Abstract
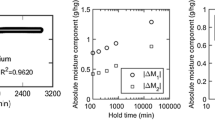
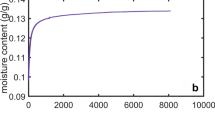
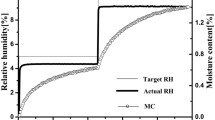
The objective of this study was to examine the water vapour sorption behaviour of three celluloses, which were originally derived from cotton fibers, using a dynamic vapour sorption apparatus, including analyses of the sorption rate and hysteresis occurring in the isotherm run. Cotton linter, α-cellulose, and microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), respectively attained equilibrium moisture contents of 14.2, 20.6, and 16.9% at a relative humidity (RH) of 95%. All three cellulosic materials exhibited sorption hysteresis to varying degrees throughout the full RH range; the MCC and α-cellulose displayed the lowest and highest total hysteresis, respectively. The sorption kinetics were analysed in terms of the parallel exponential kinetics (PEK) model, with excellent fits to the data being obtained. The PEK data is further interpreted on the basis of two Kelvin-Voigt elements operating in series. Clear differences in behaviour were seen between the α–cellulose and the other two celluloses in this study. The relative importance of capillary condensation and matrix viscoelasticity with respect to sorption hysteresis is discussed.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baillie C (2004) Green composites: polymer composites and the environment. Woodhead Publishing Limited, New York
Bakkevig MK, Nielsen R (1995) The impact of activity level on sweat accumulation and thermal comfort using different underwear. Ergonomics 38:926–939
Barnes HA, Hutton JF, Walters K (1989) An introduction to rheology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Barry SE, Soane DS (1996) Second harmonic generation in carbon dioxide processed thin polymer films. Macromolecules 29:3565–3573
Bledzki AK, Gassan J, Theis S (1998) Wood-filled thermoplastic composites. Mech Compos Mater 34:563–568
Bos HL, Donald AM (1999) In situ ESEM study of the deformation of elementary flax fibres. J Mater Sci 34:3029–3034
Buffeteau T, Natansohn A, Rochon P, Pézolet M (1996) Study of cooperative side group motions in amorphous polymers by time dependent infrared spectroscopy. Macromolecules 29:8783–8790
Cantero G, Arbeliaz A, Liano-Ponte R, Mondragon I (2003) Effects of fibre treatment on wettability and mechanical behaviour of flax/polypropylene composites. Compos Sci Technol 63:1247–1254
Christensen GN (1965) The rate of sorption of water vapour by thin materials. Humidity Moisture 4:279–293
Das DB, Mitra MK, Wareham JF (1954) Structure of cotton alpha-cellulose. Nature 174:1058–1059
Doelker F (1993) Comparative compaction properties of various microcrystalline cellulose and generic products. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 19:2399–2471
Eichhorn SJ, Young RJ (2001) The Young’s modulus of microcrystalline cellulose. Cellulose 8:197–207
Eichhorn SJ, Young RJ, Davies RJ, Riekel C (2003) Characterisation of the microstructure and deformation of high modulus cellulose fibres. Polymer 44:5901–5908
Gehlen MH (2010) Kinetics of autocatalytic acid hydrolysis of cellulose with crystalline and amorphous fractions. Cellulose 17:245–252
Gilbert RD (1994) Cellulosic polymers, blends and composites. Hanser Publishers, Munich
Gindl W, Keckes J (2005) All-cellulose nanocomposite. Polymer 46:10221–10225
Guo Y, Li Y, Tokura H, Wong T, Chung J, Wong ASW, Gohel MDI, Leung PHM (2008) Impact of fabric moisture transport properties on physiological responses when wearing protective clothing. Text Res J 78:1057–1069
Hancock BC, Clas S-D, Christensen K (2000) Micro-scale measurement of the mechanical properties of compressed pharmaceutical powders. 1: the elasticity and fracture behavior of microcrystalline cellulose. Int J Pharm 209:27–35
Hatakeyama H, Hatakeyama T (1998) Interaction between water and hydrophilic polymers. Thermochim Acta 308:3–22
Hill CAS, Norton A, Newman G (2009) The water vapor sorption behavior of natural fibers. J Appl Polym Sci 112:1524–1537
Hill CAS, Norton A, Newman G (2010a) The water vapor sorption behavior of flax fibers–analysis using the parallel exponential kinetics model and determination of the activation energies of sorption. J Appl Polym Sci 116:2166–2173
