Abstract
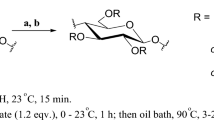
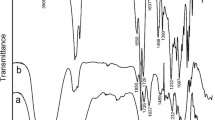
A new amphiphilic cellulose derivative phenoxyhydroxypropylhydroxyethylcellulose of substitution degree up to 0.67 was synthesized by reaction of water-soluble hydroxyethylcellulose with 2,3-epoxypropylphenylether in the presence of sodium hydroxide as a catalyst. The chemical composition of the derivative was confirmed by means of UV, IR- and 13C-NMR-spectroscopy. The derivatives with substitution degree up to 0.12 are soluble in water and water–alcohol mixtures. With increasing substitution degree, the polymers lose their water solubility, but still dissolve in water–alcohol mixtures. All products are soluble in aprotic solvents. The effect of the reaction conditions, such as temperature and molar ratios of reaction components, on both the reaction rate and degree of substitution was investigated.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DS:
-
Substitution degree
- EPPE:
-
2,3-Epoxypropylphenylether
- HEC:
-
Hydroxyethylcellulose
- IPA:
-
Isopropyl alcohol
- LD:
-
Ligand density
- PHPHEC:
-
Phenoxyhydroxypropylhydroxyethylcellulose
References
Edgar KJ, Buchanan CM, Debenham JS, Rundquist PA, Seiler BD, Shelton MC, Tindall D (2001) Advances in cellulose ester performance and application. Prog Polym Sci 26:1605–1688
Heinze T, Liebert T (2001) Unconventional methods in cellulose functionalization. Prog Polym Sci 26:1689–1762
Hoy KL, Hoy RC (1984) US Pat. 4, 228, 277
Klemm D, Philipp B, Heinze T, Heinze U (1998) Comprehensive cellulose chemistry, vol. 2. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, New-York, Chichester, Brisbane, Singapore, Toronto
Kroon G (1993) Associative behaviour of hydrophobically-modified hydroxyethylcelluloses (HMHECS) in waterborne coatings. Prog Org Coat 22:245–260
Landoll LM (1980). US Pat. 4, 426, 485
Lopez-Velazquez D, Bello A, Perez E (2004) Preparation and characterization of hydrophobically modified hydroxypropylcellulose: side-chain crystallization. Macromol Chem Phys 205:1886–1892
Pillai O, Panchagnula R (2001) Polymers in drug delivery. Curr Opin Chem Biol 5:447–451
Srokova I, Minikova S, Ebringerova A, Sasinkova V, Heinze T (2003) Tenside Surfact. Det 40:73–76
Srokova I, Tomanova V, Ebringerova A, Malovikova A, Heinze T (2004) Water-soluble amphiphilic O-(carboxymethyl)cellulose derivatives—synthesis and properties. Macromol Mat Eng 289:63–69
Stuart MAC, Fokkink RG, van der Horst PM, Lichtenbelt JWT (1998) The adsorption of hydrophobically modified carboxymethylcellulose on a hydrophobic solid: effects of pH and ionic strength. Colloid Polym Sci 276:335–341
Tanaka R, Meadows J, Williams PA, Phillips GO (1992) Interaction of hydrophobically modified (hydroxyethyl)cellulose with various added surfactants. Macromolecules 25:1304–1310
Tezuka Y, Imai K, Oshima M, Chiba T (1989) Determination of substituent distribution in cellulose ethers by means of a 13C nuclear magnetic resonance study on their acetylated derivatives: 3. Hydroxyethylcellulose. Polymer 30:2288–2291
Zadorecki P, Hjertberg T, Ardwidsson M (1987) Characterization of cellulose ethers by 13C NMR, 2. Structural determination. Makromol Chem 188:513–525
Zhang LM (2001a) New water-soluble cellulosic polymers: a review. Macromol Mater Eng 286:267–275
Zhang LM (2001b) Cellulosic associative thickeners. Carbohydr Polym 45:1–10
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Danilevicius, A., Dobiliene, J., Wutz, C. et al. Phenoxyhydroxypropylhydroxyethylcellulose—new amphiphilic cellulose derivative. Cellulose 14, 321–329 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-006-9105-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-006-9105-9