Abstract
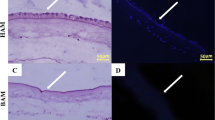
Direct application of amnion has greater risk of immunological rejection and infection. Decellularization is an effective method to lower the risk of immune complications and infections. The bioreactor assembly with multiple cassettes was designed for decellurization of multiple amnions with different cell types simultaneously in single run. A detergent-based protocol was modified to remove all cellular components from amnion and diminish the DNA content to render it non-immunogenic. Amnion (n = 10) were treated with 2% sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS), 5% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and 2% sodium deoxycholeate (SD). Decellularized amnion samples were analyzed by haematoxylin–eosin staining (HE), Alcian blue pH 1 (AB-pH-1), 4,6-diamnionidino-2-phenylindol (DAPI), Massion’s trichrome stain, DNA quantification, mechanical testing and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Histological analysis showed complete removal of cellular components and the histoarchitecture of scaffold remained intact. Amnion scaffold activated with platelet rich plasma (PRP) and calcium chloride composition supported better adherence to the wound than amnion alone. Only single application showed good healing. In vivo assessment of activated amnion revealed stable dressing. It has good promising outcome. At day 7, histologically the wounds treated with activated amnion were almost closed without scarring and showed well differentiated epidermis, proliferation of keratinocytes, hair follicles and basement membrane as compared to controls and silver nitrate gel dressings in a mouse (Mus musculus). Cryopreservation had no adverse effect on the mechanical properties of the amnion scaffold. Cryopreservation of decellularized amnion by Dulbecco’s modified eagle medium (DMEM) was expected to prepare off-the-shelf skin substitutes and preserve them to be immediately available upon request of patients’ needs.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Homing and efficacy of intra-articular injection of autologous.pdf.
References
Amable PR et al (2013) Platelet-rich plasma preparation for regenerative medicine: optimization and quantification of cytokines and growth factors. Stem Cell Res Therapy 4:1–13
Amer MS, Shamaa A et al (2015) The efficacy of cryopreserved amniotic membrane seeded with mesenchymal stem cells for management of bone defect in a canine model. Res J Pharm Biol Chem Sci 6(3):1620–1631
Aponte PM, Schlatt IIS, Luiz III, Franca LRD (2013) Biotechnological approaches to the treatment of aspermatogenic men. Clinics. https://doi.org/10.6061/clinics/2013(sup01)18
Augustine R, Kalarikkal N, Thomas S (2014) Advancement of wound care from grafts to bioengineered smart skin substitutes. Prog Biomater 3:103–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40204-014-0030-y
Bo S, Biedermann T, Reichmann E (2010) Tissue engineering of skin. Burns 36:450–460
Castellanos G, Garcia AB, Garcia C, Pinero A, Moraleda JM et al (2016) The use of amniotic membrane in the management of complex chronic wounds. In: Alexandrescu VA (ed) Wound healing - new insights into ancient challenges. InTech. https://doi.org/10.5772/64491
Chang Y et al (2015) Autologous platelet-rich plasma promotes endometrial growth and improves pregnancy outcome during in vitro fertilization. Int J Clin Exp Med 8(1):1286–1290
Ehrenreich M, Ruszczak Z (2006) Update on tissue-engineered biological dressings. Tissue Eng 12:2407–2424
Haddad AG, Giatsidis G, Orgill DP, Halvorson EG (2017) Skin substitutes and bioscaffolds temporary and permanent coverage skin substitutes bioscaffolds allografts xenografts dermal templates. Clin Plast Surg. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cps.2017.02.019
Kesting MR, Wolff K, Nobis CP, Rohleder NH (2014) Amniotic membrane in oral and maxillofacial surgery. Oral Maxillofac Surg 18:153–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-012-0382-1
Kraus KH, Kirker C (2006) Mesenchymal stem cells and bone regeneration. Vet Surg 35(3):232–242
Kuna VK et al (2016) Significantly accelerated wound healing of full-thickness skin using a novel composite gel of porcine acellular dermal matrix and human peripheral blood cells. Cell Transplant. https://doi.org/10.3727/096368916x692690
Lohana P, Hassan S, Watson SB (2014) Integra™ in burns reconstruction: our experience and report of an unusual immunological reaction. Ann Burns Fire Disasters XXVII:17–21
Macneil S (2007) Progress and opportunities for tissue-engineered skin. Nature 445:874
Maguire TJ, Yarmush ML (2011) Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: history, progress, and challenges. Annu Rev Chem Biomol Eng. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-chembioeng-061010-114257
Markeson D, Pleat JM, Sharpe JR, Harris AL, Seifalian AM (2013) Scarring, stem cells, scaffolds and skin repair. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 9(6):649–668
Mokbel A, El-Tookhy O, Shamaa AA, Sabry D, Rashed L, Mostafa A (2011) Homing and efficacy of intra-articular injection of autologous mesenchymal stem cells in experimental chondral defects in dogs. Clin Exp Rheumatol 29:275–284
Niknejad H, Peirovi H, Jorjani M, Ahmadiani A, Ghanavi J, Seifalian AM (2008) Properties of the amniotic membrane for potential use in tissue engineering. Eur Cells Mater 15:88–99
Plichta JK, Holmes CJ, Gamelli RL, Radek KA (2017) Local burn injury promotes defects in the epidermal lipid and antimicrobial peptide barriers in human autograft skin and burn margin: implications for burn wound healing and graft survival. J Burn Care Res. https://doi.org/10.1097/bcr.0000000000000357
Robiony M, Polini F, Costa F (2002) Osteogenesis distraction and platelet-rich plasma for bone restoration of the severely atrophic mandible. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. https://doi.org/10.1053/joms.2002.33107
Sheikh S, Hamid A, Kamalia N (2014) Scanning electron microscopic assessment on surface morphology of preserved human amniotic membrane after gamma sterilisation. Cell Tissue Bank 15:15–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-012-9353-x
Wen A et al (2016) Skin tissue engineering advances in severe burns: review and therapeutic applications. Burn Trauma. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41038-016-0027-y
Yamaguchi R et al (2012) effects of platelet-rich plasma on intestinal anastomotic healing in rats: PRP concentration is a key factor. J Surg Res 173:258–266
Zhang T et al (2013) The effect of amniotic membrane de-epithelialization method on its biological properties and ability to promote limbal epithelial cell culture. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.12-10805
Zhang L, Zou D, Li S, Wang J, Qu Y (2016) An ultra-thin amniotic membrane as carrier in corneal epithelium. Nat Publ Gr. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep21021
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declare no potential conflict of interest.
Human and animals rights
The inform consent were taken and the study was approved form Institutional Review Board (Ref.- 6/IAEC/2017). All animals experiments are performed after due approval from animal ethics committee of the university.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kshersagar, J., Kshirsagar, R., Desai, S. et al. Decellularized amnion scaffold with activated PRP: a new paradigm dressing material for burn wound healing. Cell Tissue Bank 19, 423–436 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-018-9688-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-018-9688-z