics modified with a novel flame retardant containing triazine and phosphorus components. Text Res J 87:1367–1376. https://doi.org/10.1177/0040517516652349
Dong CH, Sun L, Ma XB, Lu Z, He PS, Zhu P (2019) Synthesis of a novel linear alpha, omega-di (chloro phosphoramide) polydimethylsiloxane and its applications in improving flame-retardant and water-repellent properties of cotton fabrics. Polymers 11:1829. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11111829
Fan MS, Feng N, Zhang YJ, Wang ZC, Qu MJ, Zhang GX (2019) Synergistic effects of aluminium hypophosphite on the flame retardancy and thermal degradation behaviours of a novel intumescent flame retardant thermoplastic vulcanisate composite. Plast Rubber Compos 48:270–280. https://doi.org/10.1080/14658011.2019.1606580
Fang F, Chen XX, Zhang X, Cheng C, Xiao DZ, Meng YD, Ding X, Zhang H, Tian XY (2016) Environmentally friendly assembly multilayer coating for flame retardant and antimicrobial cotton fabric. Prog Org Coat 90:258–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2015.09.025
He PS, Chen XY, Zhu P, Liu J, Fan GD, Sui SY, Lu Z, Dong CH (2018) Preparation and flame retardancy of reactive flame retardant for cotton fabric. J Therm Anal Calorim 132:1771–1781. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7057-6
Huang S, Feng YJ, Li SN, Zhou Y, Zhang FX, Zhang GX (2019) A novel high whiteness flame retardant for cotton. Polym Degrad Stab 164:157–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2019.03.014
Jia YL, Lu Y, Zhang GX, Liang YJ, Zhang FX (2017) Facile synthesis of an eco-friendly nitrogen-phosphorus ammonium salt to enhance the durability and flame retardancy of cotton. J Mater Chem A 5:9970–9981. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TA01106G
Jiang ZM, Li H, He YW, Liu Y, Dong CH, Zhu P (2019) Flame retardancy and thermal behavior of cotton fabrics based on a novel phosphorus-containing siloxane. Appl Surf Sci 479:765–775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.02.159
Jin XD, Gu XY, Chen C, Tang WF, Li HF, Liu XD, Bourbigot S, Zhang ZW, Sun J, Zhang S (2017) The fire performance of polylactic acid containing a novel intumescent flame retardant and intercalated layered double hydroxides. J Mater Sci 52:12235–12250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1354-5
Laufer G, Kirkland C, Morgan AB, Grunlan JC (2012) Intumescent multilayer nanocoating, made with renewable polyelectrolytes, for flame-retardant cotton. Biomacromolecules 13:2843–2848. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm300873b
Lee DH, Jang J (2020) Synergistic flame-retardant finishing of cotton using dichlorotriazinyl phosphonate and triethanolamine. Fiber Polym 21:343–349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-020-9442-6
Li SN, Zhong L, Huang S, Wang DF, Zhang FX, Zhang GX (2019a) A novel flame retardant with reactive ammonium phosphate groups and polymerizing ability for preparing durable flame retardant and stiff cotton fabric. Polym Degrad Stab 164:145–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2019.04.009
Li SS, Lin XH, Liu Y, Li R, Ren XH, Huang TS (2019b) Phosphorus–nitrogen–silicon-based assembly multilayer coating for the preparation of flame retardant and antimicrobial cotton fabric. Cellulose 26:4213–4223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02373-5
Ling C, Guo LM (2020) Preparation of a flame-retardant coating based on solvent-free synthesis with high efficiency and durability on cotton fabric. Carbohydr Polym 230:115648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115648
Liu J, Dong CH, Zhang Z, Kong DZ, Sun H, Lu Z (2020) Multifunctional flame-retarded and hydrophobic cotton fabrics modified with a cyclic phosphorus/polysiloxane copolymer. Cellulose 27:3531–3549. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03016-w
Nguyen TMD, Chang S, Condon B, Uchimiya M, Fortier C (2012) Development of an environmentally friendly halogen-free phosphorus–nitrogen bond flame retardant for cotton fabrics. Polym Adv Technol 23:1555–1563. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.3029
Pan Y, Liu LX, Wang X, Song L, Hu Y (2018) Hypophosphorous acid cross-linked layer-by-layer assembly of green polyelectrolytes on polyester-cotton blend fabrics for durable flame-retardant treatment. Carbohydr Polym 201:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.08.044
Park SJ, Kim HC (2001) Thermal stability and toughening of epoxy resin with polysulfone resin. J Polym Sci 39:121–128. https://doi.org/10.1002/1099-0488(20010101)39:1%3c121:AID-POLB110%3e3.0.CO;2-N
Qin HL, Li XF, Zhang XL, Guo ZG (2019) Preparation and performance testing of superhydrophobic flame retardant cotton fabric. New J Chem 43:5839–5848. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NJ00307J
