Abstract
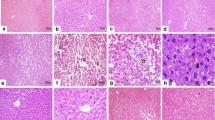
The purpose of the study was to determine whether along and in combination melatonin (MLT) and pentoxlfylline (PTX) exerted beneficial effects on histopathological changes and changes in oxidant and antioxidant systems in liver caused by CCl4-induced liver toxicity in mice. Mice were randomly divided into six groups: control, olive oil, toxicity, MLT, PTX, PTX+MLT. MLT 10 mg/kg/day, PTX 50 mg/kg/day, and the same individual doses in MLT+PTX combination were given intraperitoneally to mice for 7 day. CCl4 0.8 mg/kg/day was administered on the 4th, 5th, and 6th days of therapy in all groups except the control and olive oil groups. In the toxicity group, increased concentrations of malondialdehyde (MDA) and lipid hydroperoxides (LOOH) and decreased glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) and catalase (CAT) activities were found compared to the control and olive oil groups (p < 0.05). Compared to the toxicity group, both the PTX group and the PTX+MLT group had decreased MDA and LOOH levels, whereas MLT reduced only LOOH levels (p < 0.01). MLT, PTX and MLT+PTX increased the GSH-Px and CAT activities compared to the toxicity group (p < 0.05). MLT increased CAT activity compared to PTX and MLT+PTX (p < 0.05). Superoxide dismutase enzyme activity did not change in any group (p < 0.05). Histopatholically, ballooning, degeneration, apoptosis, and bridging necrosis were seen in the toxicity group. MLT, PTX and MLT+PTX decreased the apoptosis and bridging necrosis (p < 0.01), and PTX and MLT+PTX decreased balloon degeneration compared to the toxicity group (p < 0.01). These results indicate that administration of PTX and MLT alone and in combination before onset of liver toxicity might prevent the oxidative damage by reducing oxidative stress and increasing antioxidant enzyme levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALT:
-
alanine aminotransferase
- AST:
-
apartate aminotransferase
- CCl4 :
-
carbon tetrachloride
- HE:
-
hematoxylin–eosin
- LDH:
-
lactate dehydrogenase
- LOOH:
-
lipid hydroperoxides
- MDA:
-
malondialdehyde
- MLT:
-
melatonin
- PTX:
-
pentoxifylline
- TBARS:
-
thibarbituric acid-reactive substances
References
Abdel Salam OM, Baiuomy AR, El-Shenawy SM, Hassan NS. Effect of pentoxifylline on hepatic injury caused in the rat the administration of carbon tetrachloride or acetaminophen. Pharmacol Rep. 2005;57:596–603.
Abdollahi M, Fooladian F, Emami B, Zafari K, Bahreini-Moghadam A. Protection by sildenafil and theophylline of lead acetate-induced oxidative stress in rat submandibular gland and saliva. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2003;22:587–92.
Barlow-Walden LR, Reiter RJ, Abe M, et al. Melatonin stimulates brain glutathione peroxidase activity. Neurochem Int. 1995;26:479–502.
Basu S. Carbon tetrachloride-induced lipid peroxidation: eicosanoid formation and their regulation by antioxidant nutrients. Toxicology. 2003;189(1–2):113–27.
Britton RS, Bacon BR. Role of free radicals in liver disseases and hepatic fibrosis. Hepatogastroenterology. 1994;41:343–8.
Castro GD, Diaz Gomez MI, Castro JA. DNA bases attack by reactive metabolites produced during carbon tetrachloride biotransformation and promotion of liver microsomal lipid peroxidation. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol. 1997: 95:253–8.
Daniels WM, Reiter RJ, Melchiorri D, Sewrynek DE, Pablos MI, Oritz GG. Melatonin counteracts lipid peroxidation induced by carbon tetrachloride but does not restore glucose 6-phosphatase activity. J Pineal Res. 1995;19:1–6.
Demir S, Erden MI. Pentoxifylline and N-acetylcysteine in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Clin Chim Acta. 1998;275:127–35.
Desmouliere A, Xu G, Costa AM, Yousef IM, Gabbiani G, Tuchweber B. Effect of pentoxifylline on early proliferation and phenotypic modulation of fibrogenic cell in two rat models of liver fibrosis and on cultured hepatic stellata cells. J Hepatol. 1999;30:621–31.
Goth L. A simple method for determination of serum catalase activity, and revision of reference range. Clin Chim Acta. 1991;196:143–52.
Güven A, Güven A, Gülmez M. The effect of kefir on the activities of GSH-Px, GST, CAT, GSH and LPO levels in carbon tetrachloride-induced mice tissues. J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health. 2003;50:412–6.
