Abstract
The association between blood coagulation and cancer development is well recognized. Thrombin, the pleiotropic enzyme best known for its contribution to fibrin formation and platelet aggregation during vascular hemostasis, may also trigger cellular events through protease-activated receptors, PAR-1 and PAR-4, leading to cancer progression. Our pioneering findings provided evidence that thrombin contributes to cancer metastasis by increasing adhesive potential of malignant cells. However, there is evidence that thrombin regulates every step of cancer dissemination: (1) cancer cell invasion, detachment from primary tumor, migration; (2) entering the blood vessel; (3) surviving in vasculature; (4) extravasation; (5) implantation in host organs. Recent studies have provided new molecular data about thrombin generation in cancer patients and the mechanisms by which thrombin contributes to transendothelial migration, platelet/tumor cell interactions, angiogenesis, and other processes. Though a great deal is known regarding the role of thrombin in cancer dissemination, there are new data for multiple thrombin-mediated events that justify devoting focus to this topic with a comprehensive approach.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Konstantopoulos, K., & Thomas, S. N. (2009). Cancer cells in transit: the vascular interactions of tumor cells. Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering, 11, 177–202.
Tsopanoglou, N. E., & Maragoudakis, M. E. (2009). Thrombin’s central role in angiogenesis and pathophysiological processes. European Cytokine Network, 20(4), 171–179.
Wojtukiewicz, M. Z., Hempel, D., Sierko, E., Tucker, S. C., & Honn, K. V. (2015). Protease-activated receptors (PARs)—biology and role in cancer invasion and metastasis. Cancer and Metastasis Reviews, 34(4), 775–796.
Wojtukiewicz, M.Z., Ciarelli, J.J., Walz, D.A., Honn, K.V. (1990). Thrombin enhances cancer cell expression of an integrin receptor and increases adhesion. 81st Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research, Washington, Proceedings of AACR, 31:Abstract 476.
Wojtukiewicz, M.Z., Ciarelli, J.J., Snyder, D.A., Nelson, K.K., Walz, D.A., Honn, K.V. (1990). Increased tumor cell adhesiveness and experimental metastasis following exposure to alpha-thrombin, its precursor and analogues. American Cancer Society Michigan Division Inc., 1990 Cancer Research Conference, Ypsilanti, MI, USA, Poster 22.
Wojtukiewicz, M.Z., Ciarelli, J.J., Snyder, D., Nelson, K.K., Walz, D.A., Honn, K.V. (1990). Thrombin increases tumor cell adhesiveness via a non-proteolytic pathway. First Regional Meeting of the American Society for Cell Biology, Chicago, IL, USA, 1990, Abstract 91.
Wojtukiewicz, M. Z., Tang, D. G., Nelson, K. K., Walz, D. A., Diglio, C. A., & Honn, K. V. (1992). Thrombin enhances tumor cell adhesive and metastatic properties via increased alpha IIb beta 3 expression on the cell surface. Thrombosis Research, 68, 233–245.
Wojtukiewicz, M. Z., Tang, D. G., Ciarelli, J. J., Nelson, K. K., Walz, D. A., Diglio, C. A., et al. (1993). Thrombin increases the metastatic potential of tumor cells. International Journal of Cancer, 54, 793–806.
Pereira, L., Mariadason, J. M., Hannan, R. D., & Dhillon, A. S. (2015). Implications of epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity for heterogeneity in colorectal cancer. Frontiers in Oncology. doi:10.3389/fonc.2015.00013.
Zhang, T., Ma, Z., Wang, R., Wang, Y., Wang, S., Cheng, Z., et al. (2010). Thrombin facilitates invasion of ovarian cancer along peritoneum by inducing monocyte differentiation toward tumor-associated macrophage-like cells. Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy, 59(7), 1097–1108.
Zhang, P., Feng, S., Liu, G., Wang, H., Zhu, H., Ren, Q., et al. (2016). Mutant B-Raf (V600E) promotes melanoma paracellular transmigration by inducing thrombin-mediated endothelial junction breakdown. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 291(5), 2087–2106.
Nierodzik, M. L., Kajumo, F., & Karpatkin, S. (1992). Effect of thrombin treatment of tumor cells on adhesion of tumor cells to platelets in vitro and tumor metastasis in vivo. Cancer Research, 52, 3267–3272.
Nierodzik, M. L., & Karpatkin, S. (2006). Thrombin induces tumor growth, metastasis, and angiogenesis: evidence for a thrombin-regulated dormant tumor phenotype. Cancer Cell, 10, 355–362.
Nierodzik, M. L., Chen, K., Takeshita, K., Li, J. J., Huang, Y. Q., Feng, X. S., et al. (1998). Protease-activated receptor 1 (PAR-1) is required and rate-limiting for thrombin-enhanced experimental pulmonary metastasis. Blood, 92, 3694–3700.
Nierodzik, M., Plotkin, A., Kajumo, F., & Karpatkin, S. (1991). Thrombin stimulates tumor-platelet adhesion in vitro and metastasis in vivo. The Journal of Clinical Investment, 87, 229–236.
Zigler, M., Kamiya, T., Brantley, E. C., Villares, G. J., & Bar-Eli, M. (2011). PAR-1 and thrombin: the ties that bind the microenvironment to melanoma metastasis. Cancer Research, 71(21), 6561–6566.
Reitter, E. M., Kaider, A., Ay, C., Quehenberger, P., Marosi, C., Zielinski, C., et al. (2015). Longitudinal analysis of hemostasis biomarkers in cancer patients during the anti-tumor treatment. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. doi:10.1111/jth.13218.
Tsopanoglou, N. E., & Maragoudakis, M. E. (2004). Role of thrombin in angiogenesis and tumor progression. Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis, 30(1), 63–69.
Hu, L., Lee, M., Campbell, W., Perez-Soler, R., & Karpatkin, S. (2004). Role of endogenous thrombin in tumor implantation, seeding, and spontaneous metastasis. Blood, 104(9), 2746–2751.
Guo, R. R., Liu, Y., Lu, W. L., Zhao, J. H., Wang, X. Q., Zhang, H., et al. (2008). A recombinant peptide, hirudin, potentiates the inhibitory effects of stealthy liposomal vinblastine on the growth and metastasis of melanoma. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 31(4), 696–702.
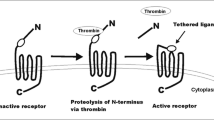
Wojtukiewicz, M. Z., Tang, D. G., Ben-Josef, E., Renaud, C., Walz, D. A., & Honn, K. V. (1995). Solid tumor cells express functional “tethered ligand” thrombin receptor. Cancer Research, 55(3), 698–704.
Queiroz, K. C., Shi, K., Duitman, J., Aberson, H. L., Wilmink, J. W., van Noesel, C. J., et al. (2014). Protease-activated receptor-1 drives pancreatic cancer progression and chemoresistance. International Journal of Cancer, 135(10), 2294–2304.
Yoon, H., Radulovic, M., Drucker, K. L., Wu, J., & Scarisbrick, I. A. (2015). The thrombin receptor is a critical extracellular switch controlling myelination. Glia, 63(5), 846–859.