Ran GW, Liu XD, Guo J, Sun J, Li HF, Gu XY, Zhang S (2019) Improving the flame retardancy and water resistance of polylactic acid by introducing polyborosiloxane microencapsulated ammonium polyphosphate. Compos Part B Eng 173:106772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.04.033
Rosace G, Castellano A, Trovato V, Iacono G, Malucelli G (2018) Thermal and flame retardant behaviour of cotton fabrics treated with a novel nitrogen-containing carboxyl-functionalized organophosphorus system. Carbohydr Polym 196:348–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.05.012
Sun YF, Liu CY, Hong Y, Liu RP, Zhou XD (2019) Synthesis and application of self-crosslinking and flame retardant waterborne polyurethane as fabric coating agent. Prog Org Coat 137:105323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2019.105323
Thota S, Somisetti V, Kulkarni S, Kumar J, Nagarajan R, Mosurkal R (2020) Covalent functionalization of cellulose in cotton and a nylon-cotton blend with phytic acid for flame retardant properties. Cellulose 27:11–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02801-6
van der Veen I, de Boer J (2012) Phosphorus flame retardants: properties, production, environmental occurrence, toxicity and analysis. Chemosphere 88:1119–1153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.03.067
Wan CY, Liu MS, Tian PX, Zhang GX, Zhang FX (2020) Renewable vitamin B5 reactive N-P flame retardant endows cotton with excellent fire resistance and durability. Cellulose 27:1745–1761. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02886-z
Wang XY, Lu CQ, Chen CX (2014) Effect of chicken-feather protein-based flame retardant on flame retarding performance of cotton fabric. J Appl Polym Sci 131:40584. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.40584
Wei YX, Deng C, Wei WC, Chen H, Wang YZ (2019) Hybrid nanorods composed of titanium, silicon, and organophosphorus as additives for flame-retardant polycarbonate. ACS Appl Nano Mater 2:4859–4868. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.9b00814
Xu F, Zhong L, Xu Y, Zhang C, Wang P, Zhang FX, Zhang GX (2019) Synthesis of three novel amino acids-based flame retardants with multiple reactive groups for cotton fabrics. Cellulose 26:7537–7552. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02599-3
Xu DH, Gao ZY, Xu B, Ren H, Zhao XS, Zhang YN, Wang SJ, Jiang ZM, Zhu P (2020a) A facile and effective flame-retardant coating for cotton fabric with α-aminodiphosphonate siloxane. Polym Degrad Stab 180:109312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2020.109312
Xu DH, Wang SJ, Wang YM, Liu Y, Dong CH, Jiang ZM, Zhu P (2020b) Preparation and mechanism of flame-retardant cotton fabric with phosphoramidate siloxane polymer through multistep coating. Polymers 12:1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071538
Zhang Z, Dong CH, Liu J, Kong DZ, Sun L, Lu Z (2020) Preparation of a synergistic reactive flame retardant based on silicon, phosphorus and nitrogen and its application to cotton fabrics. Cellulose 27:1799–1815. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02900-4
Zhao PH, Li XH, Zhang M, Liu SN, Liang WJ, Liu YQ (2014) Highly flame-retarding cotton fabrics with a novel phosphorus/nitrogen intumescent flame retardant. Korean J Chem Eng 31:1592–1597. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-014-0095-2
Zhao X, Gao S, Liu GS (2016) A THEIC-based polyphosphate melamine intumescent flame retardant and its flame retardancy properties for polylactide. J Anal Appl Pyrol 122:24–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2016.10.029
Zhao B, Liu YT, Zhang CY, Liu DY, Li F, Liu YQ (2017) A novel phosphoramidate and its application on cotton fabrics: synthesis, flammability and thermal degradation. J Anal Appl Pyrol 125:109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2017.04.011
Zheng DD, Zhou JF, Wang Y, Zhang FX, Zhang GX (2018) A reactive flame retardant ammonium salt of diethylenetriaminepenta(methylene-phosphonic acid) for enhancing flame retardancy of cotton fabrics. Cellulose 25:787–797. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1543-z
Zhu WJ, Yang MY, Huang H, Dai Z, Cheng BW, Hao SS (2020) A phytic acid-based chelating coordination embedding structure of phosphorus–boron–nitride synergistic flame retardant to enhance durability and flame retardancy of cotton. Cellulose 27:4817–4829. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03063-3
Acknowledgments
We thankfully acknowledge the funding from the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (Grant No. ZR2018MEM026) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China, China (Grant No. 51991354).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, L., Wang, H., Li, W. et al. Preparation, characterization and testing of flame retardant cotton cellulose material: flame retardancy, thermal stability and flame-retardant mechanism. Cellulose 28, 3789–3805 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03632-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03632-6