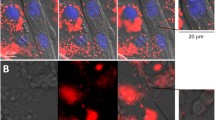
Abstract
Purified phospholipase A2 (PLA2) enzymes from Bothrops jararacussu snake venom were examined to evaluate NIH 3T3 and COS7 fibroblast cytotoxicity, as well as muscle myotoxic and inflammatory activities. Separation of fractions Bj-VII (from BthTX-I; a Lys49 PLA2 homolog) and 6-1 and 6-2 (from BthTX-II; an Asp49 PLA2) from B. jararacussu snake venom by SDS-PAGE in tricine buffer in the absence and presence of dithiothreitol revealed a homodimer with an estimated molecular mass of ∼30 kDa (monomer mass ∼15 kDa). This finding indicates that these toxins form dimeric complexes—a previously reported tendency among PLA2s. These toxins were assayed for viability with the MTT assay, which is used to examine the effects of phospholipases on the mitochondrial viability of cells. The toxins were also assayed for cytolysis of the fibroblast cell lines NIH 3T3 and COS7 by quantification of lactate dehydrogenase released into the medium. The results indicate that the PLA2s 6-1, 6-2 and the Bj-VII PLA2 homolog studied here induce moderate footpad edema and local myotoxicity. Moreover, exposure to these phospholipases led to a reduction in fibroblast viability; at the 1 μM dose of PLA2 tested, a reduction of 50% in cell viability was observed. The present findings indicate that the inflammatory activity observed in envenomation may be correlated with the cytotoxicity observed in fibroblasts.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CK:
-
Creatine kinase
- LHD:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- MTT:
-
3-[4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
References
Ahn MY, Lee BM, Kim YS. Characterization and cytotoxicity of l-amino acid oxidase from the venom of king cobra (Ophiophagus hannah). Int J Biochem Cell Biol 1997;29:911–9. doi:10.1016/S1357–2725(97)00024–1.
Andrião-Escarso SH, Soares AM, Rodrigues VM, Angulo Y, Díaz C, Lomonte B, et al. Myotoxic phospholipases A(2) in Bothrops snake venoms: effect of chemical modifications on the enzymatic and pharmacological properties of bothropstoxins from Bothrops jararacussu. Biochimie 2000;82(8):755–63. doi:10.1016/S0300–9084(00)01150–0.
Angulo Y, Lomonte B. Differential susceptibility of C2C12 myoblasts and myotubes to group II phospholipase A2 myotoxins from crotalid snake venoms. Cell Biochem Funct 2005;23(5):307–13. doi:10.1002/cbf.1208.
Arni RK, Ward RJ. Phospholipase A2—a structural review. Toxicon 1996;34(8):827–41. doi:10.1016/0041–0101(96)00036–0.
Bonfim VL, Ponce-Soto LA, Novello JC, Marangoni S. Cytotoxic action in myoblasts and myotubes (C2C12) and enzymatic characterization of a new phospholipase A2 isoform (Bj-V) from Bothrops jararacussu venom. Protein Pept Lett 2006;13(7):707–13. doi:10.2174/092986606777790520.
Bonfim VL, Toyama MH, Novello JC, Hyslop S, Oliveira CR, Rodrigues-Simioni L, Marangoni S. Isolation and enzymatic characterization of a basic phospholipase A2 from Bothrops jararacussu snake venom. J Protein Chem 2001;20(3):239–45. doi:10.1023/A:1010956126585.
Bonventre JV, Sapirstein A. Group IV cytosolic phospholipase A2 (PLA2) function: insights from the knockout mouse. Adv Exp Med Biol 2002;507:25–31.
Brazil VO. A defesa contra o ofidismo. São paulo: Pocai-Weiss 1911. 152.
Castro RC, Landucci ECT, Toyama MH, Giglio JR, Marangoni S, De Nucci G, et al. Leukocyte recruitment induced by type II phospholipases A2 into the rat pleural cavity. Toxicon 2000;38:1773–85. doi:10.1016/S0041–0101(00)00107–0.
