Abstract
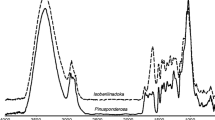
Wood-decay fungi have been mainly studied for their medicinal or nutraceutical properties, lignocellulolytic enzymes as well as their pathological role in plants. Recently they have also been recognized as a potential source of biocomposite materials due to the features of mycelial mats in several species. Chemical, physical-morphological and biological properties are affected by interspecific and intraspecific differences in composition of the cell wall regarding both major and minor constituents; thus, a preliminary characterization can optimize the strain selection for applied and research purposes. In the present study, 52 strains from 18 wood-decay fungal species were considered to build a general descriptive model based on the cell wall in the light of interspecific variability. Pure-cultured mycelia were dried and examined by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) to highlight the main different characteristics of each species. TGA profiles resulted more functional for a qualitative-quantitative description of major constituents (above all, β-glucans and chitin), whereas FTIR spectra are only qualitative and more difficult to analyze. Principal component analysis and cluster analysis confirmed the general descriptive model and allow interspecific comparison beyond intraspecific variability. In conclusion, TGA provides a simpler tool for screening of wood decay fungal strains and selection based on major cell wall constituents, namely chitin and glucans.
Graphic abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Mohsen AM, Jancar J, Massoud D, Fohlerova Z, Elhadidy H, Spotz Z, Hebeish A (2016) Novel chitin/chitosan-glucan wound dressing: isolation, characterization, antibacterial activity and wound healing properties. Int J Pharm 510(1):86–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.06.003
Ainsworth EA, Gillespie KM (2007) Estimation of total phenolic content and other oxidation substrates in plant tissues using Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. Nat Protoc 2(4):875–877. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.102
Baby S, Johnson AJ, Govindan B (2015) Secondary metabolites from Ganoderma. Phytochemistry 114:66–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2015.03.010
Barrientos RC, Clerigo MM, Paano AMC (2016) Extraction, isolation and MALDI-QTOF MS/MS analysis of β-D-Glucan from the fruiting bodies of Daedalea quercina. Int J Biol Macromol 93:226–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.08.044
Bolognesi S, Bernardi G, Callegari A, Dondi D, Capodaglio AG (2019) Biochar production from sewage sludge and microalgae mixtures: properties, sustainability and possible role in circular economy. Biomass Convers Biorefin. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-019-00572-5
Brugnerotto J, Lizardi J, Goycoolea FM, Argüelles-Monal W, Desbrieres J, Rinaudo M (2001) An infrared investigation in relation with chitin and chitosan characterization. Polymer 42(8):3569–3580. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-3861(00)00713-8
Chemical American Society (2020) SciFinder: a CAS solution. https://scifinder.cas.org. Accessed 18 Feb 2020
Corana F, Cesaroni V, Mannucci B, Baiguera RM, Picco AM, Savino E, Ratto D, Perini C, Kawagishi H, Girometta CE, Rossi P (2019) Array of metabolites in Italian Hericium erinaceus mycelium, primordium, and sporophore. Molecules 24:3511. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193511
Darmon S, Rudall K (1950) Infra-red and X-ray studies of chitin. Discuss Faraday Soc 9:251–260
Di Mario F, Rapana P, Tomati U, Galli E (2008) Chitin and chitosan from Basidiomycetes. Int J Biol Macromol 43(1):8–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2007.10.005
Erukhimovitch V, Tsror L, Hazanovsky M, Talyshinsky M, Mukmanov I, Souprun Y, Huleihel M (2005) Identification of fungal phyto-pathogens by Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) microscopy. J Agric Technol 1(1):145–152
Farinha I, Duarte P, Pimentel A, Plotnikova E, Chagas B, Mafra L, Grandfils C, Freitas F, Fortunato E, Reis MA (2015) Chitin–glucan complex production by Komagataella pastoris: downstream optimization and product characterization. Carbohydr Polym 130:455–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.05.034
Fiţigău IF, Peter F, Boeriu CG (2013) Structural analysis of lignins from different sources. Int J Chem Mol Nucl Mater Metall Eng 7(4):167–172
