Abstract
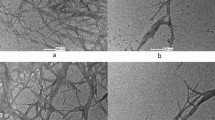
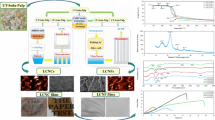
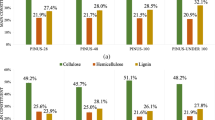
Production of nanocellulosic materials from loblolly pine (Pinus taeda) kraft pulp provides an opportunity to diversify the portfolio of traditional pulp and paper industries. In this study, pinewood was first subjected to dilute acid pre-extraction with 0.5% sulfuric acid in order to fractionate the hemicellulose, followed by kraft pulping and elemental chlorine free bleaching in order to obtain up to 97% pure cellulose fractions. CNCs (cellulose nanocrystals) were prepared by hydrolyzing the bleached kraft pulp with 64% sulfuric acid at 45 °C for 30 min; the resultant unhydrolyzed solid residues were homogenized using a microfluidizer in order to produce cellulose nanofibers (CNFs). The dilute acid pre-extraction step resulted in complete hydrolysis of galactan and arabinan from pinewood, as well as in partial removal of mannan (80%) and xylan (58%). As a result of pre-extraction, the CNC yield and crystallinity improved by 44% and 11%, respectively, from the corresponding kraft pulps. CNCs produced from the pre-extracted materials also exhibited 16% reduction in particle size, but a 70% increase in sulfur content as well as 20% increase in zeta potential. Higher purity of kraft pulps resulted in higher exposure of cellulose crystalline domains to sulfuric acid thereby resulting in the observed changes. Thus, pulp purity was found to play a significant role in determining the quantity and quality of nanocellulosic materials derived from loblolly pine.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abitbol T, Kam D, Levi-Kalisman Y, Gray DG, Shoseyov O (2018) Surface charge influence on the phase separation and viscosity of cellulose nanocrystals. Langmuir 34:3925–3933. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b04127
Agarwal UP, Ralph SA, Reiner RS, Baez C (2017) Production of cellulose nanocrystals from raw wood via hydrothermal treatment. US Patent US20170260692A1
Aguayo MG, Fernández Pérez A, Reyes G, Oviedo C, Gacitúa W, Gonzalez R, Uyarte O (2018) Isolation and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from rejected fibers originated in the kraft pulping process. Polymers 10:1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10101145
Ang TN, Ngoh GC, Chua AS, Lee MG (2012) Elucidation of the effect of ionic liquid pretreatment on rice husk via structural analyses. Biotechnol Biofuels 5:67. https://doi.org/10.1186/1754-6834-5-67
Borrega M, Orelma H (2019) Cellulose nanofibril (CNF) films and xylan from hot water extracted birch kraft pulps. Appl Sci 9:3436. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9163436
Chen W, Yu H, Liu Y, Chen P, Zhang M, Hai Y (2011) Individualization of cellulose nanofibers from wood using high-intensity ultrasonication combined with chemical pretreatments. Carbohydr Polym 83:1804–1811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.10.040
Chen L, Wang Q, Hirth K, Baez C, Agarwal UP, Zhu JY (2015) Tailoring the yield and characteristics of wood cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) using concentrated acid hydrolysis. Cellulose 22:1753–1762. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0615-1
Chieng BW, Lee SH, Ibrahim NA, Then YY, Loo YY (2017) Isolation and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from oil palm mesocarp fiber. Polymers 9:355. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9080355
Chirat C, Lachenal D, Dufrense A (2010) Biorefinery in a kraft pulp mill: From bioethanol to cellulose nanocrystals. Cellul Chem Technol 44:59–64
Colodette JL, Longue D Jr, Pedrazzi C, Oliveira RC, Gomide JL, Gomes FJB (2011) Pulpability and bleachability of xylan-depleted eucalyptus wood chips. Ind Eng Chem Res 50:1847–1852. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie101799y
Ditzel FI, Prestes E, Carvalho BM, Demiate IM, Pinheiro LA (2017) Nanocrystalline cellulose extracted from pinewood and corncob. Carbohydr Polym 157:1577–1585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.11.036
