Abstract
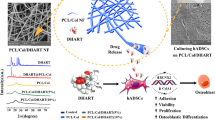
An ideal biomaterial in regenerative medicine should be able to regulate the stem cell proliferation without the loss of its pluripotency. Chrysin (Chr) is a naturally occurring flavone with a wide spectrum of biological functions including anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant properties. The present study describes the influence of Chr-loaded nanofibrous mats on the regulation of proliferation and stemness preservation of adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs). For this purpose, Chr-loaded poly (ε-caprolactone)/poly (ethylene glycol) (PCL/PEG) nanofibrous mats were produced via electrospinning process and the successful fabrication of these bioactive mats was confirmed by field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) and fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. ADSCs were seeded on the nanofibers and their morphology, viability, and stemness expression were analyzed using FE-SEM, MTT, and qPCR assays after 2 weeks of incubation, respectively. The results display that ADSCs exhibit better adhesion and significantly increased viability on the Chr-loaded PCL/PEG nanofibrous mats in relative to the PCL/PEG nanofibers and tissue culture polystyrene. The greater viability of ADSCs on Chr based nanofibers was further confirmed by higher expression levels of stemness markers Sox-2, Nanog, Oct-4, and Rex-1. These findings demonstrate that Chr-loaded PCL/PEG electrospun nanofibrous mats can be applied to improve cell adhesion and proliferation while concurrently preserving the stemness of ADSCs, thus representing a hopeful potential for application in stem cell therapy strategies.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand KV, Jaabir M, Sultan M, Thomas PA, Geraldine P (2012) Protective role of chrysin against oxidative stress in d-galactose-induced aging in an experimental rat model. Geriatr Gerontol Int 12:741–750
Baglioni S et al (2009) Characterization of human adult stem-cell populations isolated from visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue. FASEB J 23:3494–3505
Bhattacharya B et al (2004) Gene expression in human embryonic stem cell lines: unique molecular signature. Blood 103:2956–2964
Boyer LA et al (2005) Core transcriptional regulatory circuitry in human embryonic stem cells. Cell 122:947–956
Dahlin RL, Kasper FK, Mikos AG (2011) Polymeric nanofibers in tissue engineering. Tiss Eng Part B: Rev 17:349–364
Deldar Y, Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi Y, Dadashpour M, Montazer Saheb S, Rahmati-Yamchi M, Zarghami N (2017) An in vitro examination of the antioxidant, cytoprotective and anti-inflammatory properties of chrysin-loaded nanofibrous mats for potential wound healing applications. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. doi:10.1080/21691401.2017.1337022
Denu RA, Hematti P (2016) Effects of oxidative stress on mesenchymal stem cell biology. Oxid Med Cell Longev
Eatemadi A, Daraee H, Zarghami N, Melat Yar H, Akbarzadeh A (2016) Nanofiber: synthesis and biomedical applications. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 44:111–121
Fong H, Hohenstein KA, Donovan PJ (2008) Regulation of self-renewal and pluripotency by Sox2 in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 26:1931–1938
Harasymiak-Krzyżanowska I, Niedojadło A, Karwat J, Kotuła L, Gil-Kulik P, Sawiuk M, Kocki J (2013) Adipose tissue-derived stem cells show considerable promise for regenerative medicine applications. Cell Mol Biol Lett 18:479–493
Hay DC, Sutherland L, Clark J, Burdon T (2004) Oct-4 knockdown induces similar patterns of endoderm and trophoblast differentiation markers in human and mouse embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 22:225–235
Huang C-S et al (2013) Protection by chrysin, apigenin, and luteolin against oxidative stress is mediated by the Nrf2-dependent up-regulation of heme oxygenase 1 and glutamate cysteine ligase in rat primary hepatocytes. Arch Toxicol 87:167–178
Ko E, Lee KY, Hwang DS (2011) Human umbilical cord blood–derived mesenchymal stem cells undergo cellular senescence in response to oxidative stress. Stem Cells Dev 21:1877–1886
Konno M et al (2013) Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and regenerative medicine. Dev Growth Differ 55:309–318
Liu X, Wang S (2014) Three-dimensional nano-biointerface as a new platform for guiding cell fate. Chem Soc Rev 43:2385–2401
Mantawy EM, El-Bakly WM, Esmat A, Badr AM, El-Demerdash E (2014) Chrysin alleviates acute doxorubicin cardiotoxicity in rats via suppression of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Eur J Pharmacol 728:107–118
Meng X, Leslie P, Zhang Y, Dong J (2014) Stem cells in a three-dimensional scaffold environment. Springerplus 3:80
Mobarak H, Fathi E, Farahzadi R, Zarghami N, Javanmardi S (2017) L-carnitine significantly decreased aging of rat adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Vet Res Commun 41:41–47
Mohammadian F, Abhari A, Dariushnejad H, Nikanfar A, Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi Y, Zarghami N (2016a) Effects of chrysin-PLGA-PEG nanoparticles on proliferation and gene expression of miRNAs in gastric cancer cell line. Iran J Cancer Prev 9:e4190. doi:10.17795/ijcp-4190
Mohammadian F, Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi Y, Mofarrah M, Dastani-Habashi M, Zarghami N (2016b) Down regulation of miR-18a, miR-21 and miR-221 genes in gastric cancer cell line by chrysin-loaded PLGA-PEG nanoparticles. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 44:1972–1978
