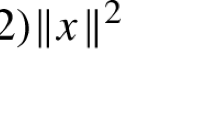Abstract
The paper reviews studies on the representations and expansions of weighted pseudoinverse matrices with positive semidefinite weights and on the construction of iterative methods and regularized problems for the calculation of weighted pseudoinverses and weighted normal pseudosolutions based on these representations and expansions. The use of these methods to solve constrained least squares problems is examined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. V. Sergienko, E. F. Galba, and V. S. Deineka, “Representations and expansions of weighted pseudoinverse matrices, iterative methods and problem regularization. Pt. 1. Positive definite weights,” Cybern. Syst. Analysis, 44, No. 1, 36–55 (2008).
J. F. Ward, T. L. Boullion, and T. O. Lewis, “Weighted pseudoinverses with singular weights,” SIAM J. Appl. Math., 21, No. 3, 480–482 (1971).
S. K. Mitra and C. R. Rao, “Projections under seminorms and generalized Moore-Penrose inverses,” Linear Algebra Appl., 9, 155–167 (1974).
L. Elden, “Perturbation theory for the least squares problem with linear equality constraints,” SIAM J. Numer. Anal., 17, No. 3, 338–350 (1980).
L. Elden, “A weighted pseudoinverse generalized singular values and constrained least squares problems,” BIT, 22, No. 4, 487–502 (1982).
E. H. Moore, “On the reciprocal of the general algebraic matrix,” Abstract. Bull. Amer. Math. Soc., 26, 394–395 (1920).
R. Penrose, “A generalized inverse for matrices,” Proc. Cambridge Phil. Soc., 51, No. 3, 406–413 (1955).
A. Albert, Regression, Pseudoinversion, and Recurrent Estimation [Russian translation], Nauka, Moscow (1977).
E. F. Galba, I. N. Molchanov, and V. V. Skopetskii, “Methods of computing weighted pseudoinverse matrices with singular weights,” Cybern. Syst. Analysis, 35, No. 5, 814–831 (1999).
E. F. Galba, V. S. Deineka, and I. V. Sergienko, “Limit representations of weighted pseudoinverses with singular weights and the regularization of problems,” Comput. Math. Math. Physics, 44, No. 11, 1833–1850 (2004).
E. F. Galba, “Iterative methods for computing weighted minimum-length least squares solution with a singular weight matrix,” Comput. Math. Math. Physics, 39, No. 6, 848–861 (1999).
P. Lancaster and P. Rozsa, “Eigenvectors of H-self-adjoint matrices,” Z. Angew. Math. Mech., 64, No. 9, 439–441 (1984).
Kh. D. Ikramov, “Algebraic properties of classes of pseudo-permutable and H-self-adjoint matrices,” Zh. Vych. Mat. Mat. Fiz., 32, No. 8, 155–169 (1992).
E. F. Galba, V. S. Deineka, and I. V. Sergienko, “Fast convergent iterative methods for the computation of weighted pseudoinverses and weighted normal pseudosolutions with singular weights,” Comput. Math. Math. Physics, 45, No. 10, 1667–1690 (2005).
I. V. Sergienko, E. F. Galba, and V. S. Deineka, “Expansion of weighted pseudoinverse matrices with singular weights into matrix power products and iteration methods,” Ukr. Math. J., 59, No. 9, 1417–1440 (2007).
E. F. Galba, “Weighted pseudoinversion of matrices with singular weights,” Ukr. Math. J., 46, No. 10, 1457–1462 (1994).
P. Lancaster, Theory of Matrices, Acad. Press, New York (1969).
I. V. Sergienko, E. F. Galba, and V. S. Deineka, “Series expansion of weighted pseudoinverse matrices and iterative methods for calculating weighted pseudoinverse matrices and weighted normal pseudosolutions,” Cybern. Syst. Analysis, 42, No. 1, 28–53 (2006).
E. F. Galba, V. S. Deineka, and I. V. Sergienko, “Expansions and polynomial limit representations of the weighted pseudoinverse matrices,” Zh. Vych. Mat. Mat. Fiz., 47, No. 5, 747–766 (2007).
I. V. Sergienko, E. F. Galba, and V. S. Deineka, “Expansion of weighted pseudoinverse matrices in matrix power products,” Ukr. Math. J., 56, No. 11, 1828–1848 (2004).
