Abstract
Purpose
Heart failure (HF) is a major public health issue. This study conducted a real-life analysis of the impact of clinical characteristics and medical management of HF on its prognosis.
Methods
Analysis was based on the EGB (“Echantillon Généraliste des Bénéficiaires”) database. A cohort comprising 1825 adult patients with a first admission for HF between 2009 and 2011 was created and followed until June 2013 (median 22.3 [7.7–34.5] months) for survival analysis.
Results
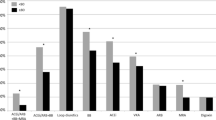
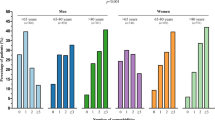
Mean age was 77.3 ± 13.2 years (53 % ≥80 years). The overall incidence of HF admission was 117 [112–122] per 100,000 population with a marked increase in patients >80 years (1297 [1217–1348]). At discharge, only 8 % of patients received recommended combination of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin receptor blockers (ACEi/ARB), beta-blockers (BB) and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRA). Only prescription levels of BB and vitamin K antagonists, at discharge, increased during the study period. In-hospital mortality was 9 % and survival was 71.6 %[69.5–73.6] and 52.0 %[49.4–54.6] at 12 and 36 months, respectively. In multivariate analysis, female gender [HR:0.78 (0.67–0.91), p = 0.001], ACEi/ARB + BB + MRA [0.41 (0.28–0.60), p < 0.001] and ACEi/ARB + BB [0.47 (0.39–0.57) p < 0.001] treatments were associated with improved survival, conversely to age 70–79 [1.90 (1.20–3.00), p = 0.003] and ≥80 [3.50 (2.30–5.40), p < 0.001], cardiogenic shock [3.00 (2.10–4.40), p < 0.001], acute pulmonary edema [1.70 (1.10–2.50), p = 0.01], denutrition [1.80 (1.45–2.24), p < 0.001], dilated cardiomyopathy [1.20 (1.00–1.40), p = 0.02] and in-hospital acute renal failure [1.36 (1.05–1.78), p = 0.002].
Conclusions
These real-life HF data provide insight into prognostic factors and “real-world” pharmacological management in this unselected HF population, confirming the benefit of ACEi/ARB + BB ± MRAs on patient survival.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ho KK, Pinsky JL, Kannel WB, Levy D. The epidemiology of heart failure: the Framingham study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1993;22:6A–13A.
Delahaye F, Roth O, Aupetit JF, de Gevigney G. Epidemiology and prognosis of cardiac insufficiency. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 2001;94:1393–403.
McMurray JJV, Adamopoulos S, Anker SD, Auricchio A, Böhm M, Dickstein K, et al. ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: the task force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012 of the European society of cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the heart failure association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. 2012;33:1787–847.
Levy D, Kenchaiah S, Larson MG, Benjamin EJ, Kupka MJ, Ho KKL, et al. Long-term trends in the incidence of and survival with heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1397–402.
Laribi S, Aouba A, Nikolaou M, Lassus J, Cohen-Solal A, Plaisance P, et al. Trends in death attributed to heart failure over the past two decades in Europe. Eur J Heart Fail. 2012;14:234–9.
Cleland JGF, Swedberg K, Follath F, Komajda M, Cohen-Solal A, Aguilar JC, et al. The EuroHeart failure survey programme– a survey on the quality of care among patients with heart failure in Europe. Part 1: patient characteristics and diagnosis. Eur Heart J. 2003;24:442–63.
Martin-Latry K, Bégaud B. Pharmacoepidemiological research using French reimbursement databases: yes we can! Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2010;19:256–65.
Tuppin P, de Roquefeuil L, Weill A, Ricordeau P, Merlière Y. French national health insurance information system and the permanent beneficiaries sample. Rev Epidemiol Sante Publique. 2010;58:286–90.
Blin P, Lassalle R, Dureau-Pournin C, Ambrosino B, Bernard MA, Abouelfath A, et al. Insulin glargine and risk of cancer: a cohort study in the French national healthcare insurance database. Diabetologia. 2012;55:644–53.
Bezin J, Pariente A, Lassalle R, Dureau-Pournin C, Abouelfath A, Robinson P, et al. Use of the recommended drug combination for secondary prevention after a first occurrence of acute coronary syndrome in France. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2014;70:429–36.
Dupouy J, Fournier J-P, Jouanjus É, Palmaro A, Poutrain J-C, Oustric S, et al. Baclofen for alcohol dependence in France: incidence of treated patients and prescription patterns–a cohort study. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014;24:192–9.
Fournier A, Zureik M. Estimate of deaths due to valvular insufficiency attributable to the use of benfluorex in France. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2012;21:343–51.
Bongue B, Laroche ML, Gutton S, Colvez A, Guéguen R, Moulin JJ, et al. Potentially inappropriate drug prescription in the elderly in France: a population-based study from the French national insurance healthcare system. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2011;67:1291–9.
Duong M, Salvo F, Pariente A, Abouelfath A, Lassalle R, Droz C, et al. Usage patterns of « over-the-counter » vs. prescription-strength nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in France. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2014;77:887–95.
Schoenfeld D. Partial residuals for the proportional hazards regression model. Biometrika. 1982;69:239–41.