Du L, Wang J, Zhang Y, Qi C, Wolcott MP, Yu Z (2017) Preparation and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from the bio-ethanol residuals. Nanomaterials 7:51. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7030051
Ehman NV, Tarrés Q, Delgado-Aguilar M, Vallejos ME, Felissia F, Area MC, Mutjé P (2016) From pine sawdust to cellulose nanofibers. Cellul Chem Technol 50:361–367
Filipova I, Fridrihsone V, Cabulis U, Berzins A (2018) Synthesis of nanofibrillated cellulose by combined ammonium persulphate treatment with ultrasound and mechanical processing. Nanomaterials 8:640. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8090640
Foster EJ, Moon RJ, Agarwal UP et al (2018) Current characterization methods for cellulose nanomaterials. Chem Soc Rev 47:2609–2679. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6cs00895j
Frederick WJ Jr, Lien SJ, Courchene CE, DeMartini NA, Ragauskas AJ, Lisa K (2008) Co-production of ethanol and cellulose fiber from southern pine: a technical and economic assessment. Biomass Bioenergy 32:1293–1302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2008.03.010
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
Hamad WY (2011) Development and properties of nanocrystalline cellulose. In: Zhu J, Zhang X, Pan X (eds) Sustainable production of fuels, chemicals, and fibers from forest biomass. American Chemical Society, Washington DC, pp 301–321. https://doi.org/10.1021/bk-2011-1067.ch012
Hamad WY, Hu TQ (2010) Structure–process–yield interrelations in nanocrystalline cellulose extraction. Can J Chem Eng 88:392–402. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.20298
Hamaguchi M, Kautto J, Vakkilainen E (2013) Effects of hemicellulose extraction on the kraft pulp mill operation and energy use: review and case study with lignin removal. Chem Eng Res Des 91:1284–1291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2013.02.006
Helmerius J, von Walter JV, Rova U, Berglund KA, Hodge DB (2010) Impact of hemicellulose pre-extraction for bioconversion on birch kraft pulp properties. Bioresour Technol 101:5996–6005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.03.029
Henrique MA et al (2015) Kinetic study of the thermal decomposition of cellulose nanocrystals with different polymorphs, cellulose I and II, extracted from different sources and using different types of acids. Ind Crops Prod 76:128–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.06.048
Houtman C (2018) Lessons learned from 150 years of pulping wood. In: Beckham GT (ed) Lignin valorization: emerging approaches. Energy and environment series no. 19. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp 62–74
Huang F, Ragauskas A (2013) Extraction of hemicellulose from loblolly pine woodchips and subsequent kraft pulping. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:1743–1749. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie302242h
Islam MS, Chen L, Sisler J, Tam KC (2018) Cellulose nanocrystal (CNC)–inorganic hybrid systems: synthesis, properties and applications. J Mater Chem B 6:864–883. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7tb03016a
Iwamoto S, Abe K, Yano H (2008) The effect of hemicelluloses on wood pulp nanofibrillation and nanofiber network characteristics. Biomacromol 9:1022–1026. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm701157n
Jiang L, Zheng A, Zhao Z, He F, Li H, Liu W (2015) Obtaining fermentable sugars by dilute acid hydrolysis of hemicellulose and fast pyrolysis of cellulose. Bioresour Technol 182:364–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.01.032
Kargarzadeh H, Ahmad I, Abdullah I, Dufresne A, Zainudin SY, Sheltami RM (2012) Effects of hydrolysis conditions on the morphology, crystallinity, and thermal stability of cellulose nanocrystals extracted from kenaf bast fibers. Cellulose 19:855–866. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9684-6
Khalil HPSA, Davoudpour Y, Islam MN, Mustapha A, Sudesh K, Dungani R, Jawaid M (2014) Production and modification of nanofibrillated cellulose using various mechanical processes: a review. Carbohydr Polym 99:649–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.08.069