I. V. Sergienko, E. F. Galba, and V. S. Deineka, “Expansion of weighted pseudoinverse matrices with positive definite weights into matrix power products. Iterative methods,” Cybern. Syst. Analysis, 43, No. 1, 34–49 (2007).
I. V. Sergienko, E. F. Galba, and V. S. Deineka, “Iterative methods with different rates of convergence for calculating weighted pseudoinverse matrices and weighted normal pseudosolutions with positive definite weights,” Cybern. Syst. Analysis, 40, No. 5, 643–664 (2004).
E. F. Galba, “Weighted singular value decomposition and weighted pseudoinversion of matrices,” Ukr. Mat. Zh., 48, No. 10, 1426–1430 (1996).
E. F. Galba, “Iterative methods to compute weighted pseudoinverse matrix,” Zh. Vych. Mat. Mat. Fiz., 36, No. 6, 28–39 (1996).
R. A. Horn and C. R. Johnson, Matrix Analysis, Cambridge Univ. Press (1985).
C. L. Lawson and R. J. Henson, Solving Least Squares Problems, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ (1974).
I. V. Sergienko, E. F. Galba, and V. S. Deineka, “Limiting representations of weighted pseudoinverse matrices with positive definite weights. Problem regularization,” Cybern. Syst. Analysis, 39, No. 6, 816–830 (2003).
G. M. Vainikko and A. Yu. Veretennikov, Iterative Procedures in Ill-Posed Problems [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1986).
E. V. Arkharov and R. A. Shafiev, “Regularization methods for the constrained pseudoinversion problem with inaccurate data,” Comput. Math. Math. Physics, 43, No. 3, 331–337 (2003).
V. E. Uvarov and R. A. Shafiev, “An iterative regularization method for the 2-constrained pseudoinversion of an operator equation,” Comput. Math. Math. Physics, 46, No. 10, 1651–1659 (2006).
Y. Censor, D. Gordon, and R. Gordon, “Component averaging: an efficient iterative parallel algorithm for large and sparse unstructured problems,” Parallel Comput., 27, No. 6, 777–808 (2001).
Y. Censor, D. Gordon, and R. Gordon, “BICAV: an inherently parallel algorithm for sparse systems with pixel-dependent weighting,” IEEE Trans. Medical Imaging, 20, 1050–1060 (2001).
Y. Censor and T. Elfving, “Block-iterative algorithms with diagonally skaled oblique projections for the linear feasibility problem,” SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl., 24, No. 1, 40–58 (2002).
Y. Censor and T. Elfving, “Iterative algorithms with seminorm-induced oblique projections,” Abstr. Appl. Anal., No. 7, 387–406 (2003).
E. F. Galba, “Representing weighted pseudoinverse matrix in terms of other pseudoinverse matrices,” Dop. NAN Ukr., No. 4, 12–17 (1997).
O. Vaarmann, Generalized Inverse Mappings [in Russian], Valgus, Tallinn (1988).
V. A. Morozov, Regular Methods of Solving Ill-Posed Problems [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1987).
V. I. Meleshko, “Applying recurrent optimal estimates with pseudoinversion in identification problems,” Avtom. Telemekh., No. 9, 79–89 (1978).
G. W. Stewart, “On the weighting method for least squares problems with linear equality constraints,” BIT, 37, 961–967 (1997).
C. Van Loan, “On the method of weighting for equality-constrained least-squares problems,” SIAM J. Numer. Anal., 22, No. 5, 851–864 (1985).
Kh. D. Ikramov and M. far Matin, “On computer-algebra procedures for linear least squares problems with linear equality constraints,” Comput. Math. Math. Physics, 44, No. 2, 190–196 (2004).
G. H. Golub, “Some modified eigenvalue problems,” SIAM Rev., 15, No. 2, 318–334 (1973).
G. H. Golub V. von Matt, “Quadratically constrained least squares and quadratic problems,” Numer. Math., 59, No. 6, 561–580 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Continued from Cybernetics and Systems Analysis, 44, No. 1, 36–55 (2008).
__________
Translated from Kibernetika i Sistemnyi Analiz, No. 3, pp. 75–102, May–June 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sergienko, I.V., Galba, E.F. & Deineka, V.S. Representations and expansions of weighted pseudoinverse matrices, iterative methods, and problem regularization. II. Singular weights. Cybern Syst Anal 44, 375–396 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10559-008-9004-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10559-008-9004-1