Bapat, A. A., Hostetter, G., Von Hoff, D. D., & Han, H. (2011). Perineural invasion and associated pain in pancreatic cancer. Nature Reviews Cancer, 11(10), 695–707.
Alexander, E. T., Minton, A. R., Hayes, C. S., Goss, A., Van Ryn, J., & Gilmour, S. K. (2015). Thrombin inhibition and cyclophosphamide synergistically block tumor progression and metastasis. Cancer Biology and Therapy, 16(12), 1802–1811.
Horowitz, N. A., Blevins, E. A., Miller, W. M., Perry, A. R., Talmage, K. E., Mullins, E. S., et al. (2011). Thrombomodulin is a determinant of metastasis through a mechanism linked to the thrombin binding domain but not the lectin-like domain. Blood, 118(10), 2889–2895.
DeFeo, K., Hayes, C., Chernick, M., Ryn, J. V., & Gilmour, S. K. (2010). Use of dabigatran etexilate to reduce breast cancer progression. Cancer Biology and Therapy, 10, 1001–1008.
Nieman, M. T., LaRusch, G., Fang, C., Zhou, Y., & Schmaier, A. H. (2010). Oral thrombostatin FM19 inhibits prostate cancer. Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 104, 1044–1048.
Ratnoff, O. D., Ratnoff, O. D., & Forbes, C. D. (Eds.). (1996). The evolution of knowledge about hemostasis. Disorders of Hemostasis (3rd ed.). Philadelphia: WB Saunders Company.
Huntington, J. A. (2005). Molecular recognition mechanisms of thrombin. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 3(8), 1861–1872.
Higgins, D. L., Lewis, S. D., & Shafer, J. A. (1983). Steady state kinetic parameters for the thrombin-catalyzed conversion of human fibrinogen to fibrin. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 258, 9276–9282.
Boknäs, N., Faxälv, L., Sanchez Centellas, D., Wallstedt, M., Ramström, S., Grenegård, M., et al. (2014). Thrombin-induced platelet activation via PAR4, pivotal role for exosite II. Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 112(3), 558–565.
Vu, T. K., Hung, D. T., Wheaton, V. I., & Coughlin, S. R. (1991). Molecular cloning of a functional thrombin receptor reveals a novel proteolytic mechanism of receptor activation. Cell, 64(6), 10557–10568.
Austin, K. M., Covic, L., & Kuliopulos, A. (2013). Matrix metalloproteases and PAR1 activation. Blood, 121(3), 431–439.
Coughlin, S. R. (2005). Protease-activated receptors in hemostasis, thrombosis and vascular biology. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 3, 1800–1814.
Ossovskaya, V. S., & Bunnett, N. W. (2004). Protease-activated receptors: contribution to physiology and disease. Physiological Reviews, 84(2), 579–621.
Lin, H., Liu, A. P., Smith, T. H., & Trejo, J. (2013). Cofactoring and dimerization of proteinase-activated receptors. Pharmacological Reviews, 65(4), 1198–1213.
Junge, C. E., Lee, C. J., Hubbard, K. B., Zhang, Z., Olson, J. J., Hepler, J. R., et al. (2004). Protease-activated receptor-1 in human brain: localization and functional expression in astrocytes. Experimental Neurology, 188(1), 94–103.
Xie, Q., Bao, X., Chen, Z. H., Xu, Y., Keep, R. F., Muraszko, K. M., et al. (2016). Role of protease-activated receptor-1 in glioma growth. Acta Neurochirurgica Supplement, 121, 355–360.
Li, S. M., Jiang, P., Xiang, Y., Wang, W. W., Zhu, Y. C., Feng, W. Y., et al. (2015). Protease-activated receptor (PAR)1, PAR2 and PAR4 expressions in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dongwuxue Yanjiu, 35(5), 420–425.
Adams, G. N., Rosenfeldt, L., Frederick, M., Miller, W., Waltz, D., Kombrinck, K., et al. (2015). Colon cancer growth and dissemination relies upon thrombin, stromal PAR-1, and fibrinogen. Cancer Research, 75(19), 4235–4243.
Sedda, S., Marafini, I., Caruso, R., Pallone, F., & Monteleone, G. (2014). Proteinase activated-receptors-associated signaling in the control of gastric cancer. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 20, 11977–11984.
Schulze, E. B., Hedley, B. D., Goodale, D., Postenka, C. O., Al-Katib, W., & Tuck, A. B. (2008). The thrombin inhibitor Argatroban reduces breast cancer malignancy and metastasis via osteopontin-dependent and osteopontin-independent mechanisms. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment, 112(2), 243–254.
Zain, J., Huang, Y. Q., Feng, X., Nierodzik, M. L., Li, J. J., & Karpatkin, S. (2000). Concentration-dependent dual effect of thrombin on impaired growth/apoptosis or mitogenesis in tumor cells. Blood, 95(10), 3133–3138.
Wojtukiewicz, M. Z., Sierko, E., & Rak, J. (2004). Contribution of the hemostatic system to angiogenesis in cancer. Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis, 30(1), 5–20.
van den Berg, Y. W., Osanto, S., Reitsma, P. H., & Versteeg, H. H. (2012). The relationship between tissue factor and cancer progression: insights from bench and bedside. Blood, 119(4), 924–932.
Schaffner, F., & Ruf, W. (2009). Tissue factor and PAR2 signaling in the tumor microenvironment. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 29(12), 1999–2004.
Lindahl, U., Peiler, G., Bozgwald, J., & Seljelid, R. (1989). A prothrominase complex of mouse peritoneal macrophages. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 273, 180–188.
Vrana, J. A., Stang, M. T., Grande, J. P., & Getz, M. J. (1996). Expression of tissue factor in tumor stroma correlates with progression to invasive human breast cancer: paracrine regulation by carcinoma cell-derived members of the transforming growth factor beta family. Cancer Research, 56(21), 5063–5070.
Wojtukiewicz, M. Z., Zacharski, L. R., Ruciñska, M., Zimnoch, L., Jaromin, J., Rózañska-Kudelska, M., et al. (1999). Expression of tissue factor and tissue factor pathway inhibitor in situ in laryngeal carcinoma. Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 82(6), 1659–1662.
Wojtukiewicz, M. Z., Sierko, E., Zacharski, L. R., Zimnoch, L., Kudryk, B., & Kisiel, W. (2003). Tissue factor-dependent coagulation activation and impaired fibrinolysis in situ in gastric cancer. Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis, 29(3), 291–300.
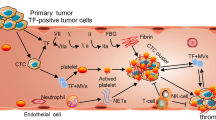
Menter, D. G., Tucker, S. C., Kopetz, S., Sood, A. K., Crissman, J. D., & Honn, K. V. (2014). Platelets and cancer: a casual or causal relationship: revisited. Cancer Metastasis Reviews, 33(1), 231–269.
Young, A., Chapman, O., Connor, C., Poole, C., Rose, P., & Kakkar, A. K. (2012). Thrombosis and cancer. Nature Reviews. Clinical Oncology, 9(8), 437–449.
Thomas, G. M., Brill, A., Mezouar, S., Crescence, L., Gallant, M., Dubois, C., et al. (2015). Tissue factor expressed by circulating cancer cell-derived microparticles drastically increases the incidence of deep vein thrombosis in mice. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 13(7), 1310–1319.
