Abstract.
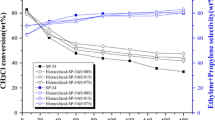
SAPO-5, −11, −31, −41, −34, ZSM-5, −22 and −23 were synthesized by using the hydrothermal method and characterized by various methods such as XRD, SEM, XRF and TPD of NH3. They are representative of large-pore, medium-pore, small-pore, weak acid, strong acid, monodimensional channel and zigzag channel type of molecular sieves. Effects of pore size, the number of acid sites over medium-pore SAPOs, acid strength and shape of medium-pore channel on hydroisomerization of n-octane were examined over Pt-loaded corresponding molecular sieves. These results indicate that the selectivity to isomerization in hydroisomerization of n-octane is highly influenced by channel structure in molecular sieves and the conversion activity of n-octane is dependent on acidity of molecular sieves. Monodimensional medium-pore molecular sieves are ideal catalytic materials for higher isomerization selectivity in hydroisomerization of n-octane regardless of acid strength, such as SAPO-11, −31, −41, ZSM-22 and −23.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.W. Smith, W.C. Starr and N.Y. Chen, Oil. Gas. J., May 26 (1980) 75.
S J. Miller, Zeolites and Related Microporous Materials: State of the Art 1994, Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal., Vol. 84, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1994, p. 2319.
S.J. Miller, U. S. Patent 5, 246, 566 (1993).
A.K. Sinha S. Sivasanker (1999) Catal. Today. 49 293 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXps1KmtA%3D%3D
M. Hochtl A. Jentys H. Vinek (2001) Catal. Today. 65 171 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXhvFCjtbc%3D
J.M. Campelo F. Lafont J.M. Marinas (1998) Appl. Catal. A 170 139 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXis1OmsLY%3D
F. Zhang C.H. Geng Z.X. Gao J.L. Zhou (2004) Chin. J. Catal. 25 431
Y.M. Liu F.M. Zhang X.T. Shu M.Y. He (2003) Chin. J. Catal. 24 781
I. Eswaqramoothi N. Lingappan (2004) J. Mol. Catal. A 218 229
P. Meriaudeau V.A. Tuan V.T. Nghiem S.Y. Lai L.N. Hung C. Naccache (1997) J. Catal. 169 55 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXksVKnsLw%3D
P. Meriaudeau V.A. Tuan G. Sapaly V.T. Nghiem S.Y. Lai C. Naccache (1999) Catal. Today. 49 285 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXps1Kmtw%3D%3D
K.C. Park S.-K. Ihm (2000) Appl. Catal. A 203 201 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXmtVCmtrg%3D
P. Raybaud A. Patrigeon H. Toulhoat (2001) J. Catal. 198 98
T.L. Maesen M. Schenk T.J.H. Vlugt J.P. Jonge B. Smit (1999) J. Catal. 188 403 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXotFeksbk%3D
M.C. Claude G. Vanbutsele J.A. Martens (2001) J. Catal. 203 213 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXntlWrtrY%3D
M.C. Claude J.A. Martens (2000) J. Catal. 190 39 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXnsVekuw%3D%3D
P. Raybaud A. Patrigeon H. Toulhoat (2001) J. Catal. 197 98 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXptVGntb8%3D
B.M. Lok, C.A. Messing, R.L. Patton, R.T. Gajek, T.R. Cannan and E.M. Flanigen, U. S. Patent 4,440,871 (1984).
S.j. Miller, U. S. Patent 5,158,665 (1992).
S.j. Miller, U. S. Patent 5,230,881 (1993).
Y.F. Hu X.S. Wang X.W. Guo P. Xu S.L. Li (2004) Chin. J. Catal. 25 87 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXisFegsb4%3D
B.M. Lowe and A. Araya, U. S. Patent 4,900,528 (1990).
S.I. Zones, J.N. Ziemer, D.S. Santilli, R.A. Innes, S. Rafael and D.L. Holtermann, U. S. Patent 5,300,210 (1994).
X.Q. Wang, X.S. Wang and X.W. Guo, CN Patent 1,240,193 (2000).
C. Baerlocher W.M. Meier D.H. Olson (2001) Atlas of Zeolite Framework Types Elsevier Amsterdam
C.M. Zicovich-wilson P. Viruela A. Corma (1995) J. Phys. Chem. 99 13224 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXnsVKqt7w%3D
V.B. Kazanski I.N. Senchenya (1989) J. Catal. 119 108
J.A. Martens P.A. Jacobs (1986) Zeolites 6 334 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XlvFOksL0%3D
J. Weitkamp S. Ernst (1994) Catal. Today. 19 107 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXisVOks7g%3D
J.A. Maetens P.A. Jacobs J. Weitkamp (1986) J. Appl. Catal. 20 283 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0166-9834(86)80021-5
I.E. Maxwell (1987) Catal. Today. 2 385
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yunfeng, H., Xiangsheng, W., Xinwen, G. et al. Effects of channel structure and acidity of molecular sieves in hydroisomerization of n-octane over bi-functional catalysts. Catal Lett 100, 59–65 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-004-3086-9
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-004-3086-9