Gargano ML, van Griensven LJ, Isikhuemhen OS, Lindequist U, Venturella G, Wasser SP, Zervakis GI (2017) Medicinal mushrooms: valuable biological resources of high exploitation potential. Plant Biosyst 151(3):548–565. https://doi.org/10.1080/11263504.2017.1301590
Girometta C, Zeffiro A, Malagodi M, Savino E, Doria E, Nielsen E, Buttafava A, Dondi D (2017) Pretreatment of alfalfa stems by wood decay fungus Perenniporia meridionalis improves cellulose degradation and minimizes the use of chemicals. Cellulose 24:3803–3813. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1395-6
Girometta C, Picco AM, Baiguera RM, Dondi D, Babbini S, Cartabia M, Pellegrini M, Savino E (2019) Physico-mechanical and thermodynamic properties of mycelium-based biocomposites: a review. Sustainability 11(1):281. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11010281
Girometta C, Bernicchia A, Baiguera RM, Bracco F, Buratti S, Cartabia M, Picco AM, Savino E (2020) An Italian research culture collection of wood decay fungi. Diversity 12(2):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12020058
Gow NAR, Latge JP, Munro CA (2017) The fungal cell wall: structure, biosynthesis, and function. Microbiol Spectr. https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.funk-0035-2016
Grienke U, Zöll M, Peintner U, Rollinger JM (2014) European medicinal polypores: a modern view on traditional uses. J Ethnopharmacol 154(3):564–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2014.04.030
Haneef M, Ceseracciu L, Canale C, Bayer IS, Heredia-Guerrero JA, Athanassiou A (2017) Advanced materials from fungal mycelium: fabrication and tuning of physical properties. Sci Rep 7:41292. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41292
Hao L, Sheng Z, Lu J, Tao R, Jia S (2016) Characterization and antioxidant activities of extracellular and intracellular polysaccharides from Fomitopsis pinicola. Carbohydr Polym 141:54–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.11.048
Heller C, Ellerbrock RH, Roßkopf N, Klingenfuß C, Zeitz J (2015) Soil organic matter characterization of temperate peatland soil with FTIR-spectroscopy: effects of mire type and drainage intensity. Eur J Soil Sci 66(5):847–858. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.12279
Huang GL (2008) Extraction of two active polysaccharides from the yeast cell wall. Z Naturforsch 63(11–12):919–921
Index Fungorum (2018). http://www.indexfungorum.org. Accessed 20 Feb 2020
Islam MR, Tudryn G, Bucinell R, Schadler L, Picu RC (2017) Morphology and mechanics of fungal mycelium. Sci Rep 7:13070. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13295-2
İspirli H, Sagdic O, Yılmaz MT, Dertli E (2019) Physicochemical characterisation of an α-glucan from Lactobacillus reuteri E81 as a potential exopolysaccharide suitable for food applications. Process Biochem 79:91–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2018.12.015
Jones M, Bhat T, Kandare E, Thomas A, Joseph P, Dekiwadia C, Yuen R, John S, Ma J, Wang C (2018) Thermal degradation and fire properties of fungal mycelium and mycelium-biomass composite materials. Sci Rep 8(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-36032-9
Kozarski M, Klaus A, Nikšić M, Vrvić MM, Todorović N, Jakovljević D, Van Griensven LJ (2012) Antioxidative activities and chemical characterization of polysaccharide extracts from the widely used mushrooms Ganoderma applanatum, Ganoderma lucidum, Lentinus edodes and Trametes versicolor. J Food Compos Anal 26(1–2):144–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2012.02.004
Lahlali R, Jiang Y, Kumar S, Karunakaran C, Liu X, Borondics F, Hallinn E, Bueckert R (2014) ATR–FTIR spectroscopy reveals involvement of lipids and proteins of intact pea pollen grains to heat stress tolerance. Front Plant Sci 5:747. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00747
Li H, Park S, Moon B, Yoo YB, Lee YW, Lee C (2012) Targeted phenolic analysis in Hericium erinaceum and its antioxidant activities. Food Sci Biotechnol 21(3):881–888. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-012-0114-1
Liu G, Song D, Zhao D, Liu JH, Zhou Y, Ou J, Sun S (2006) A study of the mushrooms of boletes by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. In: ICO20 biomedical optics. International Society for Optics and Photonics 6026, p. 60260I. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.667136