D’Asti, E., & Rak, J. (2016). Biological basis of personalized anticoagulation in cancer: oncogene and oncomir networks as putative regulators of coagulopathy. Thrombosis Research, 140(Suppl 1), 37–43.
D’Andrea, M. R., Derian, C. K., Santulli, R. J., & Andrade-Gordon, P. (2001). Differential expression of protease activated receptors-1 and -2 in stromal fibroblasts of normal, benign, and malignant human tissues. American Journal of Pathology, 158, 2031–2041.
Zhao, F., Li, L., Guan, L., Yang, H., Wu, C., & Liu, Y. (2014). Roles for GP IIb/IIIa and αvβ3 integrins in MDA-MB-231 cell invasion and shear flow-induced cancer cell mechanotransduction. Cancer Letters, 344(1), 62–73.
Radjabi, A. R., Sawada, K., Jagadeeswaran, S., Eichbichler, A., Kenny, H. A., Montag, A., et al. (2008). Thrombin induces tumor invasion through the induction and association of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and beta1-integrin on the cell surface. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 283, 2822–2834.
Shi, X., Gangadharan, B., Brass, L., Ruf, W., & Mueller, B. (2004). Protease activated receptors (PAR1 and PAR2) contribute to tumor cell motility and metastasis. Molecular Cancer Research, 2, 395–402.
Liotta, L. A., Steeg, P. S., & Stetler-Stevenson, W. (1991). Cancer metastasis and angiogenesis: an imbalance of positive and negative regulation. Cell, 64, 327–336.
Hu, L., Roth, J. M., Brooks, P., Luty, J., & Karpatkin, S. (2008). Thrombin up-regulates cathepsin D which enhances angiogenesis, growth, and metastasis. Cancer Research, 68(12), 4666–4673.
Hu, L., Roth, J. M., Brooks, P., Ibrahim, S., & Karpatkin, S. (2008). Twist is required for thrombin-induced tumor angiogenesis and growth. Cancer Research, 68(11), 4296–4302.
Chang, L. H., Chen, C. H., Huang, D. Y., Pai, H. C., Pan, S. L., & Teng, C. M. (2011). Thrombin induces expression of twist and cell motility via the hypoxia-inducible factor-1α translational pathway in colorectal cancer cells. Journal of Cell Physiology, 226(4), 1060–1068.
Beausoleil, M. S., Schulze, E. B., Goodale, D., Postenka, C. O., & Allan, A. L. (2011). Deletion of the thrombin cleavage domain of osteopontin mediates breast cancer cell adhesion, proteolytic activity, tumorgenicity, and metastasis. BioMed Central Cancer. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-11-25.
Rudland, P. S., Platt-Higgins, A., El-Tanani, M., De Silva Rudland, S., Barraclough, R., Winstanley, J. H., et al. (2002). Prognostic significance of the metastasis-associated protein osteopontin in human breast cancer. Cancer Research, 62, 3417–3427.
Tuck, A. B., Chambers, A. F., & Allan, A. L. (2007). Osteopontin overexpression in breast cancer: knowledge gained and possible implications for clinical management. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 102(4), 859–868.
Senger, D., & Peruzzi, C. (1996). Cell migration promoted by a potent GRGDS-containing thrombin-cleavage fragment of osteopontin. Biochem et Biophysica Acta, 1314, 13–24.
Senger, D. R., Ledbetter, S. R., Claffey, K. P., Papadopoulos-Sergiou, A., Peruzzi, C. A., & Detmar, M. (1996). Stimulation of endothelial cell migration by vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor through cooperative mechanisms involving the alphavbeta3 integrin, osteopontin, and thrombin. American Journal of Pathology, 149(1), 293–305.
Schulze, E. B., Hedley, B. D., Goodale, D., Postenka, C. O., Al-Katib, W., Tuck, A. B., et al. (2008). The thrombin inhibitor Argatroban reduces breast cancer malignancy and metastasis via osteopontin-dependent and osteopontin-independent mechanisms. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment, 112(2), 243–254.
Wallerand, H., Robert, G., Pasticier, G., Ravaud, A., Ballanger, P., Reiter, R. E., et al. (2010). The epithelial-mesenchymal transition-inducing factor TWIST is an attractive target in advanced and/or metastatic bladder and prostate cancers. Urologic Oncology, 28(5), 473–479.
Khan, M. A., Chen, H. C., Zhang, D., & Fu, J. (2013). Twist: a molecular target in cancer therapeutics. Tumour Biology, 34(5), 2497–2506.
Caunt, M., Hu, L., Tang, T., Brooks, P. C., Ibrahim, S., & Karpatkin, S. (2006). Growth-regulated oncogene is pivotal in thrombin-induced angiogenesis. Cancer Research, 66(8), 4125–4132.
Even-Ram, S. C., Maoz, M., Pokroy, E., Reich, R., Katz, B. Z., Gutwein, P., et al. (2001). Tumor cell invasion is promoted by activation of protease activated receptor-1 in cooperation with the alpha vbeta 5 integrin. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276(14), 10952–10962.
Bai, S. Y., Xu, N., Chen, C., Song, Y. L., Hu, J., & Bai, C. X. (2014). Integrin αvβ5 as a biomarker for the assessment of non-small cell lung cancer metastasis and overall survival. The Clinical Respiratory Journal. doi:10.1111/crj.12163.
Zhu, Q., Luo, J., Wang, T., Ren, J., Hu, K., & Wu, G. (2012). The activation of protease-activated receptor 1 mediates proliferation and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Oncology Reports, 28(1), 255–261.
Rásó, E., Tóvári, J., Tóth, K., Paku, S., Trikha, M., Honn, K. V., et al. (2001). Ectopic alphaIIbbeta3 integrin signaling involves 12-lipoxygenase- and PKC-mediated serine phosphorylation events in melanoma cells. Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 85(6), 1037–1042.
Trikha, M., Timar, J., Zacharek, A., Nemeth, J. A., Cai, Y., Dome, B., et al. (2002). Role for beta3 integrins in human melanoma growth and survival. International Journal of Cancer, 101(2), 156–167.
Xu, Z., Zhu, L., Yao, M., Zhong, G., Dong, Q., & Yu, A. (2015). PTEN plays an important role in thrombin-mediated lung cancer cell functions. Biomed Research International. doi:10.1155/2015/459170.
Mußbach, F., Henklein, P., Westermann, M., Settmacher, U., Böhmer, F. D., & Kaufmann, R. (2014). Proteinase-activated receptor 1- and 4-promoted migration of Hep3B hepatocellular carcinoma cells depends on ROS formation and RTK transactivation. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology, 141(5), 813–825.
Trejo, J., Connolly, A. J., & Coughlin, S. R. (1996). The cloned thrombin receptor is necessary and sufficient for activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and mitogenesis in mouse lung fibroblasts. Loss of responses in fibroblasts from receptor knockout mice. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 271(35), 21536–21541.
Gratio, V., Walker, F., Lehy, T., Laburthe, M., & Darmoul, D. (2009). Aberrant expression of proteinase-activated receptor 4 promotes colon cancer cell proliferation through a persistent signaling that involves Src and ErbB-2 kinase. International Journal of Cancer, 124(7), 1517–1525.
