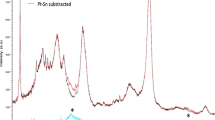
The NO x adsorption mechanism on Pt/BaO/Al2O3 catalysts was investigated by performing NO x storage/reduction cycles, NO2 adsorption and NO + O2 adsorption on 2%Pt/(x)BaO/Al2O3 (x = 2, 8, and 20 wt%) catalysts. NO x uptake profiles on 2%\Pt/20%BaO/Al2O3 at 523 K show complete uptake behavior for almost 5 min, and then the NO x level starts gradually increasing with time and it reaches 75% of the inlet NO x concentration after 30 min time-on-stream. Although this catalyst shows fairly high NO x conversion at 523 K, only ~2.4 wt% out of 20 wt% BaO is converted to Ba(NO3)2. Adsorption studies by using NO2 and NO + O2 suggest two different NO x adsorption mechanisms. The NO2 uptake profile on 2%Pt/20%BaO/Al2O3 shows the absence of a complete NO x uptake period at the beginning of adsorption and the overall NO x uptake is controlled by the gas–solid equilibrium between NO2 and BaO/Ba(NO3)2 phase. When we use NO + O2, complete initial NO x uptake occurs and the time it takes to convert ~4% of BaO to Ba(NO3)2 is independent of the NO concentration. These NO x uptake characteristics suggest that the NO + O2 reaction on the surface of Pt particles produces NO2 that is subsequently transferred to the neighboring BaO phase by spill over. At the beginning of the NO x uptake, this spill-over process is very fast and so it is able to provide complete NO x storage. However, the NO x uptake by this mechanism slows down as BaO in the vicinity of Pt particles are converted to Ba(NO3)2. The formation of Ba(NO3)2 around the Pt particles results in the development of a diffusion barrier for NO2, and increases the probability of NO2 desorption and consequently, the beginning of NO x slip. As NO x uptake by NO2 spill-over mechanism slows down due to the diffusion barrier formation, the rate and extent of NO2 uptake are determined by the diffusion rate of nitrate ions into the BaO bulk, which, in turn, is determined by the gas phase NO2 concentration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Yoon A.G. Panov R.G. Tonkyn A.C. Ebeling S.E. Barlow M.L. Balmer (2002) Catal. Today 72 243 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xis1ClsL8%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0920-5861(01)00499-0
P.L.T. Gabrielson (2004) Top. Catal. 28 177 Occurrence Handle10.1023/B:TOCA.0000024348.34477.4c
M. Takeuchi S. Matsumoto (2004) Top. Catal. 28 151 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXjt1SgtLg%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/B:TOCA.0000024344.91688.e4
N. Takahashi H. Shinjoh T. Iijima T. Suzuki K. Yamazaki K. Yokota H. Suzuki N. Miyoshi S. Matsumoto T. Tanizawa T. Tanaka S. Tateishi K. Kasahara (1996) Catal. Today 27 63 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XhtF2hs7Y%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/0920-5861(95)00173-5
W.S. Epling L.E. Campbell A. Yezerets N.W. Currier J.E. Parks (2004) Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng. 46 163 Occurrence Handle10.1081/CR-200031932
W.S. Epling J.E. Parks G.C. Campbell A. Yezerets N.W. Currier L.E. Campbell (2004) Catal. Today 96 21 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXns12isrY%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.cattod.2004.05.004
L. Olsson E. Fridell (2002) J. Catal. 210 340 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XmsFWnurY%3D Occurrence Handle10.1006/jcat.2002.3698
F. Prinetto G. Ghiotti I. Nova L. Lietti E. Tronconi P. Forzatti (2001) J. Phys. Chem. B 105 12732 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXoslSnt7k%3D Occurrence Handle10.1021/jp012702w
J. Dawody M. Skoglundh S. Wall E. Fridell (2005) J. Mol. Catal. A 225 259 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXhtVKrsbnO Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.molcata.2004.09.011
L. Olsson E. Fridell M. Skoglundh B. Andersson (2002) Catal. Today 73 263 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XktVejsrw%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0920-5861(02)00009-3
L. Olsson R.J. Blint E. Fridell (2005) Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 44 3021 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXitlSjtrk%3D Occurrence Handle10.1021/ie0494059
I. Nova L. Castoldi L. Lietti E. Tronconi P. Forzatti F. Prinetto G. Ghiotti (2004) J. Catal. 222 377 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXhvV2gsLk%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.jcat.2003.11.013
F. Prinetto G. Ghiotti I. Nova L. Castoldi L. Lietti E. Tronconi P. Forzatti (2003) Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 5 4428 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXnsl2ksLs%3D Occurrence Handle10.1039/b305815h
W.S. Epling G.C. Campbell J.E. Parks (2003) Catal. Lett. 90 45 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXnsFShu7g%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1025864109922
J. Despres M. Koebel O. Korcher M. Elsener A. Wokaun (2003) Appl. Catal. B 43 389 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXkvF2gsr4%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0926-3373(03)00004-3
J. Szanyi J.H. Kwak J. Hanson C. Wang T. Szailer C.H.F. Peden (2005) J. Phys. Chem. B 109 7339 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXit12ju7Y%3D Occurrence Handle10.1021/jp044160z
J. Szanyi J.H. Kwak D.H. Kim S.D. Burton C.H.F. Peden (2005) J. Phys. Chem. B 109 27 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXhtVKitL7P Occurrence Handle10.1021/jp044993p
L. Castoldi I. Nova L. Lietti P. Forzatti (2004) Catal. Today 96 263 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.cattod.2004.05.006
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwak, J.H., Kim, D.H., Szailer, T. et al. NO x uptake mechanism on Pt/BaO/Al2O3 catalysts. Catal Lett 111, 119–126 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-006-0153-4
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-006-0153-4