Abstract
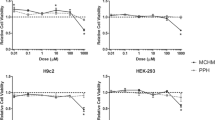
Chronic exposure to low doses of pesticides present in the environment is increasingly suspected to cause major health issues to humans. Toxicological evaluations become more complex when the exposure concerns chemical combinations. Atrazine, chlorpyrifos, and endosulfan are pesticides used worldwide in agriculture and are therefore currently found at residual levels in food and the environment, even in countries in which they are now banned. Our study aimed to use Real-Time Cell Impedance Analyzer to investigate changes in phenotypical status of primary human hepatocytes and differentiated HepaRG cells induced by short and chronic exposures to these three chemicals. In contrast to the traditionally used endpoint cytotoxicity test, this technology allows kinetic measurements in real-time throughout the entire experiment. Our data show significantly higher cytotoxic effects of mixtures as compared to individual pesticides and a greater susceptibility of human hepatocytes as compared to HepaRG to short-term exposure (24 h). Repeated exposure over 2 weeks to endosulfan and endosulfan-containing mixture induced HepaRG cell death in a time- and dose-dependent manner. Of the typical genes involved in metabolism and cell-response to xenobiotics, we found an exposure time- and condition-dependent deregulation of the expression of CYP3A4 and UGT1A in HepaRG cells exposed to low doses of pesticides and mixtures. Our data demonstrate the usefulness of real-time cell monitoring in long-term toxicological evaluations of co-exposure to xenobiotics. In addition, they support but at the same time highlight certain limitations in the use of HepaRG cells as the gold standard liver cell model in toxicity studies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abass K, Lamsa V, Reponen P, Kublbeck J, Honkakoski P, Mattila S, et al. Characterization of human cytochrome P450 induction by pesticides. Toxicology. 2012;294:17–26.
Ackerman F. The economics of atrazine. Int J Occup Environ Health. 2007;13:437–45.
Atienza JM, Zhu J, Wang X, Xu X, Abassi Y. Dynamic monitoring of cell adhesion and spreading on microelectronic sensor arrays. J Biomol Screen. 2005;10:795–805.
Bebe FN, Panemangalore M. Exposure to low doses of endosulfan and chlorpyrifos modifies endogenous antioxidants in tissues of rats. J Environ Sci Health B. 2003;38:349–63.
Bertz RJ, Granneman GR. Use of in vitro and in vivo data to estimate the likelihood of metabolic pharmacokinetic interactions. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1997;32:210–58.
Bisson M, Hontela A. Cytotoxic and endocrine-disrupting potential of atrazine, diazinon, endosulfan, and mancozeb in adrenocortical steroidogenic cells of rainbow trout exposed in vitro. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002;180:110–7.
Blair A, Zahm SH. Agricultural exposures and cancer. Environ Health Perspect. 1995;103 Suppl 8:205–8.
Cairns T, Sherma J, editors. Emerging Strategies for Pesticide Analysis. Boca Raton, Florida, USA: CRC Press; 1992.
Chade AR, Kasten M and Tanner CM. Nongenetic causes of Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm Suppl 2006; 147-151.
Cometa MF, Buratti FM, Fortuna S, Lorenzini P, Volpe MT, Parisi L, et al. Cholinesterase inhibition and alterations of hepatic metabolism by oral acute and repeated chlorpyrifos administration to mice. Toxicology. 2007;234:90–102.
Das PC, McElroy WK, Cooper RL. Differential modulation of catecholamines by chlorotriazine herbicides in pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells in vitro. Toxicol Sci. 2000;56:324–31.
Das PC, Cao Y, Rose RL, Cherrington N, Hodgson E. Enzyme induction and cytotoxicity in human hepatocytes by chlorpyrifos and N, N-diethyl-m-toluamide (DEET). Drug Metabol Drug Interact. 2008;23:237–60.
de Sousa G, Langouët S, Nicolas F, Lorenzon G, Placidi M, Rahmani R, Guillouzo A. Increase of cytochrome P-450 1A and glutathione transferase transcripts in cultured hepatocytes from dogs, monkeys, and humans after cryopreservation. Cell Biol Toxicol. 1996;12:351–8.
EJF. End of the Road for Endosulfan: pushing for a global ban on a deadly pesticide. Environmental Justice Foundation, London, UK; 2009. Second version.
Fan W, Yanase T, Morinaga H, Gondo S, Okabe T, Nomura M, et al. Atrazine-induced aromatase expression is SF-1 dependent: implications for endocrine disruption in wildlife and reproductive cancers in humans. Environ Health Perspect. 2007;115:720–7.
Gao J, Xie W. Pregnane X receptor and constitutive androstane receptor at the crossroads of drug metabolism and energy metabolism. Drug Metab Dispos. 2010;38:2091–5.
Garry VF, Schreinemachers D, Harkins ME, Griffith J. Pesticide appliers, biocides, and birth defects in rural Minnesota. Environ Health Perspect. 1996;104:394–9.
