Abstract
The present paper reports a detailed experimental vibrational analysis, performed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy in attenuated total reflectance geometry (FTIR-ATR), of water confined in the pores of cellulose nano-sponges (CNSs), prepared using TEMPO oxidized and ultra-sonicated cellulose nano-fibers (TOUS-CNFs) as three-dimensional scaffolds, and branched polyethyleneimine (bPEI) as the cross-linking agent. The analysis was carried out by varying hydration and cross-linker amount, with the aim of achieving a deep understanding of how the hydrogen bond (H-bond) scheme developed by engaged water molecules can play a role in the water adsorption process already observed at macroscopic level, furnishing at the same time evidence of a nano-porous network for CNSs. In particular, the combined investigation of the FTIR-ATR spectra of CNSs hydrated with H2O and D2O allowed for the selective analysis of vibrational modes of entrapped water molecules, namely O–H stretching and HOH bending modes. As main result, a destructuring effect of hydration on the H-bond pattern of interfacial water molecules is revealed, associated to structural modifications of the bPEI/TOUS-CNFs network previously detected by small angle neutron scattering (SANS) technique. It turned out to be more relevant for low bPEI amounts. In addition, a supercooled behavior of entrapped water molecules is detected, supporting the idea of a nano-confinement for water in these systems. The obtained information can be very helpful in view of all the possible applications of bPEI-TOCNF sponges as efficient adsorbent materials, especially for water remediation.
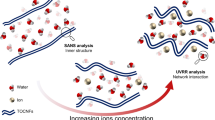
Graphic abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
10 September 2020
Co-author Andrea Fiorati’s status as one of the two corresponding authors was not originally indicated on the published version. This Correction remedies that omission.
References
Andrade DRM, Mendonça MH, Helm CV, Magalhães WLE, de Muniz GIB, Kestur SG (2015) Assessment of nano cellulose from peach palm residue as potential food additive: part II: preliminary studies. J Food Sci Technol 52:5641–5650. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1684-0
Ansaloni L, Salas-Gay J, Ligi S, Baschetti MG (2017) Nanocellulose-based membranes for CO2 capture. J Membr Sci 522:216–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.09.024
Bartolozzi I, Daddi T, Punta C, Fiorati A, Iraldo F (2020) Life cycle assessment of emerging environmental technologies in the early stage of development: a case study on nanostructured materials. J Ind Ecol 24:101–115. https://doi.org/10.1111/jiec.12959
Bayer T, Cunning BV, Selyanchyn R, Nishihara M, Fujikawa S, Sasaki K, Lyth SM (2016) High temperature proton conduction in nanocellulose membranes: paper fuel cells. Chem Mater 28:4805–4814. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.6b01990
Bellavia G, Paccou L, Achir S, Guinet Y, Siepmann J, Hédoux A (2013) Analysis of bulk and hydration water during thermal lysozyme denaturation using Raman scattering. Food Biophys 8:170–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-013-9294-3
Bellissent-Funel MC, Lal J, Bosio L (1993) Structural study of water confined in porous glass by neutron scattering. J Chem Phys 98:4246. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.465031
Bergman R, Swanson J (2000) Dynamics of supercooled water in confined geometry. Nature 403:283–286. https://doi.org/10.1038/35002027
Brubach JB, Mermet A, Filabozzi A, Gerschel A, Roy P (2005) Signatures of the hydrogen bonding in the infrared bands of water. J Chem Phys 122:184509. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1894929
Carey DM, Korenowski GM (1998) Measurement of the Raman spectrum of liquid water. J Chem Phys 108:2669–2775. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.475659
Castiglione F, Crupi V, Majolino D, Mele A, Rossi B, Trotta F, Venuti V (2012) Inside new materials: an experimental numerical approach for the structural elucidation of nanoporous cross-linked polymers. J Phys Chem B 116:13133–13140. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp307978e
Castiglione F, Crupi V, Majolino D, Mele A, Rossi B, Trotta F, Venuti V (2013) Vibrational spectroscopy investigation of swelling phenomena in cyclodextrin nanosponges. J Raman Spectrosc 44:1463–1469. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.4282
Castro C, Zuluaga R, Putaux JL, Caro G, Mondragon I, Gañán P (2011) Structural characterization of bacterial cellulose produced by Gluconacetobacter swingsii sp. from Colombian agroindustrial wastes. Carbohydr Polym 84:96–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.10.072
Chen SL, Huang XJ, Xu ZK (2011) Functionalization of cellulose nanofiber mats with phthalocyanine for decoloration of reactive dye wastewater. Cellulose 18:1295–1303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-011-9572-5
Chen HC, Lin HC, Chen HH, Mai FD, Liu YC, Lin CM, Chang CC, Tsai HY, Yang CP (2015) Innovative strategy with potential to increase hemodialysis efficiency and safety. Sci Rep 4:4425. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep04425