Ma F, Zeng Y, Wang J, Yang Y, Yang X, Zhang X (2013) Thermogravimetric study and kinetic analysis of fungal pretreated corn stover using the distributed activation energy model. Bioresour Technol 128:417–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.10.144
Mäkelä MR, Donofrio N, de Vries RP (2014) Plant biomass degradation by fungi. Fungal Genet Biol 72:2–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2014.08.010
McCann MC, Defernez M, Urbanowicz BR, Tewari JC, Langewisch T, Olek A, Wells B, Wilson RH, Carpita NC (2007) Neural network analyses of infrared spectra for classifying cell wall architectures. Plant Physiol 143(3):1314–1326. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.093054
Mohacek-Grosev V, Bozac R, Puppels GJ (2001) Vibrational spectroscopic characterization of wild growing mushrooms and toadstools. Spectrochim Acta Part A 57:2815–2829
Moussout H, Ahlafi H, Aazza M, Bourakhouadar M (2016) Kinetics and mechanism of the thermal degradation of biopolymers chitin and chitosan using thermogravimetric analysis. Polym Degrad Stab 130:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2016.05.016
Mycobank Databases (2018). http://www.mycobank.org. Accessed 20 Feb 2020
Naumann A (2009) A novel procedure for strain classification of fungal mycelium by cluster and artificial neural network analysis of Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra. Analyst 134:1215–1223. https://doi.org/10.1039/b821286d
Naumann A (2015) Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) microscopy and imaging of fungi. In: Dahms T, Czymmek K (eds) Advanced microscopy in mycology. Fungal biology. Springer, Cham, pp 61–88
Olennikov DN, Agafonova SV, Borovskii GB, Penzina TA, Rokhin AV (2009a) Water-soluble endopolysaccharides from the fruiting bodies of Laetiporus sulphureus (Bull.: Fr.) Murr. Appl Biochem Microbial 45(5):536–543
Olennikov DN, Agafonova SV, Borovskii GB, Penzina TA, Rokhin AV (2009b) Alkali-soluble polysaccharides of Laetiporus sulphureus (Bull.: Fr.) Murr fruit bodies. Appl Biochem Microbiol 45(6):626–630. https://doi.org/10.1134/S000368380906009X
Ortiz-Castellanos L, Ruiz-Herrera J (2015) Phylogenetic relationships of the wall-synthesizing enzymes of Basidiomycota confirm the phylogeny of their subphyla. Folia Microbiol 60(2):143–150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-014-0354-y
Osińska-Jaroszuk M, Wlizło K, Szałapata K, Jarosz-Wilkołazka A (2014) Correlation between the production of exopolysaccharides and oxalic acid secretion by Ganoderma applanatum and Tyromyces palustris. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30(12):3065–3074. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-014-1733-x
Ospina Álvarez SP, Ramírez Cadavid DA, Escobar Sierra DM, Ossa Orozco CP, Rojas Vahos DF, Zapata Ocampo P, Atehortúa L (2014) Comparison of extraction methods of chitin from Ganoderma lucidum mushroom obtained in submerged culture. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/16907
Prasad R, Varshney VK, Harsh NSK, Kumar M (2015) Antioxidant capacity and total phenolics content of the fruiting bodies and submerged cultured mycelia of sixteen higher Basidiomycetes mushrooms from India. Int J Med Mushrooms. https://doi.org/10.1615/intjmedmushrooms.v17.i
Prime RB, Bair HE, Vyazovkin S, Gallagher PK, Riga A (2009) Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). In: Menczel JD, Prime RB (eds) Thermal analysis of polymers. Wiley, Hoboken
Puanglek S, Kimura S, Enomoto-Rogers Y, Kabe T, Yoshida M, Wada M, Iwata T (2016) In vitro synthesis of linear α-1, 3-glucan and chemical modification to ester derivatives exhibiting outstanding thermal properties. Sci Rep 6(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep30479
Riley R et al (2014) Extensive sampling of basidiomycete genomes demonstrates inadequacy of the white-rot/brown-rot paradigm for wood decay fungi. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111(27):9923–9928. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1400592111
Robert P, Marquis M, Barron C, Guillon F, Saulnier L (2005) FT-IR investigation of cell wall polysaccharides from cereal grains. Arabinoxylan infrared assignment. J Agric Food Chem 53(18):7014–7018
Roncero C, Sanchez-Diaz A, Valdivieso MH (2016) Chitin synthesis and fungal cell morphogenesis. In: Hoffmeister D (ed) The mycota: biochemistry and molecular biology, vol III. Springer, Cham, pp 167–190
