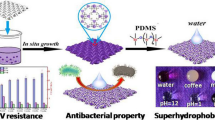
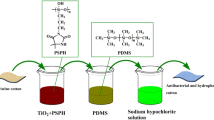
Abstract
In this study, cotton fabrics with improved antibacterial efficiency and hydrophobic properties were prepared with the coatings of N-halamine siloxanes, ZnO, and silane precursors by the ultrasonic-assisted dipping-padding assembly technique. The coated cotton fabrics were characterized by FT-IR, SEM, XRD and XPS. The chlorinated cotton fabrics showed good hydrophobicity with water contact angle of 139o ± 2o. With the addition of ZnO in the N-halamine coatings, the chlorinated samples showed good antibacterial efficacy and could inactivate both all inoculated Escherichia coli O157:H7 (ATCC 43895) and Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 6538) within 10 min. The chlorinated samples also showed good viability to mammalian cells. The stabilities of the coated cotton towards UV light and washing cycles and mechanical properties were investigated. Over 69% of the chlorine was retained after the equivalent of 25 machine washes. The N-halamine siloxanes coating of cotton with ZnO nanoparticles significantly enhanced the UV stability. In addition, the coated cotton fabrics maintained high tensile strength and fair air permeability.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aditya A, Chattopadhyay S, Gupta N, Alam S, Veedu AP, Pal M, Singh A, Santhiya D, Ansari KM, Ganguli M (2019) ZnO nanoparticles modified with an amphipathic peptide show improved photoprotection in skin. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:56–72
Bastarrachea LJ, Goddard JM (2013) Development of antimicrobial stainless steel via surface modification with N-halamines: characterization of surface chemistry and N-halamine chlorination. J Appl Polym Sci 127:821–831
Chen Q, Miyata N, Kokubo T, Nakamura T (2015) Bioactivity and mechanical properties of PDMS-modified CaO–SiO2–TiO2 hybrids prepared by sol-gel process. J Biomed Mater Res 51:605–611
de Oliveira RD, Calaça G, Santos C, Fujiwara S, Pessoa C (2016) Preparation, characterization and electrochemistry of Layer-by-Layer films of silver nanoparticles and silsesquioxane polymer. Colloid Surf A 509:638–647
Demir B, Broughton RM, Huang TS, Bozack M, Worley SD (2017) Polymeric antimicrobial N-halamine-surface modification of stainless steel. Ind Eng Chem Res 56:11773–11781
Dong Q, Dong A, Morigen (2015) Evaluation of novel antibacterial N-halamine nanoparticles prodrugs towards susceptibility of Escherichia coli induced by DksA protein. Molecules 20:7292–7308
Dong A, Huang Z, Lan S, Wang Q, Bao S, Siriguleng, Zhang Y, Gao G, Liu F, Harnoode C (2014) N-halamine-decorated polystyrene nanoparticles based on 5-allylbarbituric acid: from controllable fabrication to bactericidal evaluation. J Colloid Interface Sci 413:92–99
Dong X, Feng L, Ning Z, Xiao F, Wang J, Tan Y (2016) CO2 hydrogenation to methanol over Cu/ZnO/ZrO2 catalysts prepared by precipitation-reduction method. Appl Catal B Environ 191:8–17
Dong A, Wang Y-J, Gao Y, Gao T, Gao G (2017) Chemical insights into antibacterial N-halamines. Chem Rev 117:4806–4862
Fei Z, Liu B, Zhu M, Wang W, Yu D (2018) Antibacterial finishing of cotton fabrics based on thiol-maleimide click chemistry. Cellulose 25:3179–3188
Horsthuis WHG (2017) ZnO processing for integrated optic sensors. Thin Solid Films 137:185–192
Jang J, Kim Y (2008) Fabrication of monodisperse silica-polymer core-shell nanoparticles with excellent antimicrobial efficacy. Chem Commun 34:4016–4018
Jeong K-S, Oh S-K, Shin H-S, Yun H-J, Kim S-H, Lee H-R, Han K-M, Park H-Y, Lee H-D, Lee G-W (2014) Novel silicon surface passivation by Al2O3/ZnO/Al2O3films deposited by thermal atomic layer deposition. Jpn J Appl Phys 53:04ER191–04ER195
Jeong D, Kim HK, Jeong JP, Dindulkar SD, Cho E, Yang YH, Jung S (2016) Cyclosophoraose/cellulose hydrogels as an efficient delivery system for galangin, a hydrophobic antibacterial drug. Cellulose 23:1–17
Jin G, Qin H, Cao H, Qian S, Zhao Y, Peng X, Zhang X, Liu X, Chu PK (2014) Synergistic effects of dual Zn/Ag ion implantation in osteogenic activity and antibacterial ability of titanium. Biomaterials 35:7699–7713
Kadam AN, Bhopate DP, Kondalkar VV, Majhi SM, Bathula CD, Tran A-V, Lee S-W (2018) Facile synthesis of Ag–ZnO core–shell nanostructures with enhanced photocatalytic activity. J Ind Eng Chem 61:78–86
Kamegawa T, Seto H, Matsuura S, Yamashita H (2012) Preparation of hydroxynaphthalene-modified TiO2 via formation of surface complexes and their applications in the photocatalytic reduction of nitrobenzene under visible-light irradiation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4(12):6635–6639
Kocer HB, Akdag A, Worley SD, Acevedo O, Broughton RM, Wu Y (2010) Mechanism of photolytic decomposition of N-halamine antimicrobial siloxane coatings. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 42:2456–2464