Yuan, L., & Liu, X. (2015). Platelets are associated with xenograft tumor growth and the clinical malignancy of ovarian cancer through an angiogenesis-dependent mechanism. Molecular Medicine Reports, 11(4), 2449–2458.
Schiller, H., Bartscht, T., Arlt, A., Zahn, M. O., Seifert, A., Bruhn, T., et al. (2002). Thrombin as a survival factor for cancer cells: thrombin activation in malignant effusions in vivo and inhibition of idarubicin-induced cell death in vitro. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 40(8), 329–335.
Pang, J. H., Coupland, L. A., Freeman, C., Chong, B. H., & Parish, C. R. (2015). Activation of tumour cell ECM degradation by thrombin-activated platelet membranes: potentially a P-selectin and GPIIb/IIIa-dependent process. Clinical & Experimental Metastasis, 32(5), 495–505.
Janowska-Wieczorek, A., Wysoczynski, M., Kijowski, J., MarquezCurtis, L., Machalinski, B., Ratajczak, J., et al. (2005). Microvesicles derived from activated platelets induce metastasis and angiogenesis in lung cancer. International Journal of Cancer, 113(5), 752–760.
Janowska-Wieczorek, A., Marquez-Curtis, L. A., Wysoczynski, M., & Ratajczak, M. Z. (2006). Enhancing effect of platelet-derived microvesicles on the invasive potential of breast cancer cells. Transfusion, 46(7), 1199–1209.
Lou, X. L., Sun, J., Gong, S. Q., Yu, X. F., Gong, R., & Deng, H. (2015). Interaction between circulating cancer cells and platelets: clinical implication. Chinese Journal of Cancer Research, 27(5), 450–460.
Labelle, M., Begum, S., & Hynes, R. O. (2011). Direct signaling between platelets and cancer cells induces an epithelial-mesenchymal-like transition and promotes metastasis. Cancer Cell, 20(5), 576–590.
Cho, M. S., Bottsford-Miller, J., Vasquez, H. G., Stone, R., Zand, B., Kroll, M. H., et al. (2012). Platelets increase the proliferation of ovarian cancer cells. Blood, 120(24), 4869–4872.
Huang, Z., Miao, X., Luan, Y., Zhu, L., Kong, F., Lu, Q., et al. (2015). PAR1-stimulated platelet releasate promotes angiogenic activities of endothelial progenitor cells more potently than PAR4-stimulated platelet releasate. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 13(3), 465–476.
Sierko, E., & Wojtukiewicz, M. Z. (2007). Inhibition of platelet function: does it offer a chance of better cancer progression control? Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis, 33(7), 712–721.
Boucharaba, A., Serre, C. M., Grès, S., Saulnier-Blache, J. S., Bordet, J. C., Guglielmi, J., et al. (2004). Platelet-derived lysophosphatidic acid supports the progression of osteolytic bone metastases in breast cancer. The Journal of Clinical Investment, 114(12), 1714–1725.
Santos-Martinez, M. J., Medina, C., Jurasz, P., & Radomski, M. W. (2008). Role of metalloproteinases in platelet function. Thrombosis Research, 121(4), 535–542.
Koseoglu, S., & Flaumenhaft, R. (2013). Advances in platelet granule biology. Current Opinion in Hematology, 20(5), 464–471.
Martin, C. B., Mahon, G. M., Klinger, M. B., Kay, R. J., Symons, M., Der, C. J., et al. (2001). The thrombin receptor, PAR-1, causes transformation by activation of Rho-mediated signaling pathways. Oncogene, 20(16), 1953–1963.
Steinbrecher, K. A., Horowitz, N. A., Blevins, E. A., Barney, K. A., Shaw, M. A., Harmel-Laws, E., et al. (2010). Colitis-associated cancer is dependent on the interplay between the hemostatic and inflammatory systems and supported by integrin alpha(M)beta(2) engagement of fibrinogen. Cancer Research, 70, 2634–2643.
Liu, C. Y., Nossel, H. L., & Kaplan, K. L. (1979). The binding of thrombin by fibrin. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 254(20), 10421–10425.
Turpin, B., Miller, W., Rosenfeldt, L., Kombrinck, K., Flick, M. J., Steinbrecher, K. A., et al. (2014). Thrombin drives tumorigenesis in colitis-associated colon cancer. Cancer Research, 74(11), 3020–3030.
Sahni, A., & Francis, C. W. (2000). Vascular endothelial growth factor binds to fibrinogen and fibrin and stimulates endothelial cell proliferation. Blood, 96, 3772–3778.
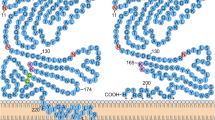
Mosesson, M. W. (2005). Fibrinogen and fibrin structure and functions. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 3, 1894–1904.
Schachtrup, C., Ryu, J. K., Helmrick, M. J., Vagena, E., Galanakis, D. K., Degen, J. L., et al. (2010). Fibrinogen triggers astrocyte scar formation by promoting the availability of active TGF-beta after vascular damage. Journal of Neuroscience, 30(17), 5843–5854.
Palumbo, J. S., Potter, J. M., Kaplan, L. S., Talmage, K., Jackson, D. G., & Degen, J. L. (2002). Spontaneous hematogenous and lymphatic metastasis, but not primary tumor growth or angiogenesis, is diminished in fibrinogen-deficient mice. Cancer Research, 62, 6966–6972.
Haralabopoulos, G., Grant, D., Kleinman, H., & Maragoudakis, M. (1997). Thrombin promotes endothelial cell alignment in Matrigel in vitro and angiogenesis in vivo. American Journal of Physiology, 273, C239–C245.
Martínez, C. E., Smithm, P. C., & Palma Alvaradom, V. A. (2015). The influence of platelet-derived products on angiogenesis and tissue repair: a concise update. Frontiers in Physiology. doi:10.3389/fphys.2015.00290.
Posch, F., Thaler, J., Zlabinger, G. J., Königsbrügge, O., Koder, S., Zielinski, C., et al. (2016). Soluble vascular endothelial growth factor (sVEGF) and the risk of venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer: results from the Vienna Cancer and Thrombosis Study (CATS). Clinical Cancer Research, 22(1), 200–206.
Ma, L., Perini, R., McKnight, W., Klein, A., Hollenberg, M. D., & Wallace, J. L. (2005). Proteinase-activated receptors 1 and 4 counter-regulate endostatin and VEGF release from human platelets. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102, 216.
Ekambaram, P., Lambiv, W., Cazzolli, R., Ashton, A. W., & Honn, K. V. (2011). The thromboxane synthase and receptor signaling pathway in cancer: an emerging paradigm in cancer progression and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Reviews, 30(3–4), 397–408.
Honn, K. V. (1983). Inhibition of tumor cell metastasis by modulation of the vascular prostacyclin/thromboxane A2 system. Clinical and Experimental Metastasis, 1(2), 103–14.
Honn, K. V., Grossi, I. M., Fitzgerald, L. A., Umbarger, L. A., Diglio, C. A., et al. (1988). Lipoxygenase products regulate IRGpIIb/IIIa receptor mediated adhesion of tumor cells to endothelial cells, subendothelial matrix and fibronectin. Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine, 189(1), 130–135.