Mohammadian F, Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi Y, Zarghami F, Akbarzadeh A, Zarghami N (2016c) Upregulation of miR-9 and Let-7a by nanoencapsulated chrysin in gastric cancer cells. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 45:1201–1206
Nabavi SF et al (2015) Neuroprotective effects of chrysin: from chemistry to medicine. Neurochem Int 90:224–231
Naderi N et al (2016) The regenerative role of adipose-derived stem cells (ADSC) in plastic and reconstructive surgery. Int Wound J 14:112–114
Nejati-Koshki K, Mortazavi Y, Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi Y, Sheoran S, Zarghami N (2017) An update on application of nanotechnology and stem cells in spinal cord injury regeneration. Biomed Pharmacother 90:85–92
Orciani M, Gorbi S, Benedetti M, Di Benedetto G, Mattioli-Belmonte M, Regoli F, Di Primio R (2010) Oxidative stress defense in human-skin-derived mesenchymal stem cells versus human keratinocytes: different mechanisms of protection and cell selection. Free Radic Biol Med 49:830–838
Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi Y, Akbarzadeh A, Moazzez-Lalaklo N, Zarghami N (2016) An update on clinical applications of electrospun nanofibers for skin bioengineering. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 44:1350–1364
Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi Y, Nouri M, Martino MM, Fattahi A, Alizadeh E, Darabi M, Rahmati-Yamchi M, Zarghami N (2017) Cytoprotection, proliferation and epidermal differentiation of adipose tissue-derived stem cells on emu oil based electrospun nanofibrous mat. Exp Cell Res 357:192–201
Pushpavalli G, Kalaiarasi P, Veeramani C, Pugalendi KV (2010) Effect of chrysin on hepatoprotective and antioxidant status in d-galactosamine-induced hepatitis in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 631:36–41
Rezaei-Sadabady R, Eidi A, Zarghami N, Barzegar A (2016) Intracellular ROS protection efficiency and free radical-scavenging activity of quercetin and quercetin-encapsulated liposomes. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 44:128–134
Rice-Evans C, Miller N (1996) Antioxidant activities of flavonoids as bioactive components of food. Portland Press Limited, London
Saei Arezoumand K, Alizadeh E, Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi Y, Esmaeillou M, Zarghami N (2016) An overview on different strategies for the stemness maintenance of MSCs. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. doi:10.1080/21691401.2016.1246452
Sart S, Song L, Li Y (2015) Controlling redox status for stem cell survival, expansion, and differentiation. Oxid Med Cell Longev. doi:10.1155/2015/105135
Shi W, Wang H, Pan G, Geng Y, Guo Y, Pei D (2006) Regulation of the pluripotency marker Rex-1 by Nanog and Sox2. J Biol Chem 281:23319–23325
Sultana S, Verma K, Khan R (2012) Nephroprotective efficacy of chrysin against cisplatin-induced toxicity via attenuation of oxidative stress. J Pharm Pharmacol 64:872–881
Valizadeh A et al (2016) Preparation and characterization of novel electrospun poly (ϵ-caprolactone)-based nanofibrous scaffolds. Artif Nanomed Biotechnol 44:504–509
Valle-Prieto A, Conget PA (2010) Human mesenchymal stem cells efficiently manage oxidative stress. Stem Cells Development 19:1885–1893
Vrtovec B, Poglajen G, Haddad F (2013) Stem cell therapy in patients with heart failure. Methodist DeBakey Cardiovasc J 9:6–10
Yan X-Z, Both SK, Yang P-S, Jansen JA, van den Beucken JJ, Yang F (2014) Human periodontal ligament derived progenitor cells: effect of STRO-1 cell sorting and Wnt3a treatment on cell behavior. BioMed Res Int. doi:10.1155/2014/145423
Yang S-R, Park J-R, Kang K-S (2015) Reactive oxygen species in mesenchymal stem cell aging: implication to lung diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2015
Zarghami N, Sheervalilou R, Fattahi A, Mohajeri A, Dadashpour M, Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi Y (2017) An overview on application of natural substances incorporated with electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds to development of innovative wound dressings. Mini reviews in medicinal chemistry
Zeineddine D, Hammoud AA, Mortada M, Boeuf H (2014) The Oct4 protein: more than a magic stemness marker. Am J Stem Cells 3:74–82
Zeng W et al (2015) Antioxidant treatment enhances human mesenchymal stem cell anti-stress ability and therapeutic efficacy in an acute liver failure model. Sci Rep 5:11100
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to thank Stem Cell Research Center, Tabriz University for supporting this project. Also, Authors gratefully acknowledge National Institute for Medical Research Development, Tehran, Iran for providing the necessary infrastructure for successful accomplishment of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Yaghoub Deldar and Faraz Zarghami are co-first author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deldar, Y., Zarghami, F., Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi, Y. et al. Antioxidant effects of chrysin-loaded electrospun nanofibrous mats on proliferation and stemness preservation of human adipose-derived stem cells. Cell Tissue Bank 18, 475–487 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-017-9654-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-017-9654-1