Hill CAS, Norton A, Newman G (2010b) Analysis of the water vapour sorption behaviour of Sitka spruce [Picea sitchensis (Bongard) Carr.] based on the parallel exponential kinetics model 64:469–473
Hill CAS, Norton A, Newman G (2010c) The water vapour sorption properties of Sitka spruce determined using a dynamic vapour sorption apparatus. Wood Sci Technol 44:497–514
Hill CAS, Moore J, Jallaludin Z, Leveneu M, Mahrdt E (2010d) The influence of earlywood/latewood and ring position upon the water vapour sorption properties of Sitka spruce. Int Wood Prod J Submitted
Hu JY, Li Y, Yeung KW, Wong A, Xu W (2005) Moisture management tester: a method to characterize fabric liquid moisture management properties. Text Res J 75:57–62
Jalaludin Z, Hill CAS, Curling S, Hashim WS, Hamdam H (2010) The kinetics of water vapour sorption: analysis using the parallel exponential kinetics model on six Malaysian tropical hardwoods. J Trop For Sci 22:107–117
Kachrimanis K, Noisternig MF, Griesser UJ, Malamataris S (2006) Dynamic moisture sorption and desorption of standard and silicified microcrystalline cellulose. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 64:307–315
Kennedy JF, Phillips GO, Wedlock DJ, Williams PA (1985) Cellulose and its derivatives: chemistry, biochemistry and applications. Ellis Horwood Limited, Chichester
Kohler R, Dück R, Ausperger B, Alex R (2003) A numeric model for the kinetics of water vapor sorption on cellulosic reinforcement fibers. Compos Int 10:255–276
Krabbenhoft K, Damkilde L (2004) A model for non-Fickian moisture transfer in wood. Matériaux et Constructions 37:615–622
Krässig HA (1993) Cellulose: structure, accessibility and reactivity. Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, Switzerland
Li Y (2005) Perceptions of temperature, moisture and comfort in clothing during environmental transients. Ergonomics 48:234–248
Lomelí-Ramírez MG, Ochoa-Ruiz HG, Fuentes-Talavera FJ, García-Enriquez S, Cerpa-Gallegos MA, Silva-Guzmán JA (2009) Evaluation of accelerated decay of wood plastic composites by Xylophagus fungi. Int Biodeter Biodegr 63:1030–1035
Lu Y, Pignatello JJ (2002) Demonstration of the ‘conditioning effect’ in soil organic matter in support of a pore deformation mechanism for sorption hysteresis. Env Sci Technol 36:4553–4561
Lu Y, Pignatello JJ (2004) History-dependent sorption in humic acids and a lignite in the context of a polymer model for natural organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 38:5853–5862
Lundin T, Falk RH, Felton C (2001) Accelerated weathering of natural fiber-thermoplastic composites: effects of ultraviolet exposure on bending strength and stiffness. In: Proceedings of the sixth international conference on wood fiber-plastic composites, Madison, Wisconsin
Madamba PS, Driscol RH, Buckle KAJ (1996) The thin layer drying characteristics of garlic slices. Food Eng 29:75–97
Matsumoto K, Nakai Y, Oguchi T, Yamamoto KY (1998) Effect of pore size on the gaseous adsorption of ethenzamide on porous crystalline cellulose and the physicochemical stability of ethenzamide after storage. Chem Pharm Bull 46:314–318
Meng X, Natansohn A, Barrett C, Rochon P (1996) Azo polymers for reversible optical storage. 10. Cooperative motion of polar side groups in amorphous polymers. Macromolecules 29:946–952
Mihranyan A, Llagostera AP, Karmhag R, Strømme M, Ek R (2004) Moisture sorption by cellulose powders of varying crystallinity. Int J Pharm 269:433–442
Nagapudi K, Brinkman WT, Leisen J, Thomas BS, Wright ER, Haller C, Wu X, Apkarian RP, Conticello VP, Chaikof EL (2005) Protein-based thermoplastic elastomers. Macromolecules 38:345–354
Nissan AH, Sternstein SS (1962) Cellulose as a viscoelastic material. Pure Appl Chem 5:131–146
Okhamafe AO, Igboechi AC, Ubrufih CE, Akinyemi BO, Ighalo MO (1992) Cellulose extracted from groundnut shell and rice husk. 2. Disintegrant properties. Pharm World J 1:11–16
Okubayashi S, Griesser UJ, Bechtold T (2004) A kinetic study of moisture sorption and desorption on lyocell fibers. Carbohydr Polym 58:293–299
Okubayashi S, Griesser UJ, Bechtold T (2005a) Water accessibilities of man-made cellulosic fibers—effects of fiber characteristics. Cellulose 12:403–410