Honn, K. V., Tang, D. G., & Chen, Y. Q. (1992). Platelets and cancer metastasis: more than an epiphenomenon. Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis, 18(4), 392–415.
Honn, K. V., Tang, D. G., Grossi, I. M., Renaud, C., Duniec, Z. M., Johnson, C. R., et al. (1994). Enhanced endothelial cell retraction mediated by 12(S)-HETE: a proposed mechanism for the role of platelets in tumor cell metastasis. Experimental Cell Research, 210(1), 1–9.
Steinert, B. W., Tang, D. G., Grossi, I. M., Umbarger, L. A., & Honn, K. V. (1993). Studies on the role of platelet eicosanoid metabolism and integrin alpha IIb beta 3 in tumor-cell-induced platelet aggregation. International Journal of Cancer, 54(1), 92–101.
Chen, Y. Q., Hagmann, W., & Honn, K. V. (1997). Regulation of 12(S)-HETE production in tumor cells. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 400A, 159–66.
Tang, D. G., Diglio, C. A., & Honn, K. V. (1993). 12(S)-HETE-induced microvascular endothelial cell retraction results from PKC-dependent rearrangement of cytoskeletal elements and alpha V beta 3 integrins. Prostaglandins, 45(3), 249–67.
Tang, D. G., Chen, Y. Q., Diglio, C. A., & Honn, K. V. (1993). Protein kinase C-dependent effects of 12(S)-HETE on endothelial cell vitronectin receptor and fibronectin receptor. Journal of Cell Biology, 121(3), 689–704.
Krishnamoorthy, S., Jin, R., Cai, Y., Maddipati, K. R., Nie, D., Pagès, G., et al. (2010). 12-Lipoxygenase and the regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor in prostate cancer cells. Experimental Cell Research, 316(10), 1706–1715.
Krishnamoorthy, S., & Honn, K. V. (2011). Eicosanoids and other lipid mediators and the tumor hypoxic microenvironment. Cancer Metastasis Reviews, 30(3–4), 613–618.
Krishnamoorthy, S., & Honn, K. V. (2008). Eicosanoids in tumor progression and metastasis. Subcellular Biochemistry, 49, 145–168.
Tucker, S. C., & Honn, K. V. (2013). Emerging targets in lipid-based therapy. Biochemical Pharmacology, 85(5), 673–688.
Dilly, A. K., Ekambaram, P., Guo, Y., Cai, Y., Tucker, S. C., Fridman, R., et al. (2013). Platelet-type 12-lipoxygenase induces MMP9 expression and cellular invasion via activation of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB. International Journal of Cancer, 133(8), 1784–1791.
Pidgeon, G. P., Lysaght, J., Krishnamoorthy, S., Reynolds, J. V., O’Byrne, K., Nie, D., et al. (2007). Lipoxygenase metabolism: roles in tumor progression and survival. Cancer Metastasis Reviews, 26(3–4), 503–524.
Pidgeon, G. P., Tang, K., Cai, Y. L., Piasentin, E., & Honn, K. V. (2003). Overexpression of platelet-type 12-lipoxygenase promotes tumor cell survival by enhancing alpha(v)beta(3) and alpha(v)beta(5) integrin expression. Cancer Research, 63(14), 4258–4267.
Rásó, E., Döme, B., Somlai, B., Zacharek, A., Hagmann, W., Honn, K. V., et al. (2004). Molecular identification, localization and function of platelet-type 12-lipoxygenase in human melanoma progression, under experimental and clinical conditions. Melanoma Research, 14(4), 245–250.
Tang, K., Cai, Y., Joshi, S., Tovar, E., Tucker, S. C., Maddipati, K. R., et al. (2015). Convergence of eicosanoid and integrin biology: 12-lipoxygenase seeks a partner. Molecular Cancer, 3(14), 111.
Timar, J., Bazaz, R., Tang, D. G., Kimler, V., Taylor, J. D., & Honn, K. V. (1997). Post-translational regulation of surface integrin expression in tumor cells by 12(S)-HETE. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 400B, 757–763.
Maragoudakis, M. E., Tsopanoglou, N. E., & Andriopoulou, P. (2002). Mechanism of thrombin-induced angiogenesis. Biochemical Society Transactions, 30(2), 173–177.
Zania, P., Kritikou, S., Flordellis, C. S., Maragoudakis, M. E., & Tsopanoglou, N. E. (2006). Blockade of angiogenesis by small molecule antagonists to protease-activated receptor-1: association with endothelial cell growth suppression and induction of apoptosis. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 318, 246–254.
Tsopanoglou, N. E., & Maragoudakis, M. E. (1999). On the mechanism of thrombin-induced angiogenesis: potentiation of vascular endothelial growth factor activity on endothelial cells by upregulation of its receptors. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 274(34), 23969–23976.
Tsopanoglou, N. E., Andriopoulou, P., & Maragoudakis, M. E. (2002). On the mechanism of thrombin-induced angiogenesis: involvement of alphavbeta3-integrin. American Journal of Physiology. Cell Physiology, 83(5), C1501–1510.
Andrikopoulos, P., Kieswich, J., Harwood, S. M., Baba, A., Matsuda, T., Barbeau, O., et al. (2015). Endothelial angiogenesis and barrier function in response to thrombin require Ca2+ influx through the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 290(30), 18412–18428.
Olivot, J. M., Estebanell, E., Lafay, M., Brohard, B., Aiach, M., & Rendu, F. (2001). Thrombomodulin prolongs thrombin-induced extracellular signal-regulated kinase phosphorylation and nuclear retention in endothelial cells. Circulation Research, 88, 681.
D’Asti, E., Kool, M., Pfister, S. M., & Rak, J. (2014). Coagulation and angiogenic gene expression profiles are defined by molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma: evidence for growth factor-thrombin cross-talk. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 12(11), 1838–1849.
Xu, Y., Gu, Y., Keep, R. F., Heth, J., Muraszko, K. M., Xi, G., et al. (2009). Thrombin up-regulates vascular endothelial growth factor in experimental gliomas. Neurological Research, 31(7), 759–765.
Zania, P., Gourni, D., Aplin, A. C., Nicosia, R. F., Flordellis, C. S., Maragoudakis, M. E., et al. (2009). Parstatin, the cleaved peptide on proteinase-activated receptor 1 activation, is a potent inhibitor of angiogenesis. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 328(2), 378–389.
Koolwijk, P., van Erck, M. G., de Vree, W. J., Vermeer, M. A., Weich, H. A., Hanemaaijer, R., et al. (1996). Cooperative effect of TNF-alpha, bFGF, and VEGF on the formation of tubular structures of human microvascular endothelial cells in a fibrin matrix. Role of urokinase activity. Journal of Cellular Biology, 132, 1177.
Mittermayr, R., Slezak, P., Haffner, N., Smolen, D., Hartinger, J., Hofmann, A., et al. (2016). Controlled release of fibrin matrix-conjugated platelet derived growth factor improves ischemic tissue regeneration by functional angiogenesis. Acta Biomaterialia, 29, 11–20.
Smadja, D. M., Basire, A., Amelot, A., Conte, A., Bièche, I., Le Bonniec, B. F., et al. (2008). Thrombin bound to a fibrin clot confers angiogenic and haemostatic properties on endothelial progenitor cells. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 12, 975.
