Abstract
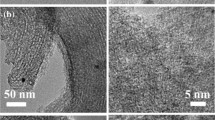
Ordered mesoporous carbon supported cobalt-based catalysts (Co/MC) were synthesized via incipient wetness impregnation with different amounts of furfuryl alcohol (FA) as carbon precursor. The characterizations of obtained Co/MC were subjected to N2 adsorption, XRD, XPS, TEM, H2-TPR, H2-TPD and H2-TPSR. The results indicate that the reducibility and dispersion of Co active species vary significantly due to the difference of FA amount. By simply tuning the FA content from 25 to 100 wt%, the reduction temperature of deriving metallic Co shifts gradually to lower. The catalytic performance of Co/MC was evaluated for Fischer–Tropsch (FT) synthesis. The observed FT activity exhibits a volcano-type curve with the amount of FA due to the effect of both reducibility and dispersion of active species. As the precursor concentration overweighs 50 wt%, the ability of CO to dissociate over the active surface and the selectivity to the C5+ products level off after experiencing an initial increase. Substantially, the catalysts with higher concentration of FA render the larger crystallites having an average size of more than 6 nm, which facilitates the CO hydrogenation by way of carbon chain propagation. It seems that the sample with FA content of 50 wt% is optimum in terms of FT activity and C5+ selectivity.
Graphical Abstract
By simply tuning the carbon precursor furfuryl alcohol (FA) content from 25 to 100 wt%, the textural property of mesoporous carbon varies significantly, which further induces the different reducibility and dispersion of Co active species and the temperature of deriving metallic Co shifts gradually to lower. The catalytic performance of as-synthesized catalysts was evaluated for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis (FTS). The observed FT activity exhibits a volcano-type curve with the amount of FA due to the effect of both reducibility and dispersion of active species. At the FA concentration of support over 50 wt%, the selectivity to the C5+ heavy molecular maintain invariant after experiencing an initial increase. It seems that the sample with respect to 50 wt% FA is optimum in terms of FT activity and C5+ selectivity.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Okabe K, Wei M, Arakawa H (2003) Energy Fuels 17:822
Yu ZX, Borg O, Chen D, Enger BC, Froseth V, Rytter E, Wigum H, Holmen A (2006) Catal Lett 109:43
Sun S, Tsubaki N, Fujimoto K (2000) Appl Catal A 202:121
MartInez A, López C, Márquez F, Diaz I (2003) J Catal 220:486
Sapag K, Rojas S, Granados ML, Fierro JLG, Mendioroz S (2001) J Mol Catal A 167:81
Jacobs G, Das TK, Zhang Y, Li J, Racoillet G, Davis BH (2002) Appl Catal A 233:263
Jacobs G, Ji Y, Davis BH, Cronauer D, Kropf AJ, Marshall CL (2007) Appl Catal A 333:177
Khodakov AY, Griboval-Constant A, Bechara R, Zholobenko VL (2002) J Catal 206:230
Prieto G, Martínez A, Murciano R, Arribas MA (2009) Appl Catal A 367:146
Yin D, Li W, Yang W, Xiang H, Sun Y, Zhong B, Peng S (2001) Microporous Mesoporous Mater 47:15
Mu S, Li D, Hou B, Jia L, Chen J, Sun Y (2010) Energy Fuels 24:3715
Xiong H, Zhang Y, Liew K, Li J (2008) J Mol Catal A 295:68
Wang W-J, Chen Y-W (1991) Appl Catal 77:223
Zhang J, Chen J, Ren J, Li Y, Sun Y (2003) Fuel 82:581
Zhang Y, Nagamori S, Hinchiranan S, Vitidsant T, Tsubaki N (2006) Energy Fuels 20:417
den Breejen JP, Radstake PB, Bezemer GL, Bitter JH, Frøseth V, Holmen A, Jong KPd (2009) J Am Chem Soc 131:7197
Xiong K, Li J, Liew K, Zhan X (2010) Appl Catal A 389:173
Lu A-H, Li W-C, Schmidt W, Kiefer W, Schüth F (2004) Carbon 42:2939
Trépanier M, Tavasoli A, Dalai AK, Abatzoglou N (2009) Appl Catal A 353:193
Rameswaran M, Bartholomew CH (1989) J Catal 117:218
Lu AH, Schmidt W, Schuth F (2003) New Carbon Mater 18:181
Li H, Wang S, Ling F, Li J (2006) J Mol Catal A 244:33
Zhao D, Feng J, Huo Q, Melosh N, Fredrickson GH, Chmelka BF, Stucky GD (1998) Science 279:548
Ernst B, Hilaire L, Kiennemann A (1999) Catal Today 50:413
Wang T, Ding YJ, Xiong JM, Yan L, Zhu HJ, Lu Y, Lin LW (2006) Catal Lett 107:47
Khodakov AY, Bechara R, Griboval-Constant A (2003) Appl Catal A 254:273
Guerrero-Ruiz A, Sepúlveda-Escribano A, Rodríguez-Ramos I (1994) Appl Catal A 120:71
Oades RD, Morris SR, Moyes RB (1990) Catal Today 7:199
Chen W, Fan Z, Pan X, Bao X (2008) J Am Chem Soc 130:9414
Grass ME, Zhang Y, Butcher DR, Park JY, Li Y, Bluhm H, Bratlie KM, Zhang T, Somorjai GA (2008) Angew Chem Int Ed 47:8893
Fujimoto K, Kameyama M, Kunugi T (1980) J Catal 61:7
Tsubaki N, Sun S, Fujimoto K (2001) J Catal 199:236
Iglesia E, Soled SL, Fiato RA (1992) J Catal 137:212
Tavasoli A, Sadagiani K, Khorashe F, Seifkordi AA, Rohani AA, Nakhaeipour A (2008) Fuel Process Technol 89:491
Kuipers EW, Scheper C, Wilson JH, Vinkenburg IH, Oosterbeek H (1996) J Catal 158:288
Tsubaki N, Yoshii K, Fujimoto K (2002) J Catal 207:371
Puskas I, Hurlbut RS (2003) Catal Today 84:99
Bezemer GL, Bitter JH, Kuipers H, Oosterbeek H, Holewijn JE, Xu XD, Kapteijn F, van Dillen AJ, de Jong KP (2006) J Am Chem Soc 128:3956
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21003149 and 21076218).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Jia, L., Meng, Y. et al. Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis over Ordered Mesoporous Carbon Supported Cobalt Catalysts: The Role of Amount of Carbon Precursor in Catalytic Performance. Catal Lett 142, 195–204 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-011-0747-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-011-0747-3