Abstract
Purpose
Studies have shown that nifedipine protects against atherosclerotic progression, but its underlying mechanisms remain unclear. In this study, we examined if nifedipine increases macrophage cholesterol efflux, a pathway known to inhibit atherogenesis.
Methods
We evaluated the ability of different doses of nifedipine to affect cholesterol efflux in RAW264.7 macrophages and its relationship with mRNA and protein levels of several well-characterized proteins involved in cholesterol efflux, including ABCA1, ABCG1, SR-BI and LXRα, using quantitative real-time PCR, Western blotting, and siRNA techniques.
Results
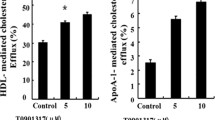
Nifedipne at 1, 10, and 100 nmol/L increased apoA-I-mediated cholesterol efflux from 2.55 % to 5.65 %, 6.20 %, and 6.10 %, as well as HDL-mediated cholesterol efflux from 31.0 % to 42.5 %, 46.0 %, and 43.5 %, respectively, in RAW264.7 macrophages (p < 0.05), which was associated with increased mRNA expression levels of ABCA1, ABCG1, SR-BI, and LXRα (405 %, 381 %, 336 %; 890 %, 960 %, 1002 %; 285 %, 325 %, 336 %; 482 %, 445 %, 405 %, respectively, p < 0.05), and with increased protein levels of ABCA1, ABCG1, SR-BI, and LXRα (428 %, 492 %, 361 %; 288 %, 331 %, 365 %; 283 %, 320 %, 505 %; 581 %, 678 %, 608 %, respectively, p < 0.05). SiRNA-mediated silencing of LXRα revealed that LXRα was involved in these increases and the enhanced cholesterol efflux.
Conclusion
Nifedipine may protect against atherosclerosis partly by promoting macrophage cholesterol efflux through the stimulation of LXRα-dependent expression of ABCA1, ABCG1, and SR-BI.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lusis AJ. Atherosclerosis. Nature. 2000;407:233–41.
Bobryshev YV. Monocyte recruitment and foam cell formation in atherosclerosis. Micron. 2006;37:208–22.
Viles-Gonzalez JF, Fuster V, Badimon JJ. Atherothrombosis: a widespread disease with unpredictable and life-threatening consequences. Eur Heart J. 2004;25:1197–207.
Moreno PR, Sanz J, Fuster V. Promoting mechanisms of vascular health: circulating progenitor cells, angiogenesis, and reverse cholesterol transport. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53:2315–23.
Rader DJ. Regulation of reverse cholesterol transport and clinical implications. Am J Cardiol. 2003;92:42J–9J.
Escolà-Gil JC, Rotllan N, Julve J, Blanco-Vaca F. In vivo macrophage-specific RCT and antioxidant and antiinflammatory HDL activity measurements: new tools for predicting HDL atheroprotection. Atherosclerosis. 2009;206:321–7.
Oram JF, Vaughan AM. ABCA1-mediated transport of cellular cholesterol and phospholipids to HDL apolipoproteins. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2000;11:253–60.
Wang N, Lan D, Chen W, Matsuura F, Tall AR. ATP-binding cassette transporters G1 and G4 mediate cellular cholesterol efflux to high-density lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;10:9774–9.
Sung JY, Choi HC. Nifedipine inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and reactive oxygen species production through AMP-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Vasc Pharmacol. 2012;56:1–8.
Takase B, Hamabe A, Satomura K, Akima T, Uehata A, Ohsuzu F, et al. Beneficial effects of nifedipine on vasodilator response to acetylcholine in coronary and brachial arteries in the patients with coronary artery disease. Int J Cardiol. 2006;113:305–10.
Poole-Wilson PA, Lubsen J, Kirwan BA, van Dalen FJ, Wagener G, Danchin N, et al. A Coronary disease Trial Investigating Outcome with Nifedipine gastrointestinal therapeutic system investigators. Effect of long-acting nifedipine on mortality and cardiovascular morbidity in patients with stable angina requiring treatment (ACTION trial): randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2004;364:849–57.
Suzuki S, Nishimaki-Mogami T, Tamehiro N, Inoue K, Arakawa R, Abe-Dohmae S, et al. Verapamil increases the apolipoprotein-mediated release of cellular cholesterol by induction of ABCA1 expression via Liver X receptor-independent mechanism. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24:519–25.
Nissen SE, Tuzcu EM, Libby P, Thompson PD, Ghali M, Garza D, et al. Effect of antihypertensive agents on cardiovascular events in patients with coronary disease and normal blood pressure: the CAMELOT study: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2004;292:2217–25.
Ishii N, Matsumura T, Kinoshita H, Fukuda K, Motoshima H, Senokuchi T, et al. Nifedipine induces peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma activation in macrophages and suppresses the progression of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010;30:1598–605.
Jessup W, Gelissen IC, Gaus K, Kritharides L. Roles of ATP binding cassette transporters A1 and G1, scavenger receptor BI and membrane lipid domains in cholesterol export from macrophages. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2006;17:247–57.
Calpe-Berdiel L, Rotllan N, Palomer X, Ribas V, Blanco-Vaca F, Escolà-Gil JC. Direct evidence in vivo of impaired macrophage-specific reverse cholesterol transport in ATP-binding cassette transporter A1-deficient mice. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1738:6–9.
Fitzgerald ML, Mujawar Z, Tamehiro N. ABC transporters, atherosclerosis and inflammation. Atherosclerosis. 2010;211:361–70.
Hasegawa K, Wakino S, Kanda T, Yoshioka K, Tatematsu S, Homma K, et al. Divergent action of calcium channel blockers on ATP-binding cassette protein expression. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2005;46:787–93.
Willy PJ, Umesono K, Ong ES, Evans RM, Heyman RA, Mangelsdorf DJ. LXR, a nuclear receptor that defines a distinct retinoid response pathway. Genes Dev. 1995;9:1033–45.
Repa JJ, Mangelsdorf DJ. The role of orphan nuclear receptors in the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Ann Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2000;16:459–81.
Tang SL, Chen WJ, Yin K, Zhao GJ, Mo ZC, Lv YC, et al. PAPP-A negatively regulates ABCA1, ABCG1 and SR-B1 expression by inhibiting LXR through the IGF-I-mediated signaling pathway. Atherosclerosis. 2012;222:344–54.
Pannu PS, Allahverdian S, Francis GA. Oxysterol generation and liver X receptor-dependent reverse cholesterol transport: Not all roads lead to Rome. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013;368:99–107.
Conflict of Interest
None declared
Funding
This work was supported by a grant (No. 8110219) from the Natural Science Foundation of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Qian Zhang and A Zhi Sha Ma contributed equally to this publication.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Ma, A.Z.S., Song, Z.Y. et al. Nifedipine Enhances Cholesterol Efflux in RAW264.7 Macrophages. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 27, 425–431 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-013-6472-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-013-6472-y