Jolly, M. K., Boareto, M., Huang, B., Jia, D., Lu, M., Ben-Jacob, E., et al. (2015). Implications of the hybrid epithelial/mesenchymal phenotype in metastasis. Frontiers in Oncology. doi:10.3389/fonc.2015.00155.
Talmadge, J. E., & Fidler, I. J. (2010). AACR centennial series: the biology of cancer metastasis: historical perspective. Cancer Research, 70(14), 5649–5669.
Liu, H., Zhang, X., Li, J., Sun, B., Qian, H., & Yin, Z. (2015). The biological and clinical importance of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in circulating tumor cells. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology, 141(2), 189–201.
Ozdemir, T., Zhang, P., Fu, C., & Dong, C. (2012). Fibrin serves as a divalent ligand that regulates neutrophil-mediated melanoma cells adhesion to endothelium under shear conditions. American Journal of Physiology - Cell Physiology, 302(8), C1189–1201.
Otsuki, T., Fujimoto, D., Hirono, Y., Goi, T., & Yamaguchi, A. (2014). Thrombin conducts epithelial mesenchymal transition via protease activated receptor 1 in human gastric cancer. International Journal of Oncology, 45, 2287–2294.
Pavese, J. M., & Bergan, R. C. (2014). Circulating tumor cells exhibit a biologically aggressive cancer phenotype accompanied by selective resistance to chemotherapy. Cancer Letters, 352(2), 179–186.
Lecharpentier, A., Vielh, P., Perez-Moreno, P., Planchard, D., Soria, J. C., & Farace, F. (2011). Detection of circulating tumour cells with a hybrid (epithelial/mesenchymal) phenotype in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. British Journal of Cancer, 105, 1338–1341.
Hou, J. M., Krebs, M., Ward, T., Sloane, R., Priest, L., Hughes, A., et al. (2011). Circulating tumor cells as a window on metastasis biology in lung cancer. The American Journal of Pathology, 178, 989–996.
Armstrong, A. J., Marengo, M. S., Oltean, S., Kemeny, G., Bitting, R. L., Turnbull, J. D., et al. (2011). Circulating tumor cells from patients with advanced prostate and breast cancer display both epithelial and mesenchymal markers. Molecular Cancer Research, 9, 997–1007.
Konstantoulaki, M., Kouklis, P., & Malik, A. B. (2003). Protein kinase C modifications of VE-cadherin, p120, and beta-catenin contribute to endothelial barrier dysregulation induced by thrombin. American Journal of Physiology Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology, 285, L434–442.
Yokota, N., Zarpellon, A., Chakrabarty, S., Bogdanov, V. Y., Gruber, A., Castellino, F. J., et al. (2014). Contributions of thrombin targets to tissue factor-dependent metastasis in hyperthrombotic mice. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 12(1), 71–81.
Crissman, J. D., Hatfield, J., Schaldenbrand, M., Sloane, B. F., & Honn, K. V. (1985). Arrest and extravasation of B16 amelanotic melanoma in murine lungs. A light and electron microscopic study. Laboratory Investigation, 53(4), 470–478.
Crissman, J. D., Hatfield, J. S., & Honn, K. V. (1986). Clinical and experimental morphologic parameters predictive of tumor metastasis. Progress in Clinical and Biological Research, 212, 251–267.
Crissman, J. D., Hatfield, J. S., Menter, D. G., Sloane, B., & Honn, K. V. (1988). Morphological study of the interaction of intravascular tumor cells with endothelial cells and subendothelial matrix. Cancer Research, 48(14), 4065–4072.
Qian, W., Tao, L., Wang, Y., Zhang, F., Li, M., Huang, S., et al. (2015). Downregulation of integrins in cancer cells and anti-platelet properties are involved in Holothurian glycosaminoglycan-mediated disruption of the interaction of cancer cells and platelets in hematogenous metastasis. Journal of Vascular Research, 52(3), 197–209.
Lova, P., Canobbio, I., Guidetti, G. F., Balduini, C., & Torti, M. (2010). Thrombin induces platelet activation in the absence of functional protease activated receptors 1 and 4 and glycoprotein Ib-IX-V. Cellular Signalling, 22(11), 1681–1687.
De Candia, E., Hall, S. W., Rutella, S., Landolfi, R., Andrews, R. K., & De Cristofaro, R. (2001). Binding of thrombin to glycoprotein Ib accelerates the hydrolysis of Par-1 on intact platelets. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276, 4692–4698.
Tanaka, N. G., Tohgo, A., & Ogawa, H. (1986). Platelet-aggregating activities of metastasizing tumor cells. V. In situ roles of platelets in hematogenous metastases. Invasion & Metastasis, 6(4), 209–224.
Gasic, G., Gasic, T., Galanti, N., Johnson, T., & Murphy, S. (1973). Platelet tumor-cell interactions in mice. The role of platelets in the spread of malignant disease. International Journal of Cancer, 11, 704–718.
Oleksowicz, L., Mrowiec, Z., Schwartz, E., Khorshidi, M., Dutcher, J. P., & Puszkin, E. (1995). Characterization of tumor-induced platelet aggregation: the role of immunorelated GPIb and GPIIb/IIIa expression by MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Thrombosis Research, 79(3), 261–274.
Naimushin, Y. A., & Mazurov, A. V. (2004). Von Willebrand factor can support platelet aggregation via interaction with activated GPIIb-IIIa and GPIb. Platelets, 15(7), 419–425.
Naimushin, Y. A., & Mazurov, A. V. (2005). Ability of different glycoprotein IIb-IIIa ligands to support platelet aggregation induced by activating antibody CRC54. Biochemistry (Mosc), 70(7), 782–789.
Ünlü, B., & Versteeg, H. H. (2014). Effects of tumor-expressed coagulation factors on cancer progression and venous thrombosis: is there a key factor? Thrombosis Research, 133(Suppl 2), S76–84.
Maskrey, B. H., Bermúdez-Fajardo, A., Morgan, A. H., Stewart-Jones, E., Dioszeghy, V., Taylor, G. W., et al. (2007). Activated platelets and monocytes generate four hydroxyphosphatidylethanolamines via lipoxygenase. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 282(28), 20151–20163.
Nieswandt, B., Hafner, M., Echtenacher, B., & Mannel, D. (1999). Lysis of tumor cells by natural killer cells in mice is impeded by platelets. Cancer Research, 59, 1295–1300.
Ohana, O. M., Ozer, J., Prinsloo, I., Benharroch, D., & Gopas, J. (2015). Hodgkin lymphoma cell lines bind to platelets. Incubation with platelets induces CD15 and P-selectin dependent adhesion of the cell lines to human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). Cancer Biology and Therapy, 16(11), 1651–1659.
Fidler, I. (1970). Metastases: quantitative analysis of distribution and fate of tumor emboli labeled with 125I-5-iodo-2′-deoxyuridine. Journal of National Cancer Institute, 45, 773–782.
Coupland, L. A., Chong, B. H., & Parish, C. R. (2012). Platelets and P-selectin control tumor cell metastasis in an organ-specific manner and independently of NK cells. Cancer Research, 72(18), 4662–4671.