Halliwell B. Antioxidants and human disease: a general introduction. Nutr Rev. 1997;55:44–52.
Jaeschke H. Glutathione disulfide formation and oxidant stress during acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice in vivo: the protective effect of allopurinol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990;255:935–41.
Jiang ZY, Woollard ACS, Wolff SP. Lipid hydroperoxide measurement by oxidation of Fe2 in the presence of xylenol orange. Comparison with the TBA assay and an iodometric method. Lipids. 1991;26:853–6.
Kaye AD, Ibrahim IN, Kadowitz PJ, Nossaman BD. Analysis of response to pentoxifylline in the pulmonary vasculare bed of the cat. Crit Care Med. 1996;24:263–7.
Kozaki K, Egawa H, Bermidez Ci, Feducu NJ, So SK, Esquival CO. Pentoxifylline inhibits production of superoxide anion and tumor necrosis factor by Kupffer cell in rat liver preservation. Transplant Proc. 1993;25:3025–6.
Lee KS, Cottam HB, Houglum K, Wasson DB, Carson D, Chojkier M. Pentoxifylline blocks hepatic stellate cell activation independently of phosphodiesterase inhibitory activity. Am J Physiol. 1997;273:1094–100.
MacDonald-Wicks LK, Garg ML. Modulation of carbon tetrachloride-induced oxidative stress by dietary fat in rats. J Nutr Bioch. 2002;13:87–95.
Mandell GL. ARDS, neutrophils and pentoxifylline. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988;138:1103–5.
Noyan T, Önem Ö, Sekeroglu MR, et al. Effects of erythropoietin and pentoxifylline on the oxidant and antioxidant systems in the experimental short bowel syndrome. Cell Biochem Funct. 2003;21:49–54.
Noyan T, Sahin I, Sekeroglu MR, Dülger H. The serum vitamin C levels in Behĉet’s disease. Yonsei Med J. 2003;44(5):771–78.
Ohta Y, Kongo M, Sasaki E, Nishida K, Ishigura I. Therapeutic effect of melatonin on carbon tetrachloride induced acute liver damage in rats. J Pineal Res. 2000;28:119–26.
Paglia DE, Valentine WN. Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med. 1967;70:158–69.
Pierrefiche G, Laborit H. Oxygen free radicals, melatonin, and aging. Exp Gerontol. 1995;30:213–27.
Pierrefiche G, Topall G, Courboin G, Henriet I, Laborit H. Antioxidant activity of melatonin in mice. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1993;80:211–23.
Recknagel RO, Glende EA, Dolak JA, Waller RL. Mechanisms of carbon tetrachloride toxicity. Pharmacol Ther. 1989;43:139–54.
Reiter RJ, Tang L, Garcia JJ, Munoz-Hoyos A. Pharmacological actions of melatonin in oxygen radical pathophysiology. Life Sci. 1997;60:2255–71.
Sener G, Akgün U, Satroglu H, Topaloglu U, Keyer-Uysal M. The effect of pentoxifylline on ischemia/reperfusion injury. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2001;15:19–22.
Stoyanovsky DA, Cederbaum, AI. Metabolism of carbon tetrachloride to trichloromethyl radical: an ESR and HPLC-EC study. Chem Res Toxicol. 1999; 12:730–36.
Sun Y, Oberley LW, Li Y. A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem. 1988;34:497–500.
Tan DX, Chen LD, Poeggeler B, Manchester LC, Reiter RJ. Melatonin: a potent, endogenous hydroxyl radical scavenger. Endocr J. 1993;1:57–60.
Tan DX, Manchester LC, Reiter RS, et al. Melatonin directly scavenger hydrogen peroxidation a potential new metabolic, pathway of melatonin biotransformation. Free Radic Biol Med. 2000;1177–85.
Ward A, Clissold SP. Pentoxifylline. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and its therapeutic efficacy. Drugs. 1987;34:50–97.
Wasowicz W, Neve J, Peretz A. Optimized steps in fluorometric determination of thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances in serum: importance of extraction pH and influence of sample preservation and storage. Clin Chem. 1993;39(12):2522–6.
Zavodnik LB, Zavodnik IB, Lapshina EA, et al. Protective effects of melatonin against carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxicity in rats. Cell Biochem Funct. 2005;23(5):353–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noyan, T., Kömüroğlu, U., Bayram, İ. et al. Comparison of the effects of melatonin and pentoxifylline on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver toxicity in mice. Cell Biol Toxicol 22, 381–391 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-006-0019-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-006-0019-y