Chacur M, Longo I, Picolo G, Gutierrez JM, Lomonte B, Guerra JL, et al. Hyperalgesia induced by Asp49 and Lys49 phospholipases A2 from Bothrops asper snake venom: pharmacological mediation and molecular determinants. Toxicon 2003;41(6):667–78. doi:10.1016/S0041–0101(03)00007–2.
Chaves F, Barboza M, Gutierrez JM. Pharmacological study of edema induced by venom of the Bothrops asper (Terciopelo) in mice. Toxicon 1995;33:331–9. doi:10.1016/0041–0101(94)00135-U.
Chaves F, Leon G, Alvarado VH, Gutierrez JM. Pharmacological modulation of edema induced by Lys-49 and Asp-49 myotoxic phospholipases A2 isolated from the venom of the snake Bothrops asper (terciopelo). Toxicon 1998;36(12):1861–9. doi:10.1016/S0041–0101(98)00107-X.
Chioato L, de Oliveira AHR, Ruller JM, Ward RJ. Distinct sites for myotoxic and membrane-damaging activities in the C-terminal region of a Lys49-phospholipase A2. Biochem J 2002;366:971–6.
Chioato L, Ward RJ. Mapping structural determinants of biological activities in snake venom phospholipases A2 by sequence analysis and site directed mutagenesis. Toxicon 2003;42:869–83. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2003.11.027.
Cintra ACO, Marangoni S, Oliveira B, Giglio JR. Bothropstoxin-I: amino acid sequence and function. J Protein Chem 1993;12:57–64. doi:10.1007/BF01024915.
Daniele JJ, Bianco ID, Delgado C, Carrillo DB, Fidelio GD. A new phospholipase A2 isoform isolated from Bothrops neuwiedii (Yarará chica) venom with novel kinetic and chromatographic properties. Toxicon 1997;35(8):1205–15. doi:10.1016/S0041–0101(97)00023–8.
De Carvalho DD, Costa FTM, Duran N, Haun M. Cytotoxicity activity of violacein in colon cancer cells. Toxicol In Vitro 2006;20:1514–21. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2006.06.007.
De Faria L, Antunes E, Bon C, de Araújo AL. Pharmacological characterization of the rat paw edema induced by Bothrops lanceolatus (Fer de lance) venom. Toxicon 2001;39(6):825–30. doi:10.1016/S0041–0101(00)00213–0.
Díaz C, Gutiérrez JM, Lomonte B. Isolation and characterization of basic myotoxic phospholipases A2 from Bothrops godmani (Godman’s pit viper) snake venom. Arch Biochem Biophys 1992;298(1):135–42. doi:10.1016/0003–9861(92)90104–5.
Díaz-Oreiro C, Gutiérrez JM. Chemical modification of histidine and lysine residues of myotoxic phospholipases A2 isolated from Bothrops asper and Bothrops godmani snake venoms: effects on enzymatic and pharmacological properties. Toxicon 1997;35(2):241–52. doi:10.1016/S0041–0101(96)00128–6.
Dijkstra BW, Drenth J, Kalk KH. Active site and catalytic mechanism of phospholipase A2. Nature 1981;289:604–6. doi:10.1038/289604a0.
Dijkstra BW, Renetseder R, Kalk KH, Wim GJ, Holand DJ. Structure of Porcine Pancreatic Phospholipase A2 at 26 A Resolution and Comparison with Bovine Phospholipase A2. J Mol Biol 1983;168:163–79. doi:10.1016/S0022–2836(83)80328–3.
Dixon RW, Harris JB. Myotoxic activity of the toxic phospholipase, notexin, from the venom of the Australian tiger snake. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 1996;55(12):1230–7. doi:10.1097/00005072–199612000–00006.
Gutiérrez JM, Lomonte B. Venom phospholipase A2 enzymes: structure, function and mechanism. Chichester: Wiley, 1997.
Gutiérrez JM, Ownby CL. Skeletal muscle degeneration induced by venom phospholipases A2: insights into the mechanisms of local and systemic myotoxicity. Toxicon 2003;42:915–31. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2003.11.005.