Gerets HH, Tilmant K, Gerin B, Chanteux H, Depelchin BO, Dhalluin S, et al. Characterization of primary human hepatocytes, HepG2 cells, and HepaRG cells at the mRNA level and CYP activity in response to inducers and their predictivity for the detection of human hepatotoxins. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2012;28:69–87.
Gilot D, Loyer P, Corlu A, Glaise D, Lagadic-Gossmann D, Atfi A, et al. Liver protection from apoptosis requires both blockage of initiator caspase activities and inhibition of ASK1/JNK pathway via glutathione S-transferase regulation. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:49220–9.
Gomez-Lechon M, Donato M, Castell J, Jover R. Human hepatocytes as a tool for studying toxicity and drug metabolism. Curr Drug Metab. 2003;4:292–312.
Gripon P, Rumin S, Urban S, Le Seyec J, Glaise D, Cannie I, Guyomard C, Lucas J, Trepo C, Guguen-Guillouzo C. Infection of a human hepatoma cell line by hepatitis B virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:15655–60.
Guillouzo A, Corlu A, Aninat C, Glaise D, Morel F, Guguen-Guillouzo C. The human hepatoma HepaRG cells: a highly differentiated model for studies of liver metabolism and toxicity of xenobiotics. Chem Biol Interact. 2007;168:66–73.
Hanioka N, Obika N, Nishimura M, Jinno H, Tanaka-Kagawa T, Saito K, et al. Inducibility of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1As by beta-naphthoflavone in HepG2 cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 2006;44:1251–60.
Haviland JA, Butz DE, Porter WP. Long-term sex selective hormonal and behavior alterations in mice exposed to low doses of chlorpyrifos in utero. Reprod Toxicol. 2010;29:74–9.
Heistad DD. Oxidative Stress and Vascular Disease 2005 Duff Lecture. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:689–95.
Jondeau A, Dahbi L, Bani-Estivals MH, Chagnon MC. Evaluation of the sensitivity of three sublethal cytotoxicity assays in human HepG2 cell line using water contaminants. Toxicology. 2006;226:218–28.
Lafiura KM, Bielawski DM, Posecion Jr NC, Ostrea Jr EM, Matherly LH, Taub JW, et al. Association between prenatal pesticide exposures and the generation of leukemia-associated T(8;21). Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2007;49:624–8.
Lambert CB, Spire C, Claude N, Guillouzo A. Dose- and time-dependent effects of phenobarbital on gene expression profiling in human hepatoma HepaRG cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2009;234:345–60.
Larsen JC, Binderup M-L, Dalgaard M, Dragsted LO, Hossaini A, Ladefoged O, et al. Combined actions and interactions of chemicals in mixtures. The toxicological effects of exposure to mixtures of industrial and environmental chemicals. Danish Veterinary and Food Administration. FødevareRapport 12. 2003.
LeCluyse E, Madan A, Hamilton G, Carroll K, DeHaan R, Parkinson A. Expression and regulation of cytochrome P450 enzymes in primary cultures of human hepatocytes. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2000;14:177–88.
Lemaire G, de Sousa G, Rahmani R. A PXR reporter gene assay in a stable cell culture system: CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 induction by pesticides. Biochem Pharmacol. 2004;68:2347–58.
McMullin TS, Andersen ME, Nagahara A, Lund TD, Pak T, Handa RJ, et al. Evidence that atrazine and diaminochlorotriazine inhibit the estrogen/progesterone induced surge of luteinizing hormone in female Sprague–Dawley rats without changing estrogen receptor action. Toxicol Sci. 2004;79:278–86.
Medina-Diaz IM, Rubio-Ortiz M, Martinez-Guzman MC, Davalos-Ibarra RL, Rojas-Garcia AE, Robledo-Marenco ML, et al. Organophosphate pesticides increase the expression of alpha glutathione S-transferase in HepG2 cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 2011;25:2074–9.
Meinert R, Schuz J, Kaletsch U, Kaatsch P, Michaelis J. Leukemia and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in childhood and exposure to pesticides: results of a register-based case–control study in Germany. Am J Epidemiol. 2000;151:639–46. discussion 647-650.
Mendola P, Selevan SG, Gutter S, Rice D. Environmental factors associated with a spectrum of neurodevelopmental deficits. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2002;8:188–97.
Nakata K, Tanaka Y, Nakano T, Adachi T, Tanaka H, Kaminuma T, et al. Nuclear receptor-mediated transcriptional regulation in Phase I, II, and III xenobiotic metabolizing systems. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2006;21:437–57.
Pistl J, Kovalkovicova N, Holovska V, Legath J, Mikula I. Determination of the immunotoxic potential of pesticides on functional activity of sheep leukocytes in vitro. Toxicology. 2003;188:73–81.