Coleman MM, Graf JF, Painter PC (1991) Specific interactions and the miscibility of polymer blends. Technomic Publishing Co., Lancaster
Corsi I, Winther-Nielsen M, Sethi R, Punta C, Della Torre C, Libralato G, Lofrano G, Sabatini L, Aiello M, Fiordi L, Cinuzzi F, Caneschi F, Pellegrini D, Buttino I (2018) Ecofriendly nanotechnologies and nanomaterials for environmental applications: key issue and consensus recommendations for sustainable and ecosafe nanoremediation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 154:237–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.02.037
Crupi V, Longo F, Majolino D, Venuti V (2005) T dependence of vibrational dynamics of water in ion-exchanged zeolites a: a detailed Fourier transform infrared attenuated total reflection study. J Chem Phys 123:154702. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2060687
Crupi V, Longo F, Majolino D, Venuti V (2007) Raman spectroscopy: probing dynamics of water molecules confined in nanoporous silica glasses. Eur Phys J Spec Top 141:61–64. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2007-00018-x
Crupi V, Majolino D, Longo F, Migliardo P, Venuti V (2006) FTIR/ATR study of water encapsulated in Na-A and Mg-exchanged A-zeolites. Vib Spectrosc 42:375–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vibspec.2006.05.007
Crupi V, Majolino D, Migliardo P, VenutiBellissent-Funel VMC (2003) Structure and dynamics of water confined in a nanoporous sol-gel silica glass: a neutron scattering study. Mol Phys 101:3323–3333. https://doi.org/10.1080/00268970310001638790
Crupi V, Majolino D, Migliardo P, Venuti V, Dianoux AJ (2002) Low-frequency dynamical response of confined water in normal and supercooled regions obtained by IINS. Appl Phys A 74:s555–s556. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390101120
David JG, Gierszal KP, Wang P, Ben-Amotz D (2012) Water structural transformation at molecular hydrophobic interfaces. Nature 491:582–585. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11570
Dong H, Snyder JF, Williams KS, Andzelm JW (2013) Cation-induced hydrogels of cellulose nanofibrils with tunable moduli. Biomacromol 14:3338–3345. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm400993f
Erlandsson J, Durán VL, Granberg H, Sandberg M, Larsson PA, Wågberg L (2016) Macro-and mesoporous nanocellulose beads for use in energy storage devices. Appl Mater Today 5:246–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2016.09.008
Fackler K, Stevanic JS, Ters T, Hinterstoisser B, Schwanninger M, Salmén L (2011) FT-IR imaging microscopy to localise and characterise simultaneous and selective white-rot decay within spruce wood cells. Holzforschung 65:411–420. https://doi.org/10.1515/hf.2011.048
Fiorati A, Grassi G, Graziano A, Liberatori G, Pastori N, Melone L, Bonciani L, Pontorno L, Punta C, Corsi I (2020) Eco-design of nanostructured cellulose sponges for sea-water decontamination from heavy metal ions. J Clean Prod 246:119009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119009
Fiorati A, Pastori N, Punta C, Melone L (2019) Spongelike functional materials from TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers. In: Trotta F, Mele A (eds) Nanosponges: synthesis and applications. Wiley-VCH, New York, pp 123–141
Fiorati A, Turco G, Travan A, Caneva E, Pastori N, Cametti M, Punta C, Melone L (2017) Mechanical and drug release properties of sponges from crosslinked cellulose nanofibers. ChemPlusChem 82:848–858. https://doi.org/10.1002/cplu.201700185
Goldman N, Saykally RJ (2004) Elucidating the role of many-body forces in liquid water. I. Simulations of water clusters on the VRT(ASP-W) potential surfaces. J Chem Phys 120:477. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1645777
Hospodarova V, Singovszka E, Stevulova N (2018) Characterization of cellulosic fibers by FTIR spectroscopy for their further implementation to building materials. Am J Analyt Chem 9:303–310. https://doi.org/10.4236/ajac.2018.96023
Isogai A, Saito T, Fukuzumi H (2011) TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers. Nanoscale 3:71–85. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0NR00583E
Li R, Jiang Z, Guan Y, Yang H, Liu B (2009) Effects of metal ion on the water structure studied by the Raman O–H stretching spectrum. J Raman Spectrosc 40:1200–1204. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.2262
Maréchal Y (2003) Observing the water molecule in macromolecules and aqueous media using infrared spectrometry. J Mol Struct 648:27–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2860(02)00493-3
Melone L, Bonafede S, Tushi D, Punta C, Cametti M (2015a) Dip in colorimetric fluoride sensing by a chemically engineered polymeric cellulose/bPEI conjugate in the solid state. RSC Adv 5:83197–83205. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA16764G
Melone L, Rossi B, Pastori N, Panzeri W, Mele A, Punta C (2015b) TEMPO-oxidized cellulose cross-linked with branched polyethyleneimine: nanostructured adsorbent sponges for water remediation. ChemPlusChem 80:1408–1415. https://doi.org/10.1002/cplu.201500145