Lahtinen P, Liukkonen S, Pere J, Sneck A, Kangas H (2014) A comparative study of fibrillated fibers from different mechanical and chemical pulps. BioResources 9:2115–2127
Li Q, Renneckar S (2011) Supramolecular structure characterization of molecularly thin cellulose I nanoparticles. Biomacromol 12:650–659. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm101315y
Li Y, Liu Y, Chen W, Wang Q, Liu Y, Li J, Yu H (2016) Facile extraction of cellulose nanocrystals from wood using ethanol and peroxide solvothermal pretreatment followed by ultrasonic nanofibrillation. Green Chem 18:1010–1018. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5gc02576a
Liu W, Hou Q, Mao C, Yuan Z, Li K (2012) Effect of hemicellulose pre-extraction on the properties and bleachability of aspen (Populus tremuloides) chemithermomechanical pulp. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:11122–11127. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie300265s
Loureiro PEG, Domingues EF, Evtuguin DV, Carvalho MGVS (2010) ECF bleaching with final hydrogen peroxide stage: impact on the chemical composition of Eucalyptus globulus kraft pulps. BioResources 5:2567–2580
Lu QL, Li XY, Tang LR, Lu BL, Huang B (2015) One-pot tandem reactions for the preparation of esterified cellulose nanocrystals with 4-dimethylaminopyridine as a catalyst. RSC Adv 5:56198–56204. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA08690F
Marzialetti T, Olarte MBV, Sievers C, Hoskins TJC, Agrawal PK, Jones CW (2008) Dilute acid hydrolysis of Loblolly pine: a comprehensive approach. Ind Eng Chem Res 47:7131–7140. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie800455f
Mathew AP, Oksman K, Karim Z, Liu P, Khan SA, Naseri N (2014) Process scale up and characterization of wood cellulose nanocrystals hydrolysed using bioethanol pilot plant. Ind Crop Prod 58:212–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.04.035
Meng Q, Wan J, Ma Y, Wang Y (2013) Effects of different deinking processes on fiber morphology, hydrogen bond models, and cellulose supramolecular structure. BioResources 8:2398–2416
Misture ST, Snyder RL (2001) X-ray diffraction. In: Buschow KHJ, Cahn RW, Flemings MC, Ilschner B, Kramer EJ, Mahajan S, Veyssière P (eds) Encyclopedia of materials: science and technology, vol 10, 2nd edn. Elsevier, Pergamon, pp 9799–9808. https://doi.org/10.1016/B0-08-043152-6/01778-2
Ngwabebhoh FA, Erdem A, Yildiz U (2018) A design optimization study on synthesized nanocrystalline cellulose, evaluation and surface modification as a potential biomaterial for prospective biomedical applications. Int J Biol Macromol 114:536–546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.03.155
Oh SY, Yoo DI, Shin Y, Seo G (2005) FTIR analysis of cellulose treated with sodium hydroxide and carbondioxide. Carbohydr Res 340:417–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2004.11.027
Oksman K, Aitomäki Y, Mathew AP et al (2016) Review of the recent developments in cellulose nanocomposite processing. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 83:2–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2015.10.041
Oswalt SN, Smith WB, Miles PD, Pugh SA (2019) Forest resources of the United States, 2017: a technical document supporting the Forest Service 2020 RPA assessment. United States Department of Agriculture, Washington, DC, p 223. https://doi.org/10.2737/WO-GTR-97
Park S, Baker JO, Himmel ME, Parilla PA, Johnson DK (2010) Cellulose crystallinity index: measurement techniques and their impact on interpreting cellulase performance. Biotechnol Biofuels 3:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1754-6834-3-10
Poletto M, Júnior HLO, Zattera AJ (2014) Native cellulose: structure, characterization and thermal properties. Materials 7:6105–6119. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7096105
Reid MS, Villalobos M, Cranston ED (2017) Benchmarking cellulose nanocrystals: from the laboratory to industrial production. Langmuir 33:1583–1598. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b03765
Segal L, Creely JJ, Martin AE Jr, Conrad CM (1959) An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-ray diffractometer. Text Res J 29:786–794. https://doi.org/10.1177/004051755902901003
