Abstract
We developed an isocyanate group containing quaternary ammonium salt (IQAS) as a potential antimicrobial finishing agent that can be stored in a high purity form for more than a year in dry environments to permit convenient transportation and storage. Additionally, we report a facile and eco-friendly finishing technique to fabricate durable antimicrobial cotton fabrics using IQAS as an antimicrobial finishing agent by a dipping–padding–drying process. IQAS was bound onto the surface of cotton fabrics by a covalent bond to obtain a cotton fabric with excellent bactericidal activity, tearing strength, breaking elongation, bending rigidity, water vapor permeability, surface roughness and smoothness. The antimicrobial rates of these fabrics reached 92.2% and 98.5% against gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli and gram-positive bacterium Staphylococcus aureus, respectively, even after 50 laundering cycles. These values are much higher than the reference antimicrobial rates of AAA class antimicrobial fabrics, as well as those of conventionally finished cotton fabrics, indicating that the IQAS finished cotton fabrics maintained excellent antimicrobial activity even after long-term repeated launderings. Moreover, the results indicate that the IQAS-treated cotton fabrics could improve the breaking strength (increased by 13.5% in the warp direction and 20.3% in the weft direction), the bursting strength (increased by 11.9%), the air permeability (increased by 12.6%) and the hydrophilicity compared to untreated cotton fabrics. Additionally, our non-leaching antimicrobial cotton fabrics treated with IQAS were non-toxic and showed no skin stimulation. Therefore, IQAS and the antimicrobial finishing technique reported here have great potential applications in antimicrobial fabrics used in hospitals, hotels and other susceptible situations.
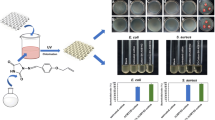
Graphical abstract
An isocyanate group containing quaternary ammonium salt that permits convenient transportation and storage was developed as a potential antimicrobial finishing agent to fabricate excellent antimicrobial cotton fabrics with well-preserved physical properties and security using a dipping–padding–drying process.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amrit URB, Hendrix R, Dutschk V, Warmoeskerken M (2013) Time survivor study of Escherichia coli with polyhexamethylene biguanide on cotton. Text Res J 83(16):1663–1672
Bacciarelli-Ulacha A, Rybicki E, Matyjas-Zgondek E, Pawlaczyk A, Szynkowska MI (2014) A new method of finishing of cotton fabric by in situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Ind Eng Chem Res 53(11):4147–4155
Beyth N, Houri-Haddad Y, Baraness-Hadar L, Yudovin-Farber I, Domb AJ, Weiss EI (2008) Surface antimicrobial activity and biocompatibility of incorporated polyethylenimine nanoparticles. Biomaterials 29(31):4157–4163
Brochier Salon M-C, Abdelmouleh M, Boufi S, Belgacem MN, Gandini A (2005) Silane adsorption onto cellulose fibers: hydrolysis and condensation reactions. J Colloid Interface Sci 289(1):249–261
Chen SG, Chen SJ, Jiang S, Xiong ML, Luo JX, Tang JN, Ge ZC (2011) Environmentally friendly antibacterial cotton textiles finished with siloxane sulfopropylbetaine. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3(4):1154–1162
Chen SG, Guo YJ, Zhong HQ, Chen SJ, Li JN, Ge ZC, Tang JN (2014) Synergistic antibacterial mechanism and coating application of copper/titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Chem Eng J 256:238–246
Chen SG, Yuan LJ, Li QQ, Li JN, Zhu XL, Jiang YG, Sha O, Yang XH, Xin JH, Wang JX, Stadler FJ, Huang P (2016) Durable antibacterial and nonfouling cotton textiles with enhanced comfort via zwitterionic sulfopropylbetaine coating. Small 12(26):3516–3521
Chen S, Chen Q, Li Q, An J, Sun P, Ma J, Gao H (2018) Biodegradable synthetic antimicrobial with aggregation-induced emissive luminogens for temporal antibacterial activity and facile bacteria detection. Chem Mater 30(5):1782–1790
Dong A, Wang YJ, Gao Y, Gao T, Gao G (2017) Chemical insights into antibacterial N-halamines. Chem Rev 117(6):4806–4862
Gao Y, Cranston R (2008) Recent advances in antimicrobial treatments of textiles. Text Res J 78(1):60–72
Gao D, Chen C, Ma J, Duan X, Zhang J (2014) Preparation, characterization and antibacterial functionalization of cotton fabric using dimethyl dialyl ammonium chloride-allyl glycidyl ether-methacrylic/nano-ZnO composite. Chem Eng J 258:85–92
Gao D, Duan X, Chen C, Lyu B, Ma JZ (2015) Synthesis of polymer quaternary ammonium salt containing epoxy group/nano ZnO long-acting antimicrobial coating for cotton fabrics. Ind Eng Chem Res 54(43):10560–10567
Ghosh S, Goudar VS, Padmalekha KG, Bhat SV, Indi SS, Vasan HN (2012) ZnO/Ag nanohybrid: synthesis, characterization, synergistic antibacterial activity and its mechanism. RSC Adv 2(3):930–940