Romero L, Andrews K, Ng L, O'Rourke K, Maslen A, Kirby G. Human GSTA1-1 reduces c-Jun N-terminal kinase signalling and apoptosis in Caco-2 cells. Biochem J. 2006;400:135–41.
Rouimi P, Zucchini-Pascal N, Dupont G, Razpotnik A, Fouche E, De Sousa G, et al. Impacts of low doses of pesticide mixtures on liver cell defence systems. Toxicol In Vitro. 2012;26:718–26.
Roy JR, Chakraborty S, Chakraborty TR. Estrogen-like endocrine disrupting chemicals affecting puberty in humans–a review. Med Sci Monit. 2009;15:RA137–45.
Sawicki B, Durand G, Dewitte JD, Ratanasavanh D, Riche C, Leglise MC. Myelosuppressive activity of two herbicides, atrazine and dinoterb, on human haematopoietic progenitor cells: An in vitro assay to evaluate the effects of intermediate or long-term exposure. Toxicol In Vitro. 1998;12:183–90.
Scremin OU, Chialvo DR, Lavarello S, Berra HH, Lucero MA. The environmental pollutant endosulfan disrupts cerebral cortical function at low doses. Neurotoxicology. 2011;32:31–7.
Silva MH, Gammon D. An assessment of the developmental, reproductive, and neurotoxicity of endosulfan. Birth Defects Res B Dev Reprod Toxicol. 2009;86:1–28.
Soars MG, Petullo DM, Eckstein JA, Kasper SC, Wrighton SA. An assessment of udp-glucuronosyltransferase induction using primary human hepatocytes. Drug Metab Dispos. 2004;32:140–8.
Solly K, Wang X, Xu X, Strulovici B, Zheng W. Application of real-time cell electronic sensing (RT-CES) technology to cell-based assays. Assay and drug development technologies. 2004;2:363–72.
Sugatani J, Kojima H, Ueda A, Kakizaki S, Yoshinari K, Gong QH, et al. The phenobarbital response enhancer module in the human bilirubin UDP-glucuronosyltransferase UGT1A1 gene and regulation by the nuclear receptor CAR. Hepatology. 2001;33:1232–8.
Sugatani J, Uchida T, Kurosawa M, Yamaguchi M, Yamazaki Y, Ikari A, et al. Regulation of pregnane X receptor (PXR) function and UGT1A1 gene expression by posttranslational modification of PXR protein. Drug Metab Dispos. 2012;40(10):2031–40.
Tchounwou PB, Wilson BA, Ishaque AB, Schneider J. Atrazine potentiation of arsenic trioxide-induced cytotoxicity and gene expression in human liver carcinoma cells (HepG2). Mol Cell Biochem. 2001;222:49–59.
Thrasher JD, Heuser G, Broughton A. Immunological abnormalities in humans chronically exposed to chlorpyrifos. Arch Environ Health. 2002;57:181–7.
Tyler Mehler W, Schuler LJ, Lydy MJ. Examining the joint toxicity of chlorpyrifos and atrazine in the aquatic species: Lepomis macrochirus, Pimephales promelas and Chironomus tentans. Environ Pollut. 2008;152:217–24.
Urquhart BL, Tirona RG, Kim RB. Nuclear receptors and the regulation of drug-metabolizing enzymes and drug transporters: implications for interindividual variability in response to drugs. J Clin Pharmacol. 2007;47:566–78.
Warren N, Allan I, Carter J, House W, Parker A. Pesticides and other micro-organic contaminants in freshwater sedimentary environments: a review. Appl Geochem. 2003;18:159–94.
Wirdefeldt K, Adami HO, Cole P, Trichopoulos D, Mandel J. Epidemiology and etiology of Parkinson’s disease: a review of the evidence. Eur J Epidemiol. 2011;26 Suppl 1:S1–S58.
Xi B, Yu N, Wang X, Xu X, Abassi YA. The application of cell-based label-free technology in drug discovery. Biotechnol J. 2008;3:484–95.
Xie W, Barwick JL, Simon CM, Pierce AM, Safe S, Blumberg B, et al. Reciprocal activation of xenobiotic response genes by nuclear receptors SXR/PXR and CAR. Genes Dev. 2000;14:3014–23.
Xie W, Yeuh MF, Radominska-Pandya A, Saini SP, Negishi Y, Bottroff BS, et al. Control of steroid, heme, and carcinogen metabolism by nuclear pregnane X receptor and constitutive androstane receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:4150–5.
Fundings
The authors received a Public Institutional Funding from INRA, the French National Research Program 07-PNRA-006, and the ANSES (ES-021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ahmad Nawaz and Andrej Razpotnik equally contributed to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nawaz, A., Razpotnik, A., Rouimi, P. et al. Cellular impact of combinations of endosulfan, atrazine, and chlorpyrifos on human primary hepatocytes and HepaRG cells after short and chronic exposures. Cell Biol Toxicol 30, 17–29 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-013-9266-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-013-9266-x