Ruiz-Herrera J (2016) Fungal cell wall: structure, synthesis, and assembly, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Salman A, Tsror L, Pomerantz A, Moreh R, Mordechai S, Huleihel M (2010) FTIR spectroscopy for detection and identification of fungal phytopathogenes. Spectroscopy 24(3–4):261–267. https://doi.org/10.3233/SPE-2010-0448
Salman A, Pomerantz A, Tsror L, Lapidot I, Zwielly A, Moreh R, Mordechai S, Huleihel M (2011) Distinction of Fusarium oxysporum fungal isolates (strains) using FTIR-ATR spectroscopy and advanced statistical methods. Analyst 136(5):988–995. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0AN00801J
Savino E, Girometta C, Chinaglia S, Guglielminetti M, Rodolfi M, Bernicchia A, Perini C, Salerni E, Picco AM (2014) Medicinal mushrooms in Italy and their ex situ conservation through culture collection. In: Proceedings of the 8th international conference on mushroom biology and mushroom products, New Delhi, India, pp 50–54
Savino E, Girometta C, Miteva-Staleva J, Kostadinova A, Krumova E (2016) Wood decay macrofungi: strain collection and studies about antioxidant properties. Comptes rendus de l’Académie bulgare des Sciences 69(6):747–755
Schwarze FW (2007) Wood decay under the microscope. Fungal Biol Rev 21(4):133–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbr.2007.09.001
Stalpers JA (1978) Identification of wood-inhabiting fungi in pure culture. Stud Mycol 16:1–248
Strandberg A, Holmgren P, Broström M (2017) Predicting fuel properties of biomass using thermogravimetry and multivariate data analysis. Fuel Process Technol 156:107–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2016.10.021
Sun B, Hong W, Aziz H, Li Y (2012) Diketopyrrolopyrrole-based semiconducting polymer bearing thermocleavable side chains. J Mater Chem 22(36):18950–18955. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM33818A
Vadivel D, Speltini A, Zeffiro A, Bellani V, Pezzini S, Buttafava A, Dondi D (2017) Reactive carbons from Kraft lignin pyrolysis: stabilization of peroxyl radicals at carbon/silica interface. J Anal Appl Pyrol 128:346–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2017.09.016
Wang J, Zhang L (2009) Structure and chain conformation of five water-soluble derivatives of a β-D-glucan isolated from Ganoderma lucidum. Carbohydr Res 344(1):105–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2008.09.024
Wasser S (2014) Medicinal mushroom science: current perspectives, advances, evidences, and challenges. Biomed J 37(6):345–356. https://doi.org/10.4103/2319-4170.138318
Weete JD, Abril M, Blackwell M (2010) Phylogenetic distribution of fungal sterols. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0010899
Werner K, Pommer L, Broström M (2014) Thermal decomposition of hemicelluloses. J Anal Appl Pyrol 110:130–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2014.08.013
Yang X, Zeng Y, Ma F, Zhang X, Yu H (2010) Effect of biopretreatment on thermogravimetric and chemical characteristics of corn stover by different white-rot fungi. Bioresour Technol 101(14):5475–5479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.01.129
Zechner-Krpan V, Petravić-Tominac V, Gospodarić I, Sajli L, Đaković S, Filipović-Grčić J (2010) Characterization of 13-glucans isolated from Brewer’s yeast and dried by different methods. Food Technol Biotechnol 48(2):189–196
Zhang P, Zhang L, Cheng S (1999) Chemical structure and molecular weights of α-(1 → 3)-D-glucan from Lentinus edodes. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 63(7):1197–1202
Zhu F, Du B, Bian Z, Xu B (2015) Beta-glucans from edible and medicinal mushrooms: characteristics, physicochemical and biological activities. J Food Compos Anal 41:165–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2015.01.019
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by Fondazione Cariplo, Grant No. 2018-1765 entitled “MYCO-ADVANCED LEATHER MATERIALS (MATER)” and by Savino’s “Fondo Ricerca e Giovani” (Grant for Research and Young Researchers), University of Pavia (Italy). The authors thank Riserva Naturale Integrale Statale Bosco Siro Negri – State Strict Natural Reserve Bosco Siro Negri (Zerbolò, PV – Italy) for authorization to sampling and detaining isolated strains.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Girometta, C., Dondi, D., Baiguera, R.M. et al. Characterization of mycelia from wood-decay species by TGA and IR spectroscopy. Cellulose 27, 6133–6148 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03208-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03208-4