Giesz P, Celichowski G, Puchowicz D, Kamińska I, Grobelny J, Batory D, Cieślak M (2016) Microwave-assisted TiO2: anatase formation on cotton and viscose fabric surfaces. Cellulose 23(3):2143–2159
He L, Gao C, Li S, Chung CTW, Xin JH (2017) Non-leaching and durable antibacterial textiles finished with reactive zwitterionic sulfobetaine. J Ind Eng Chem 46:373–378
Ibrahim HMM, Hassan MS (2016) Characterization and antimicrobial properties of cotton fabric loaded with green synthesized silver nanoparticles. Carbohyd Polym 151:841–850
Jiang S, Cao Z (2010) Ultralow-fouling, functionalizable, and hydrolyzable zwitterionic materials and their derivatives for biological applications. Adv Mater 22(9):920–932
Jin Y, Pei H, Hu W, Zhu Y, Xu H, Ma C, Sun J, Li H (2017) A promising application of chitosan quaternary ammonium salt to removal of Microcystis aeruginosa cells from drinking water. Sci Total Environ 583:496–504
Kang CK, Kim SS, Kim S, Lee J, Lee JH, Roh C, Lee J (2016) Antibacterial cotton fibers treated with silver nanoparticles and quaternary ammonium salts. Carbohyd Polym 151:1012–1018
Li P, Poon YF, Li W, Zhu HY, Yeap SH, Cao Y, Qi X, Zhou C, Lamrani M, Beuerman RW, Kang ET, Mu Y, Li CM, Chang MW, Leong SSJ, Chan-Park MB (2011) A polycationic antimicrobial and biocompatible hydrogel with microbe membrane suctioning ability. Nat Mater 10(2):149–156
Liu Y, Li J, Cheng X, Ren X, Huang TS (2015) Self-assembled antibacterial coating by N-halamine polyelectrolytes on a cellulose substrate. J Mater Chem B 3(7):1446–1454
Liu Q, Huang J, Zhang J, Hong Y, Wan Y, Wang Q, Gong M, Wu Z, Guo CF (2018) Thermal, waterproof, breathable, and antibacterial cloth with a nanoporous structure. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(2):2026–2032
Patil AJ, Zhao Y, Liu X, Wang X (2018) Durable superhydrophobic and antimicrobial cotton fabrics prepared by electrostatic assembly of polyhexamethylene biguanide and subsequent hydrophobization. Text Res J 88(15):1788–1799
Sadeghi-Kiakhani M, Tehrani-Bagha AR, Safapour S (2018) Enhanced anti-microbial, anti-creasing and dye absorption properties of cotton fabric treated with chitosan-cyanuric chloride hybrid. Cellulose 25(1):883–893
Simoncic B, Tomsic B (2010) Structures of novel antimicrobial agents for textiles - A review. Text Res J 80(16):1721–1737
Tian H, Zhai Y, Xu C, Liang J (2017) Durable antibacterial cotton fabrics containing stable acyclic N-halamine groups. Ind Eng Chem Res 56(28):7902–7909
Wang C, Lv J, Ren Y, Zhou Q, Chen J, Zhi T, Lu Z, Gao D, Ma Z, Jin L (2016) Cotton fabric with plasma pretreatment and ZnO/carboxymethyl chitosan composite finishing for durable UV resistance and antibacterial property. Carbohyd Polym 138:106–113
White A, Jiang S (2011) Local and bulk hydration of zwitterionic glycine and its analogues through molecular simulations. J Phys Chem B 115(4):660–667
Xu QB, Ke XT, Cai DR, Zhang YY, Fu FY, Endo T, Liu XD (2018) Silver-based, single-sided antibacterial cotton fabrics with improved durability via an l-cysteine binding effect. Cellulose 25(3):2129–2141
Yin XZ, Weng PX, Han L, Liu JC, Tan YQ, Chen DZ, Zhou YS, Li S, Wang LX, Wang H (2018) Enhanced wettability and moisture retention of cotton fabrics coated with self-suspended chitosan derivative. Cellulose 25(4):2721–2732
Yu M, Wang Z, Lv M, Hao R, Zhao R, Qi L, Liu S, Yu C, Zhang B, Fan C, Li J (2016) Antisuperbug cotton fabric with excellent laundering durability. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(31):19866–19871
Zhang L, Cao Z, Bai T, Carr L, Ella-Menye J-R, Irvin C, Ratner BD, Jiang S (2013) Zwitterionic hydrogels implanted in mice resist the foreign-body reaction. Nat Biotechnol 31(6):553–556
Zhang SB, Yang XH, Tang B, Yuan LJ, Wang K, Liu XY, Zhu XL, Li JN, Ge ZC, Chen SG (2018) New insights into synergistic antimicrobial and antifouling cotton fabrics via dually finished with quaternary ammonium salt and zwitterionic sulfobetaine. Chem Eng J 336:123–132
Zhi Z, Su Y, Xi Y, Tian L, Xu M, Wang Q, Padidan S, Li P, Huang W (2017) Dual-functional polyethylene glycol-b-polyhexanide surface coating with in vitro and in vivo antimicrobial and antifouling activities. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(12):10383–10397
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51773117, 51573097), the Science and Technology Project of Guangdong Province (2015A010105033), the Collaborative Innovation and Technology Project for Shenzhen-Hong Kong Innovation Circle of Shenzhen city (SGLH 20120926161415782), and the Nanshan District Key lab for Biopolymers and safety evaluation (KC2014ZDZJ0001A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, J., Yuan, L., Zhang, Z. et al. Non-leaching bactericidal cotton fabrics with well-preserved physical properties, no skin irritation and no toxicity. Cellulose 25, 5415–5426 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1943-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1943-8