Abstract
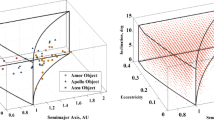
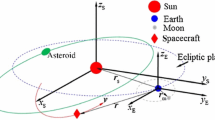
This paper presents a novel approach to the robust design of deflection actions for near Earth objects (NEO). In particular, the case of deflection by means of solar-pumped laser ablation is studied here in detail. The basic idea behind laser ablation is that of inducing a sublimation of the NEO surface, which produces a low thrust thereby slowly deviating the asteroid from its initial Earth threatening trajectory. This work investigates the integrated design of the space-based laser system and the deflection action generated by laser ablation under uncertainty. The integrated design is formulated as a multi-objective optimisation problem in which the deviation is maximised and the total system mass is minimised. Both the model for the estimation of the thrust produced by surface laser ablation and the spacecraft system model are assumed to be affected by epistemic uncertainties (partial or complete lack of knowledge). Evidence Theory is used to quantify these uncertainties and introduce them in the optimisation process. The propagation of the trajectory of the NEO under the laser-ablation action is performed with a novel approach based on an approximated analytical solution of Gauss’ variational equations. An example of design of the deflection of asteroid Apophis with a swarm of spacecraft is presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Battin, R.H.: An introduction to the mathematics and methods of astrodynamics. AIAA Education Series, American Institute for Aeronautics and Astronautics Inc., New York (1999)
Britt D.T., Yeomans D., Housen K., Consolmagno G.: Asteroid density, porosity, and structure. Asteroids III 1, 485–500 (2002)
Campbell J.W., Phipps C., Smalley L., Reilly J., Boccio D.: The impact imperative: laser ablation for deflecting asteroids, meteoroids, and comets from impacting the Earth. AIP Conf. Proc. 664, 509–522 (2003)
Colombo c., Vasile M., Radice G.: Optimal low-thrust trajectories to asteroids through an algorithm based on differential dynamic programming. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 105, 75–112 (2009)
Colombo C., Vasile M., Radice G.: Semi-analytical solution for the optimal low-thrust deflection of near-Earth objects. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 32(3), 796–809 (2009b)
Gibbings, A., Vasile, M., Hopkins, J.M., Burns, D., Watson, I.: Exploring and Exploiting Asteroids with Laser Ablation, UK Space Conference, Warwick, UK, 4–5th July (2011a)
Gibbings, A., Vasile, M., Hopkins, J.M., Burns, D.: On testing Laser ablation processes for asteroid deflection. In: 2011 IAA Planetary Defence Conference, Bucharest, Romania, 9–12th May (2011b)
Glassmeier K.H., Boehnhardt H., Koschny D., Kührt E., Richter I.: The rosetta mission: flying towards the origin of the solar system. Space Sci. Rev. 128(1–4), 1–21 (2007)
Hampton D., Baer J., Huisjen M., Varner C., Delamere A., Wellnitz D., A’Hearn M., Klaasen K.: An overview of the instrument suite for the deep impact mission. Space Sci. Rev. 117(1–2), 43–93 (2005)
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Near Earth Object Program. http://neo.jpl.nasa.gov/neo/groups.html (2012). Accessed 7 Apr 2012
Kahle R., Kuhrt E., Hahn G., Knollenberg J.: Physical limits of solar collectors in deflecting Earth-threatening asteroids. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 10(3), 256–263 (2006)
Klir G.J., Smith R.M.: On measuring uncertainty and uncertainty-based information: recent developments. Ann. Math. Artif. Intell. 32(1–4), 5–33 (2001)
Lu, E.T., Love, S.G.: Gravitational tractor for towing asteroids. Nature 438(7065), 177–178 (2005)
Maddock C.A., Vasile M.: Design of optimal spacecraft-asteroids formation through a hybrid global optimization approach. Int. J. Intell. Comput. Cyber. 1(2), 239–268 (2008)
McAdams, J.V., Dunham, D.W., Mosher, L.E., Ray, J.C., Antreasian, P.G., Helfrich, C.E., et al.: Maneuver history for the NEAR mission—launch through Eros orbit insertion. In: Proceedings of the AIAA/AAS Astrodynamics Specialist Conference, AIAA-2000-4141 (2000)
McInnes C.: Deflection of near-Earth asteroids by kinetic energy impacts from retrograde orbits. Planet. Space Sci. 52(7), 587–590 (2004)
Melosh H.J., Nemchinov I.V., Zetzer I.I.: Non-nuclear Strategies for Deflecting Comets and Asteroids, Hazards Due to Comets and Asteroids. University of Arizona, Tucson (1994)
Nakamura, A.M., Michel, P.: Asteroids and their collisional disruption. In: Lecture Notes in Physics, Small Bodies in Planetary Systems, pp. 1–27. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Oberkampf, W., Helton, J.: Investigation of Evidence Theory in Engineering Applications. AIAA-Paper 2002-1569 (2002)