Li J, Li R, Du J, Ren X, Worley SD, Huang TS (2013) Improved UV stability of antibacterial coatings with N-halamine/TiO2. Cellulose 20:2151–2161
Li J, Liu Y, Jiang Z, Ma K, Ren X, Huang T-S (2014) Antimicrobial cellulose modified with nanotitania and cyclic N-halamine. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:13058–13064
Lin X, Yin M, Liu Y, Li L, Ren X, Sun Y, Huang T (2018) Biodegradable polyhydroxybutyrate/poly-ɛ-caprolactone fibrous membranes modified by silica composite hydrol for super hydrophobic and outstanding antibacterial application. J Ind Eng Chem 63:303–311
Ma W, Li J, Liu Y, Ren X, Gu Z-G, Xie Z, Liang J (2016) Preparation and characterization of excellent antibacterial TiO2/N-halamines nanoparticles. Colloid Surf A 506:284–290
Mallakpour S, Nikkhoo E (2013) Production and characterization of nanocomposites based on poly(amide-imide) containing 4,4′-methylenebis(3-chloro-2,6-diethylaniline) using nano-TiO2 surface-coupled by 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane. Prog Org Coat 76:231–237
Mu Q, David CA, Galceran J, Rey-Castro C, Krzemiński Ł, Wallace R, Bamiduro F, Milne SJ, Hondow NS, Brydson R et al (2014) Systematic investigation of the physicochemical factors that contribute to the toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles. Chem Res Toxicol 27:558–567
Navik R, Thirugnanasampanthan L, Venkatesan H, Kamruzzaman M, Shafiq F, Cai Y (2017) Synthesis and application of magnesium peroxide on cotton fabric for antibacterial properties. Cellulose 24:3573–3587
Olson DC, Lee YJ, White MS, Kopidakis N, Shaheen SE, Ginley DS, Voigt JA, Hsu JWP (2015) Effect of ZnO processing on the photovoltage of ZnO/Poly(3-hexylthiophene) solar cells. J Phys Chem C 112:9544–9547
Pan N, Liu Y, Ren X, Huang T-S (2018) Fabrication of cotton fabrics through in situ reduction of polymeric N-halamine modified graphene oxide with enhanced ultraviolet-blocking, self-cleaning, and highly efficient, and monitorable antibacterial properties. Colloid Surf A 555:765–771
Shahidi S, Rezaee H, Rashidi A, Ghoranneviss M (2017) In situ synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles on plasma treated cotton fabric utilizing durable antibacterial activity. J Nat Fibers 15:1–9
Silva LFD, M’Peko JC, Catto AC, Bernardini S, Mastelaro VR, Aguir K, Ribeiro C, Longo E (2017) UV-enhanced ozone gas sensing response of ZnO–SnO2 heterojunctions at room temperature. Sens Actuators B-Chem 240:573–579
Worley SD, Chen Y, Wang JW, Wu R, Cho U, Broughton RM, Kim J, Wei CI, Williams JF, Chen J et al (2005) Novel N-halamine siloxane monomers and polymers for preparing biocidal coatings. Surf Coat Int Part B Coat Trans 88:93–99
Xu Q, Xie L, Diao H, Li F, Zhang Y, Fu F, Liu X (2017) Antibacterial cotton fabric with enhanced durability prepared using silver nanoparticles and carboxymethyl chitosan. Carbohydr Polym 177:187–193
Yazhini KB, Prabu HG (2015) Antibacterial activity of cotton coated with ZnO and ZnO–CNT composites. Appl Biochem Biotech 175:85–92
Yu H, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Liu J, Zhang H (2013) Development of a hydrophilic PES ultrafiltration membrane containing SiO2@N-Halamine nanoparticles with both organic antifouling and antibacterial properties. Desalination 326:69–76
Zabihi E, Babaei A, Shahrampour D, Arab Z, Mirshahidi K, Joz Majidi H (2019) Facile and rapid in situ synthesis of chitosan-ZnO nano-hybrids applicable in medical purposes; a novel combination of biomineralization, ultrasound, and bio-safe morphology-conducting agent. Int J Biol Macromol 131:107–116
Zhang J, Sun L, Yin J, Su H, Chunsheng Liao A, Yan C (2016a) Control of ZnO morphology via a simple solution route. Chem Mater 14:4172–4177
Zhang L, Zhang L, Yang Y, Zhang W, Lv H, Yang F, Lin C, Tang P (2016b) Inhibitory effect of super-hydrophobicity on silver release and antibacterial properties of super-hydrophobic Ag/TiO2 nanotubes. J Biomed Mater Res B 104:1004–1012
Zhao L, Yan X, Jie Z, Yang H, Yang S, Liang J (2014) Regenerable antimicrobial N -halamine/silica hybrid nanoparticles. J Biomed Mater Res B 16:1–12
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the support the national first-class discipline program of Light Industry Technology and Engineering (LITE2018-21), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Nos. JUSRP51722B and JUSRP11806), the Project of Jiangsu Science and Technological Innovation Team, and 111 Projects (B17021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, W., Li, L., Ren, X. et al. Rational design of cotton substrates with enhanced UV–blocking, high antibacterial efficiency and prominent hydrophobicity. Cellulose 26, 5757–5768 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02455-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02455-4