Palumbo, J. S., Talmage, K. E., Massari, J. V., La Jeunesse, C. M., Flick, M. J., Kombrinck, K. W., et al. (2005). Platelets and fibrin(ogen) increase metastatic potential by impeding natural killer cell-mediated elimination of tumor cells. Blood, 105, 178.
Placke, T., Orgel, M., Schaller, M., Jung, G., Rammensee, H. G., Kopp, H. G., et al. (2012). Platelet-derived MHC class I confers a pseudonormal phenotype to cancer cells that subverts the antitumor reactivity of natural killer immune cells. Cancer Research, 72, 440–448.
Jain, S., Zuka, M., Liu, J., Russell, S., Dent, J., Guerrero, J. A., et al. (2007). Platelet glycoprotein Ib alpha supports experimental lung metastasis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104(21), 9024–9028.
Boukerche, H., Berthier-Vergnes, O., Tabone, E., Dore, J., Leung, L., & McGregor, J. (1989). Platelet-melanoma cell interaction is mediated by the glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex. Blood, 74, 658–663.
McGregor, B., McGregor, J., Weiss, L., Wood, G., Hu, C., Boukerche, H., et al. (1989). Presence of cytoadhesins (IIb-IIIa-like glycoproteins) on human metastatic melanomas but not on benign melanocytes. American Journal of Clinical Pathology, 92, 495–499.
McCarty, O., Mousa, S., Bray, P., & Konstantopoulos, K. (2000). Immobilized platelets support human colon carcinoma cell tethering, rolling, and firm adhesion under dynamic flow conditions. Blood, 96, 1789–1797.
Aigner, S., Ramos, C., Hafezi-Moghadam, A., Lawrence, M., Friederichs, J., Altevogt, P., et al. (1998). CD24 mediates rolling of breast carcinoma cells on P-selectin. Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology Journal, 12, 1241–1251.
Lou, X. L., Deng, J., Deng, H., Ting, Y., Zhou, L., Liu, Y. H., et al. (2014). Aspirin inhibit platelet-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of circulating tumor cells (review). Biomedical Reports, 2(3), 331–334.
Humphries, M., Olden, K., & Yamada, K. (1986). A synthetic peptide from fibronectin inhibits experimental metastases of murine melanoma cells. Science, 467, 467–470.
Klepfish, A., Greco, M., & Karpatkin, S. (1993). Thrombin stimulates melanoma tumor-cell binding to endothelial cells and subendothelial matrix. International Journal of Cancer, 53, 978–982.
Dardik, R., Savion, N., Kaufmann, Y., & Varon, D. (1998). Thrombin promotes platelet-mediated melanoma cell adhesion to endothelial cells under flow conditions: role of platelet glycoproteins P-selectin and GPIIb-IIIa. British Journal of Cancer, 77, 2069–2075.
Wang, J., Xiao, J., Wen, D., Wu, X., Mao, Z., Zhang, J., et al. (2016). Endothelial cell-anchored tissue factor pathway inhibitor regulates tumor metastasis to the lung in mice. Molecular Carcinogenesis, 55(5), 882–896.
Nie, D., Tang, K., Szekeres, K., Trikha, M., & Honn, K. V. (2000). The role of eicosanoids in tumor growth and metastasis. Ernst Schering Research Foundation Workshop Journal, 31, 201–217.
Honn, K. V., Tang, D. G., Grossi, I., Duniec, Z. M., Timar, J., Renaud, C., et al. (1994). Tumor cell-derived 12(S)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid induces microvascular endothelial cell retraction. Cancer Research, 54(2), 565–574.
Weiler, H., & Isermann, B. H. (2003). Thrombomodulin. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 1, 1515–1524.
Van Sluis, G. L., Niers, T. M., Esmon, C. T., Tigchelaar, W., Richel, D. J., & Buller, H. R. (2009). Endogenous activated protein C limits cancer cell extravasation through sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1-mediated vascular endothelial barrier enhancement. Blood, 114(9), 1968–1973.
Palumbo, J. S., Kombrinck, K. W., Drew, A. F., Grimes, T. S., Kiser, J. H., Degen, J. L., et al. (2000). Fibrinogen is an important determinant of the metastatic potential of circulating tumor cells. Blood, 96, 3302.
Palumbo, J. S. (2008). Mechanisms linking tumor cell-associated procoagulant function to tumor dissemination. Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis, 34, 154–160.
Palumbo, J.S., Talmage, K.E., Massari, J.V., La Jeunesse, C.M., Flick, M.J., Kombrinck, K.W., et al. (2007). Tumor cell-associated tissue factor and circulating hemostatic factors cooperate to increase metastatic potential through natural killer cell-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Blood. 19.
Palumbo, J. S., Barney, K. A., Blevins, E. A., Shaw, M. A., Mishra, A., Flick, M. J., et al. (2008). Factor XIII transglutaminase supports hematogenous tumor cell metastasis through a mechanism dependent on natural killer cell function. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 6, 812–819.
Biggerstaff, J. P., Seth, N., Amirkhosravi, A., Amaya, M., Fogarty, S., Meyer, T. V., Siddiqui, F., Francis, J. L., et al. (1999). Soluble fibrin augments platelet/tumor cell adherence in vitro and in vivo, and enhances experimental metastasis. Clinical & Experimental Metastasis, 17, 723–730.
Zhang, P., Ozdemir, T., Chung, C. Y., Robertson, G. P., & Dong, C. (2011). Sequential binding of α(v)β(3) and ICAM-1 determines fibrin-mediated melanoma capture and stable adhesion to CD11b/CD18 on neutrophils. Journal of Immunology, 186, 242–254.
Gaddes, E. R., Lee, D., Gydush, G., Wang, Y., & Dong, C. (2015). Regulation of fibrin-mediated tumor cell adhesion to the endothelium using anti-thrombin aptamer. Experimental Cell Research. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.10.010.
Yokoyama, K., Erickson, H. P., Ikeda, Y., & Takada, Y. (2000). Identification of amino acid sequences in fibrinogen γ-chain and tenascin CC-terminal domains critical for binding to integrin α(v)β(3). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275, 16891–16898.
Lee, S. H., Suh, I. B., Lee, E. J., Hur, G. Y., Lee, S. Y., Lee, S. Y., et al. (2013). Relationships of coagulation factor XIII activity with cell-type and stage of non-small cell lung cancer. Yonsei Medical Journal, 54(6), 1394–1399.
Vairaktaris, E., Vassiliou, S., Yapijakis, C., Spyridonidou, S., Vylliotis, A., Derka, S., et al. (2007). Increased risk for oral cancer is associated with coagulation factor XIII but not with factor XII. Oncology Reports, 18, 1537–1543.
An, Y., Bekesova, S., Edwards, N., & Goldman, R. (2010). Peptides in low molecular weight fraction of serum associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. Disease Markers, 29, 11–20.
Kiss, F., Hevessy, Z., Veszprémi, A., Katona, E., Kiss, C., Vereb, G., et al. (2006). Leukemic lymphoblasts, a novel expression site of coagulation factor XIII subunit A. Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 96, 176–182.
Andersson, C., Kvist, P. H., McElhinney, K., Baylis, R., Gram, L. K., Pelzer, H., et al. (2015). Factor XIII transglutaminase supports the resolution of mucosal damage in experimental colitis. Public Library of Science One, 10(6), e0128113.