Harrell Jr FE, Lee KL, Mark DB. Multivariable prognostic models: issues in developing models, evaluating assumptions and adequacy, and measuring and reducing errors. Stat Med. 1996;15:361–87.
Malek MH, Berger DE, Coburn JW. On the inappropriateness of stepwise regression analysis for model building and testing. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2007;101:263–4. author reply 265–6.
Logeart D, Isnard R, Resche-Rigon M, Seronde M-F, de Groote P, Jondeau G, et al. Current aspects of the spectrum of acute heart failure syndromes in a real-life setting: the OFICA study. Eur J Heart Fail. 2013;15:465–76.
Tuppin P, Cuerq A, de Peretti C, Fagot-Campagna A, Danchin N, Juillière Y, et al. First hospitalization for heart failure in France in 2009: patient characteristics and 30-day follow-up. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2013;106:570–85.
Komajda M, Follath F, Swedberg K, Cleland J, Aguilar JC, Cohen-Solal A, et al. The euroheart failure survey programme–a survey on the quality of care among patients with heart failure in Europe. Part 2: treatment. Eur Heart J. 2003;24:464–74.
Fonarow GC, Heywood JT, Heidenreich PA, Lopatin M, Yancy CW, ADHERE. Scientific advisory committee and investigators. Temporal trends in clinical characteristics, treatments, and outcomes for heart failure hospitalizations, 2002 to 2004: findings from acute decompensated heart failure national registry (ADHERE). Am Heart J. 2007;153:1021–8.
Jhund PS, Macintyre K, Simpson CR, Lewsey JD, Stewart S, Redpath A, et al. Long-term trends in first hospitalization for heart failure and subsequent survival between 1986 and 2003: a population study of 5.1 million people. Circulation. 2009;119:515–23.
Yeung DF, Boom NK, Guo H, Lee DS, Schultz SE, Tu JV. Trends in the incidence and outcomes of heart failure in Ontario, Canada: 1997 to 2007. CMAJ. 2012;184:E765–73.
Bui AL, Horwich TB, Fonarow GC. Epidemiology and risk profile of heart failure. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2011;8:30–41.
Komajda M, Hanon O, Hochadel M, Lopez-Sendon JL, Follath F, Ponikowski P, et al. Contemporary management of octogenarians hospitalized for heart failure in Europe: euro heart failure survey II. Eur Heart J. 2009;30:478–86.
Zannad F, Briancon S, Juilliere Y, Mertes PM, Villemot JP, Alla F, et al. Incidence, clinical and etiologic features, and outcomes of advanced chronic heart failure: the EPICAL study. Epidémiologie de l’insuffisance cardiaque avancee en lorraine. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999;33:734–42.
Stewart S, MacIntyre K, Hole DJ, Capewell S, McMurray JJ. More « malignant » than cancer? Five-year survival following a first admission for heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail. 2001;3:315–22.
Van Gelder IC, Hagens VE, Bosker HA, Kingma JH, Kamp O, Kingma T, et al. A comparison of rate control and rhythm control in patients with recurrent persistent atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1834–40.
Roy D, Talajic M, Nattel S, Wyse DG, Dorian P, Lee KL, et al. Rhythm control versus rate control for atrial fibrillation and heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2667–77.
Oluleye OW, Rector TS, Win S, McMurray JJ, Zile M, Komajda M, et al. History of atrial fibrillation as a risk factor in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction. Circ Heart Fail. 2014.
Güder G, Frantz S, Bauersachs J, Allolio B, Wanner C, Koller MT, et al. Reverse epidemiology in systolic and nonsystolic heart failure: cumulative prognostic benefit of classical cardiovascular risk factors. Circ Heart Fail. 2009;2:563–71.
Kjekshus J, Apetrei E, Barrios V, Böhm M, Cleland JGF, Cornel JH, et al. Rosuvastatin in older patients with systolic heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:2248–61.
Gissi-HF I, Tavazzi L, Maggioni AP, Marchioli R, Barlera S, Franzosi MG, et al. Effect of rosuvastatin in patients with chronic heart failure (the GISSI-HF trial): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2008;372:1231–9.
Shekelle PG, Rich MW, Morton SC, Atkinson CSW, Tu W, Maglione M, et al. Efficacy of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and beta-blockers in the management of left ventricular systolic dysfunction according to race, gender, and diabetic status: a meta-analysis of major clinical trials. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;41:1529–38.
Cowburn PJ, Cleland JG, Coats AJ, Komajda M. Risk stratification in chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J. 1998;19:696–710.
Dickstein K, Cohen-Solal A, Filippatos G, McMurray JJV, Ponikowski P, Poole-Wilson PA, et al. ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2008: the task force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2008 of the European society of cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the heart failure association of the ESC (HFA) and endorsed by the European society of intensive care medicine (ESICM). Eur Heart J. 2008;29:2388–442.
Acknowledgments
We thank Mr. Pierre Pothier for the editing of this manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Romain Eschalier and Chouki Chenaf are both first co-authors; Alain Eschalier and Jean-René Lusson are both last co-authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eschalier, R., Chenaf, C., Mulliez, A. et al. Impact of Clinical Characteristics and Management on the Prognosis of Unselected Heart Failure Patients. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 29, 89–98 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-015-6572-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-015-6572-y