Olds, J., Charania, A., Schaffer, M.G.: Multiple Mass Drivers as an Option for Asteroid Deflection Missions, 2007 Planetary Defense Conference, Washington, DC, Paper 2007 S3-7 (2007)
Palmas, A.: Approximations of Low-Thrust Trajectory Arcs by Means of Perturbative Approaches, M.D. Thesis, Politecnico di Torino (2010)
Park S.Y., Mazanek D.D.: Deflection of earth-crossing asteroids/comets using rendezvous spacecraft and laser ablation. J. Astronaut. Sci. 53(1), 21–37 (2005)
Phipps, C.: Laser Deflection of NEO’s, Report of the NASA Near-Earth-Object Interception Workshop (1992)
Phipps, C.: Laser deflection of near Earth asteroids and comet nuclei. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Lasers 96 (1997)
Phipps C.: Can lasers play a rôle in planetary defense?. AIP Conf. Proc. 1278, 502–508 (2010)
Phipps C., Bohn W., Eckel H.A., Horisawa H., Lippert T., Michaelis M. et al.: Review: laser-ablation propulsion. J. Propuls. Power 26(4), 609–637 (2010)
Pieters C.M., McFadden L.A.: Meteorite and asteroid reflectance spectroscopy: clues to early solar system processes. Ann. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 22, 457–497 (1994)
Price, S.D.: The surface properties of asteroids. Adv. Space Res. 33(9), 1548–1557 (2004); Elsevier
Project Icarus, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA (1968)
Rayman M., Varghese P., Lehman D., Livesay L.: Results from the deep space 1 technology validation mission. Acta Astronaut. 47(2), 475–487 (2000)
Russell C.T., Capaccioni F., Coradini A., De Sanctis M.C., Feldman W.C., Jaumann R., Keller H.U., McCord T.B., McFadden L.A., Mottola S., Pieters C.M., Prettyman T.H., Raymond C.A., Sykes M.V., Smith D.E., Zuber M.T.: Dawn mission to Vesta and Ceres. Earth Moon Planets 101(1–2), 65–91 (2007)
Sanchez J.P., Colombo C., Vasile M., Radice G.: Multicriteria comparison among several mitigation strategies for dangerous near-Earth objects. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 32(1), 121–142 (2009)
Scheeres, D.J., Schweickart, R.L.: The Mechanics of Moving Asteroids, AIAA planetary Defense Conference, Orange County, CA, AIAA Paper 2004-1447 (2004)
Smith, P.L., Barrera, M.J., et al.: Deflecting a Near Earth Object with Today’s Space Technology, AIAA planetary Defense Conference, Orange County, CA, AIAA Paper 2004-1447 (2004)
Spitale J.N.: Asteroid hazard mitigation using the Yarkovsky effect. Science 296(5565), 77 (2002)
Vasile, M., Colombo, C.: Optimal impact strategies for asteroid deflection. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 31(4), 858–872 (2008)
Vasile M., Croisard N.: Robust Preliminary Space Mission Design Under Uncertainty, Computational Intelligence in Expensive Optimization Problems, pp. 543–570. Springer, Berlin (2010)
Vasile M., Maddock C.A.: On the deflection of asteroids with mirrors. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 107(1), 265–284 (2010)
Vasile M., Zuiani F.: Multi-agent collaborative search: an agent-based memetic multi-objective optimization algorithm applied to space trajectory design. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part G: J. Aerosp. Eng. 225(11), 1211–1227 (2011)
Vasile, M., Maddock, C., Radice, G.: Mirror formation control in the vicinity of an asteroid. In: AIAA/AAS Astrodynamics Specialist Conference and Exhibit, 18–21 August 2008, Honolulu, Hawaii (2008)
Vasile, M., Maddock, C.A., Summerer, L.: Conceptual design of a multi-mirror system for asteroid deflection. 27th International Symposium on Technology and Science, Tsukuba City (2009a)
Vasile M., Maddock C., Radice G., McInnes C.: NEO Deflection though a Multi-Mirror System, ESA Call for Proposals: Encounter 2029, Final Report for Ariadna Study Contract 08/4301, Technical officer: Summerer L. (2009b)
Vasile M., Minisci E., Locatelli M.: An inflationary differential evolution algorithm for space trajectory optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 15(2), 267–281 (2011a)
Vasile, M., Minisci, E., Zuiani, F., Komninou, E., Wijnands, Q.: Fast Evidence-based Systems Engineering, Paper IAC-11.D1.3.3, 62nd International Astronautical Congress, Cape Town, South Africa, 3rd–7th October (2011b)
Wertz, J.R., Larson, W.J.: Space mission analysis and design. Microcosm. Microcosm Press, California (1999)
Zuiani F., Vasile M., Palmas A., Avanzini G.: Direct transcription Of low-thrust trajectories with finite trajectory elements. Acta Astronaut. 72, 108–120 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zuiani, F., Vasile, M. & Gibbings, A. Evidence-based robust design of deflection actions for near Earth objects. Celest Mech Dyn Astr 114, 107–136 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-012-9423-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-012-9423-1