Menter, D. G., Hatfield, J. S., Harkins, C., Sloane, B. F., Taylor, J. D., Crissman, J. D., et al. (1987). Tumor cell-platelet interactions in vitro and their relationship to in vivo arrest of hematogenously circulating tumor cells. Clinical and Experimental Metastasis, 5(1), 65–78.
Helland, I., Klemensten, B., & Jorgensen, L. (1997). Addition of both platelets and thrombin in combination accelerates tumor cells to adhere to endothelial cells in vitro. In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology, 33, 182–186.
Pilch, J., Habermann, R., & Felding-Habermann, B. (2002). Unique ability of integrin alpha(v)beta 3 to support tumor cell arrest under dynamic flow conditions. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277(24), 21930–21938.
Chen, Y. Q., & Honn, K. V. (1993). Eicosanoid regulation of tumor cell-platelet and -endothelium interaction during arrest and extravasation. In S. Nigam, K. Honn, L. Barnett, & T. Walden Jr. (Eds.), Developments in oncology. Eicosanoids and other bioactive lipids in cancer, inflammation and radiation injury (Vol. 71, pp. 613–617). New York: Springer.
Chen, Y. Q., Duniec, Z. M., Liu, B., Hagmann, W., Gao, X., Shimoji, K., et al. (1994). Endogenous 12(S)-HETE production by tumor cells and its role in metastasis. Cancer Research, 54(6), 1574–1579.
Baserga, R., & Saffiotti, U. (1955). Experimental studies on histogenesis of blood-borne metastases. AMA Archives of Pathology, 59(1), 26–34.
Schumacher, D., Strilic, B., Sivaraj, K. K., Wettschureck, N., & Offermanns, S. (2013). Platelet-derived nucleotides promote tumor-cell transendothelial migration and metastasis via P2Y2 receptor. Cancer Cell, 24(1), 130–137.
Khuon, S., Liang, L., Dettman, R. W., Sporn, P. H., Wysolmerski, R. B., & Chew, T. L. (2010). Myosin light chain kinase mediates transcellular intravasation of breast cancer cells through the underlying endothelial cells: a three-dimensional FRET study. Journal of Cellular Science, 123(Pt 3), 431–440.
Mierke, C. T., Zitterbart, D. P., Kollmannsberger, P., Raupach, C., Schlotzer-Schrehardt, U., Goecke, T. W., et al. (2008). Breakdown of the endothelial barrier function in tumor cell transmigration. Biophysical Journal, 94, 2832–2846.
Dejana, E., Orsenigo, F., & Lampugnani, M. G. (2008). The role of adherens junctions and VE-cadherin in the control of vascular permeability. Journal of Cell Science, 121(Pt 13), 2115–2122.
Dudek, S. M., & Garcia, J. G. (2001). Cytoskeletal regulation of pulmonary vascular permeability. Journal of Applied Physiology, 91, 1487–1500.
Rabiet, M. J., Plantier, J. L., Rival, Y., Genoux, Y., Lampugnani, M. G., & Dejana, E. (1996). Thrombin-induced increase in endothelial permeability is associated with changes in cell-to-cell junction organization. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 16, 488–496.
Vincent, P. A., Xiao, K., Buckley, K. M., & Kowalczyk, A. P. (2004). VE-cadherin: adhesion at arm’s length. American Journal o Physiology - Cell Physiology, 286(5), C987–997.
Potter, M. D., Barbero, S., & Cheresh, D. A. (2005). Tyrosine phosphorylatio of VE-cadherin prevents binding of p120- and beta-catenin and maintains the cellular mesenchymal state. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280, 31906–31912.
Sandoval, R., Malik, A. B., Minshall, R. D., Kouklis, P., Ellis, C. A., & Tiruppathi, C. (2001). Ca(2+) signalling and PKCalpha activate increased endothelial permeability by disassembly of VE-cadherin junctions. Journal of Physiology, 533(Pt 2), 433–445.
Stockton, R. A., Schaefer, E., & Schwartz, M. A. (2004). p21-activated kinase regulates endothelial permeability through modulation of contractility. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279(45), 46621–46630.
Hugo, H., Ackland, M. L., Blick, T., Lawrence, M. G., Clements, J. A., & Williams, E. D. (2007). Epithelial–mesenchymal and mesenchymal–epithelial transitions in carcinoma progression. Journal of Cell Physiology, 213(2), 374–383.
Nierodzik, M. L., Klepfish, A., & Karpatkin, S. (1995). Role of platelets, thrombin, integrin IIb-IIIa, fibronectin and von Willebrand factor on tumor adhesion in vitro and metastasis in vivo. Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 74(1), 282–290.
Esumi, N., Fan, D., & Fidler, I. (1991). Inhibition of murine melanoma experimental metastasis by recombinant-desulfatohirudin, a highly specific thrombin inhibitor. Cancer Research, 51, 4549–4556.
Rousseau, A., Van Dreden, P., Mbemba, E., Elalamy, I., Larsen, A., & Gerotziafas, G. T. (2015). Cancer cells BXPC3 and MCF7 differentially reverse the inhibition of thrombin generation by apixaban, fondaparinux and enoxaparin. Thrombosis Research, 136(6), 1273–1279.
Villares, G. J., Zigler, M., Wang, H., Melnikova, V. O., Wu, H., Friedman, R., et al. (2008). Targeting melanoma growth and metastasis with systemic delivery of liposome-incorporated protease-activated receptor-1 small interfering RNA. Cancer Research, 68, 9078–9086.
Cowan, C., Muraleedharan, C. K., O’Donnell, J. J., Singh, P. K., Lum, H., Kumar, A., et al. (2014). MicroRNA-146 inhibits thrombin-induced NF-κB activation and subsequent inflammatory responses in human retinal endothelial cells. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science, 55(8), 4944–4951.
Saleiban, A., Faxälv, L., Claesson, K., Jönsson, J. I., & Osman, A. (2014). miR-20b regulates expression of proteinase-activated receptor-1 (PAR-1) thrombin receptor in melanoma cells. Pigment Cell & Melanoma Research, 27(3), 431–441.
Wang, H. J., Huang, Y. L., Shih, Y. Y., Wu, H. Y., Peng, C. T., & Lo, W. Y. (2014). MicroRNA-146a decreases high glucose/thrombin-induced endothelial inflammation by inhibiting NAPDH oxidase 4 expression. Mediators of Inflammation. doi:10.1155/2014/379537.
Sun, X., Lin, J., He, S., Franck, G., Wara, A., Icli, B., Li, D., & Feinberg, M. W. (2015). MicroRNA-181b inhibits thrombin-mediated activation of endothelial cells and arterial thrombosis by targeting card10. Circulation, 132, A12208.
Peng, C. T., Lo, W. Y., & Wang, H. J. (2014). High glucose/thrombin-induced endothelial inflammation via microRNA-146a and Nox4 regulation. Blood, 124(21), 5952–5952.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wojtukiewicz, M.Z., Hempel, D., Sierko, E. et al. Thrombin—unique coagulation system protein with multifaceted impacts on cancer and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 35, 213–233 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-016-9626-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-016-9626-0