Seo Y-R, Kim J-W, Seonwoo H, Kim J, Chung JH, Lim K-T (2018) Cellulose-based nanocrystals: sources and applications via agricultural byproducts. J Biosyst Eng 43:59–71. https://doi.org/10.5307/JBE.2018.43.1.059
Shak KPY, Pang YL, Mah SK (2018) Nanocellulose: recent advances and its prospects in environmental remediation. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 9:2479–2498. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.9.232
Sinha A, Martin EM, Lim KT, Carrier DJ, Han H, Zharov VP, Kim J-W (2015) Cellulose nanocrystals as advanced “green” materials for biological and biomedical engineering. J Biosyst Eng 40:373–393. https://doi.org/10.5307/JBE.2015.40.4.373
Sofla MRK, Brown RJ, Tsuzuki T, Rainey TJ (2016) A comparison of cellulose nanocrystals and cellulose nanofibres extracted from bagasse using acid and ball milling methods. Adv Nat Sci Nanosci Nanotechnol 7:035004. https://doi.org/10.1088/2043-6262/7/3/035004
Szymanska-Chargot M, Zdunek A (2013) Use of FT-IR spectra and PCA to the bulk characterization of cell wall residues of fruits and vegetables along a fraction process. Food Biophys 8:29–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-012-9279-7
Taheri H, Samyn P (2016) Effect of homogenization (microfluidization) process parameters in mechanical production of micro and nanofibrillated cellulose on its rheological and morphological properties. Cellulose 23:1221–1238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0866-5
Tayeb AH, Amini E, Ghasemi S, Tajvidi M (2018) Cellulose nanomaterials-binding properties and applications: a review. Molecules 23:2684. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102684
Tian C, Yi J, Wu Y, Wu Q, Qing Y, Wang L (2016) Preparation of highly charged cellulose nanofibrils using high-pressure homogenization coupled with strong acid hydrolysis pretreatments. Carbohydr Polym 136:485–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.09.055
Vena PF, García-Aparicio MP, Brienzo M, Gorgens JF, Rypstra T (2013) Impact of hemicellulose pre-extraction on pulp properties of sugarcane bagasse. Cellul Chem Technol 47:425–441
Wang QQ, Zhu JY, Reiner RS, Verrill SP, Baxa U, McNeil SE (2012) Approaching zero cellulose loss in cellulose nanocrystal (CNC) production: recovery and characterization of cellulosic solid residues (CSR) and CNC. Cellulose 19:2033–2047. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9765-6
Wang Q, Zhao X, Zhu JY (2014) Kinetics of strong acid hydrolysis of a bleached kraft pulp for producing cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs). Ind Eng Chem Res 53:11007–11014. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie501672m
Wu H, Nagarajan S, Zhou L, Duan Y, Zhang J (2016) Synthesis and characterization of cellulose nanocrystal-graft-poly(D-lactide) and its nanocomposite with poly(L-lactide). Polymer 103:365–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2016.09.070
Yildirim N, Shaler S (2017) A study on thermal and nanomechanical performance of cellulose nanomaterials (CNs). Materials 10:718. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10070718
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the Center for Advanced Surface Engineering (CASE) under the National Science Foundation (NSF) Grant Number OIA-1457888 and the Arkansas EPSCoR program, ASSET III. We would like to thank B.A. Babst and W.L. Headlee from the University of Arkansas, Monticello for providing the pine biomass, and A. Kuchuk and E. Martin at the Institute for Nanoscience and Engineering, University of Arkansas, Fayetteville for assisting with XRD analysis and TEM imaging, respectively. We would also like to thank C. Hamilton for conducting the ICP-OES analysis at the Center for Renewable Carbon, University of Tennessee, Knoxville.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajan, K., Djioleu, A., Kandhola, G. et al. Investigating the effects of hemicellulose pre-extraction on the production and characterization of loblolly pine nanocellulose. Cellulose 27, 3693–3706 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03018-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03018-8