Gutiérrez JM, Ponce-Soto LA, Marangoni S, Lomonte B. Systemic and local myotoxicity induced by snake venom group II phospholipases A2: comparison between crotoxin, crotoxin B and a Lys49 PLA2 homologue. Toxicon 2008;51(1):80–92. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2007.08.007.
Gutiérrez JM, Ownby CL. Skeletal muscle degeneration induced by venom phospholipases A2: insights into the mechanisms of local and systemic myotoxicity. Toxicon 2003;42:915–31. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2003.11.005.
Hirabayashi T, Murayama T, Shimizu T. Regulatory mechanism and physiological role of cytosolic phospholipase A2. Biol Pharm Bull 2004;27:1168–73. doi:10.1248/bpb.27.1168.
Jung YK, Miura M, Yuan J. Suppression of interleukin-1β-converting enzyme-mediated cell death by insulin-like growth factor J. Biol Chem 1996;271:5112–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.9.5112.
Kanashiro MM, de Cássia M, Escocard R, Petretski JH, Prates MV, Alves EW, et al. Biochemical and biological properties of phospholipases A(2) from Bothrops atrox snake venom. Biochem Pharmacol 2002;64(7):1179–86. doi:10.1016/S0006–2952(02)01288–1.
Kato T, Ishiwata M, Nagai T. Mitochondrial calcium response in human transformed lymphoblastoid cells. Life Sci 2002;71:581–90. doi:10.1016/S0024–3205(02)01725–3.
Kini RM, Evans HJ. A common cytolytic region in myotoxins, hemolysins, cardiotoxins and antibacterial peptides. Int J Pept Protein Res 1989;34:277–86.
Kini RM. Excitement ahead: structure, function and mechanism of snake venom phospholipase A2 enzymes. Toxicon 2003;42:827–40. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2003.11.002.
Kudo I, Murakami M. Phospholipase A2 enzymes. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 2002;68–69:3–58. doi:10.1016/S0090–6980(02)00020–5.
Lambeau G, Lazdunski M. Receptors for a growing family of secreted phospholipases A2. Trends Pharmacol Sci 1999;20:162–70. doi:10.1016/S0165–6147(99)01300–0.
Landucci ECT, Castro RC, Toyama MH, Marangoni S, Oliveira B, Antunes E. De Nucci G. Inflammatory effects induced by piratoxin I, a PLA2 homologue isolated from Bothrops pirajai snake venom. In: Programas e Resumos da IV Simpósio da Sociedade Brasileira de Toxinología 1996; 160.
Lomonte B, Angulo Y, Calderon L. An overview of lysine-49 phospholipase A2 myotoxins from crotalid snake venoms and their structural determinants of myotoxic action. Toxicon 2003;15;42(8):885–901.
Lomonte B, Angulo Y, Rufini S, Cho W, Giglio JR, Ohno M, et al. Comparative study of the cytolytic activity of myotoxic phospholipases A2 on mouse endothelial (tEnd) and skeletal muscle (C2C12) cells in vitro. Toxicon 1999;37:145–58. doi:10.1016/S0041–0101(98)00171–8.
Lomonte B, Moreno E, Tarkowski A, Hanson LA, Maccarana M. Neutralizing interaction between heparins and myotoxin II, a lysine 49 phospholipase A2 from Bothrops asper snake venom. Identification of a heparin-binding and cytolytic toxin region by the use of synthetic peptides and molecular modeling. J Biol Chem 1994;25;269(47):29867–73.
Mora R, Valverde B, Díaz C, Lomonte B, Gutierrez JMA. Lys49 phospholipase A2 homologue from Bothrops asper snake venom induces proliferation, apoptosis and necrosis in a lymphoblastoid cell line. Toxicon 2005;45:651–60. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2005.01.008.
Núñez CE, Angulo Y, Lomonte B. Identification of the myotoxic site of Lys49 phospholipase A2 from Agkistrodon piscivorus piscivorus snake venom: synthetic C-terminal peptides from Lys49, but not from Asp49 myotoxins, exert membrane-damaging activity. Toxicon 2001;39:1587–94. doi:10.1016/S0041–0101(01)00141–6.