Okubayashi S, Griesser UJ, Bechtold T (2005b) Moisture sorption/desorption behavior of various manmade cellulosic fibers. J Appl Polym Sci 97:1621–1625
Ott E, Spurlin HM, Grafflin MW (1954) Cellulose and cellulose derivatives. Wiley, New York
Paes SS, Sun S, MacNaughtan W, Ibbett R, Ganster J, Foster TJ, Mitchell JR (2010) The glass transition and crystallization of ball milled cellulose. Cellulose 17:693–709
Peralta PN (1995) Modeling wood moisture sorption hysteresis using the independent-domain theory. Wood Fiber Sci 27:250–257
Peralta PN (1996) Moisture sorption hysteresis and the independent-domain theory: the moisture distribution function. Wood Fiber Sci 28:406–410
Rahman MS, Perera CO, Thebaud C (1998) Desorption isotherm and heat pump drying kinetics of peas. Food Res Int 30:485–491
Schirp A, Wolcott M (2006) Fungal degradation of wood-plastic composites and evaluation using dynamic mechanical analysis. J Appl Polym Sci 99:3138–3146
Skaar C (1972) Water in wood. Syracuse University Press
Smith CW, Cothren JT (1999) Cotton: origin, history, technology and protection. Wiley, New York
Spontak RJ, Vratsanos MS (2000) Stress relaxation activation in rubber-modified polymer systems exhibiting controlled miscibility through blending. Macromolecules 33:2290–2292
Stana-Kleinschek K, Strnad S, Ribitsch V (1993) Surface characterization and adsorption abilities of cellulose fibers. Polym Eng Sci 39:1412–1424
Strømme M, Mihranyan A, Ek R, Niklasson GA (2003) Fractal dimension of cellulose powders analyzed by multilayer BET adsorption of water and nitrogen. J Phys Chem B 107:14378–14382
Tang X, De Rooij MR, Van Duynhoven J, Van Breugel K (2008) Dynamic volume change measurements of cereal materials by environmental scanning microscopy and videomicroscopy. J Microsc 230:100–107
Usha r, Ramasami T (1999) Effect of pH on the dimensional stability of rat tail tendon collagen fiber. J Appl Polym Sci 75:1577–1584
Van der Voort Maarschalk K, Zuurman K, Vromas H, Bolhuis GK, Lerk CF (1997) Stress relaxation of compacts produced from viscoelastic materials. Int J Pharm 151:27–34
Vrentas JS, Vrentas CM (1996) Hysteresis effect for sorption in glassy polymers. Macromolecules 29:4391–4396
Wakelin JH, Virgin HS, Crystal E (1959) Development and comparison of two X-ray methods for determining the crystallinity of cotton cellulose. J Appl Phys 30:1654–1662
Wallenberger FT, Weston N (2004) Natural fibers, plastics and composites. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Massachusetts
Winkelhahn HJ, Schrader S, Neher D, Wegner G (1995) Relaxation of polar order in poled polymer systems: a comparison between an isothermal and thermally stimulated experiment. Macromolecules 28:2882–2885
Xiang Q, Lee YY, Pettersson PO, Torget RW (2003) Heterogeneous aspects of acid hydrolysis of α-cellulose. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 105–108:505–514
Xie Y, Hill CAS, Jalaludin Z, Curling S, Anandjiwala RD, Norton A, Newman G (2010a) The dynamic water vapour sorption behaviour of natural fibres and kinetic analysis using the parallel exponential kinetics model. J Mater Sci Submitted
Xie Y, Hill CAS, Xiao Z, Militz H, Mai C (2010b) Dynamic water vapour sorption properties of wood treated with glutaraldehyde. Wood Sci Technol DOI: 10.1007/s00226-010-0311-0
Xie Y, Hill CAS, Xiao Z, Zaihan J, Militz H, Mai C (2010c) Water vapor sorption kinetics of wood modified with glutaraldehyde. J Appl Polym Sci 117:1674–1682
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express their gratitude to the anonymous reviewer of an earlier version of this article for help with formulating the relationship between the Kelvin-Voigt model and sorption kinetics. Callum Hill acknowledges the support of the Scottish Funding Council for the Joint Research Institute in Civil and Environmental Engineering, which is part of the Edinburgh Research Partnership in Engineering and Mathematics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Y., Hill, C.A.S., Jalaludin, Z. et al. The water vapour sorption behaviour of three celluloses: analysis using parallel exponential kinetics and interpretation using the Kelvin-Voigt viscoelastic model. Cellulose 18, 517–530 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-011-9512-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-011-9512-4