Millo A, Raichlin Y, Katzir A (2005) Mid-infrared fiber-optic attenuated total reflection spectroscopy of the solid–liquid phase transition of water. Appl Spectrosc 59:460–466. https://doi.org/10.1366/0003702053641469
Murphy WF, Bernstein HJ (1972) Raman spectra and an assignment of the vibrational stretching region of water. J Phys Chem 76:1147–1152. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100652a010
O’Neill H, Pingali SV, Petridis L, He J, Mamontov E, Hong L, Urban V, Evans B, Langan P, Smith JC, Davison BH (2017) Dynamics of water bound to crystalline cellulose. Sci Rep 7:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-12035-w
Paladini G, Venuti V, Almásy L, Melone L, Crupi V, Majolino D, Pastori N, Fiorati A, Punta C (2019) Cross-linked cellulose nano-sponges: a small angle neutron scattering (SANS) study. Cellulose 26:9005–9019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02732-2
Perkins EL, Batchelor WJ (2012) Water Interaction in paper cellulose fibres as investigated by NMR pulsed field gradient. Carbohydr Polym 87:361–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.07.065
Petersen N, Gatenholm P (2011) Bacterial cellulose-based materials and medical devices: current state and perspectives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 5:1277–1286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3432-y
Pierre G, Punta C, Delattre C, Melone L, Dubessay P, Fiorati A, Pastori N, Galante YM, Michaud P (2017) TEMPO-mediated oxidation of polysaccharides: an ongoing story. Carbohydr Polym 165:71–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.02.028
Rossi B, Venuti V, Mele A, Punta C, Melone L, Crupi V, Majolino D, Trotta F, D’Amico F, Gessini A, Masciovecchio C (2015) Probing the molecular connectivity of water confined in polymer hydrogels. J Chem Phys 142:014901. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4904946
Rovere M, Gallo P (2003) Effects of confinement on static and dynamical properties of water. Eur Phys J E 12:77–81. https://doi.org/10.1140/epje/i2003-10027-5
Scherer JR, Go MK, Kint S (1974) Raman spectra and structure of water from − 10 to 90.deg. J Phys Chem 78:1304–1313. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100606a013
Schmidt DA, Miki K (2007) Structural correlations in liquid water: a new interpretation of IR spectroscopy. J Phys Chem A 111:10119–10122. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp074737n
Stefanutti E, Bove LE, Alabarse FG, Lelong G, Bruni F, Ricci MA (2019) Vibrational dynamics of confined supercooled water. J Chem Phys 150:224504. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5094147
Tomlinson-Phillips J, Davis J, Ben-Amotz D (2011) Structure and dynamics of water dangling OH bonds in hydrophobic hydration shells. comparison of simulation and experiment. J Phys Chem A 115:6177–6183. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp111346s
Valenzuela LM, Knight DD, Kohn J (2016) Developing a suitable model for water uptake for biodegradable polymers using small training sets. Int J Biomater 2016:6273414. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6273414
Venuti V, Rossi B, Crupi V, D'Amico F, Gessini A, Majolino D, Masciovecchio C, Stancanelli R, Ventura CA (2016) Solute-solvent interactions in aqueous solutions of sulfobutyl ether-beta-cyclodextrin as probed by UV-Raman and FTIR-ATR analysis. J Phys Chem B 120:3746–3753. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.6b02261
Venuti V, Rossi B, D'Amico F, Mele A, Castiglione F, Punta C, Melone L, Crupi V, Majolino D, Trotta F, Gessini A, Masciovecchio C (2015) Combining Raman and infrared spectroscopy as a powerful tool for the structural elucidation of cyclodextrin-based polymeric hydrogels. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17:10274–10282. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP00607D
Wall TT, Hornig DF (1965) Raman intensities of HDO and structure in liquid water. J Chem Phys 43:2079–2087. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1697078
Walrafen GE, Hokmababi MS, Yang WH (1986) Raman isosbestic points from liquid water. J Chem Phys 85:6964. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.451383
Xu F, Yu J, Tesso T, Dowell F, Wang D (2013) Qualitative and quantitative analysis of lignocellulosic biomass using infrared techniques: a mini-review. Appl Energy 104:801–809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2012.12.019
Yu S, Guccini V, Demmel F, Salazar-Alvarez G (2019) Water dynamics in hydrated carboxylated cellulose nanofibril membranes. ChemRxiv. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.26434/chemrxiv.9828308.v1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paladini, G., Venuti, V., Crupi, V. et al. FTIR-ATR analysis of the H-bond network of water in branched polyethyleneimine/TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nano-fiber xerogels. Cellulose 27, 8605–8618 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03380-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03380-7