Ponce-Soto LA, Baldasso PA, Romero-Vargas FF, Winck FV, Novello JC, Marangoni S. Biochemical, pharmacological and structural characterization of two PLA2 isoforms Cdr-12 and Cdr-13 from Crotalus durissus ruruima snake venom. Biochim Biophys Acta 2007;25;1726(1):75–86.
Ponce-Soto LA, Bonfim VL, Rodrigues-Simioni L, Novello JC, Marangoni S. Determination of primary structure of two isoforms 6–1 and 6–2 PLA2 D49 from Bothrops jararacussu snake venom and neurotoxic characterization using in vitro neuromuscular preparation. Protein J 2006;25(2):147–55. doi:10.1007/s10930–006–0006–4.
Ponraj D, Gopalakrishnakone P. Establishment of an animal model for myoglobinuria by use of a myotoxin from Pseudechis australis (king brown snake) venom in mice. Lab Anim Sci 1996;46(4):393–8.
Rosenberg P. Lethal potency of snake venom phospholipase A2 enzymes. Pitfalls to avoid in the study of correlations between enzymatic activity and pharmacological properties of phospholipase A2 enzymes. In: Kini RM, editor. Venom phospholipase A2 enzymes: structure, function and mechanism. New York: Wiley; 1997. p. 129–54.
Ruffini S, Cesaroni M, Balestro N, Luly P. Proliferative effect of ammodytin L from the venom of Vipera ammodytes on 208F rat fibroblasts in culture. Biochem J 1996;320:467–72.
Salvini TF, Amaral AC, Miyabara EH, Turri JAO, Danella PM, Selistre de Araujo HS. Systemic skeletal muscle necrosis induced by crotoxin. Toxicon 2001;39:1141–9. doi:10.1016/S0041–0101(00)00245–2.
Serhan CN. Eicosanoids in leukocyte function. Curr Opin Hematol 1994;1:69–77
Six DA, Dennis EA. The expanding superfamily of phospholipase A(2) enzymes: classification and characterization. Biochim Biophys Acta 2000;1488:1–19.
Soares AM, Rodrigues VM, Homsi-Brandeburgo MI, Toyama MH, Lombardi FR, Arni RK, Giglio JR. A rapid procedure for the isolation of the Lys-49 myotoxin IIfrom Bothrops moojeni (caissaca) venom: biochemical characterization, crystallization, myotoxic and edematogenic activity. Toxicon 1998;36:503–14. doi:10.1016/S0041–0101(97)00133–5.
Suzuki K, Nakamura M, Hatanaka Y, Kayanoki Y, Tatsumi H, Taniguchi N. Induction of apoptotic cell death in human endothelial cells treated with snake venom: implication of intracellular reactive oxygen species and protective effects of glutathione and superoxide dismutases. J Biochem 1997;122:1260–4.
Todaro GJ, Green H. Quantitative studies of the growth of mouse embryo cells in culture and their development into established lines. J Cell Biol 1963;17:299–313. doi:10.1083/jcb.17.2.299.
Vane J. Control of the circulation by endothelial mediators. Inaugural G.B. West Memorial Lecture. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 1993;101:333–45.
Yamakawa M, Nozaky M, Hokama Z. Fractionation of sakishimahabu (Trimeresurus elegans) venom and lethal, hemorrhagic and edema-forming activities of the fractions. In: Ohsaka A, Hayashi K, Sawai Y, editors. Toxins: animal, plant and microbial. New York: Plenum Press; 1976. p. 97–109.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mr. Paulo A. Baldasso for general technical help. This work was supported by CAPES and FAPESP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonfim, V.L., de Carvalho, D.D., Ponce-Soto, L.A. et al. Toxicity of phospholipases A2 D49 (6-1 and 6-2) and K49 (Bj-VII) from Bothrops jararacussu venom. Cell Biol Toxicol 25, 523–532 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-008-9106-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-008-9106-6