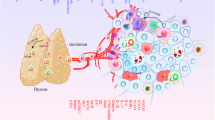
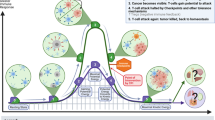
Abstract
The metastasis of cancer is a complex and life-threatening process that is only partially understood. Immune suppressive cells are recognized as important contributors to tumour progression and may also promote the development and growth of tumour metastases. Specifically, regulatory T cells (Tregs) have been found to promote primary tumour progression, and emerging pre-clinical data suggests that Tregs may promote metastasis and metastatic tumour growth. While the precise role that Tregs play in metastatic progression is understudied, recent findings have indicated that by suppressing innate and adaptive anti-tumour immunity, Tregs may shield tumour cells from immune detection, and thereby allow tumour cells to survive, proliferate and acquire characteristics that facilitate dissemination. This review will highlight our current understanding of Tregs in metastasis, including an overview of pre-clinical findings and discussion of clinical data regarding Tregs and therapeutic outcome. Evolving strategies to directly ablate Tregs or to inhibit their function will also be discussed. Improving our understanding of how Tregs may influence tumour metastasis may lead to novel treatments for metastatic cancer.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Tregs:
-
Regulatory T cells
- pTregs:
-
Peripheral regulatory T cells
- tTregs:
-
Thymic regulatory T cells
- Foxp3:
-
Forkhead box P3
References
Beyer, M., & Schultze, J. L. (2006). Regulatory T cells in cancer. Blood, 108(3), 804–811.
Maizels, R. M., & Smith, K. A. (2011). Regulatory T cells in infection. Advances in Immunology, 112, 73–136.
Gershon, R. K., & Kondo, K. (1970). Cell interactions in the induction of tolerance: the role of thymic lymphocytes. Immunology, 18(5), 723–737.
Berendt, M. J., & North, R. J. (1980). T-cell-mediated suppression of anti-tumor immunity. An explanation for progressive growth of an immunogenic tumor. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 151(1), 69–80.
Sakaguchi, S., Sakaguchi, N., Asano, M., Itoh, M., & Toda, M. (1995). Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune diseases. Journal of Immunology, 155(3), 1151–1164.
Bennett, C. L., Christie, J., Ramsdell, F., Brunkow, M. E., Ferguson, P. J., Whitesell, L., et al. (2001). The immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome (IPEX) is caused by mutations of FOXP3. Nature Genetics, 27(1), 20–21.
Williams, L. M., & Rudensky, A. Y. (2007). Maintenance of the Foxp3-dependent developmental program in mature regulatory T cells requires continued expression of Foxp3. Nature Immunology, 8(3), 277–284.
McMurchy, A. N., Bushell, A., Levings, M. K., & Wood, K. J. (2011). Moving to tolerance: clinical application of T regulatory cells. Seminars in Immunology, 23(4), 304–313.
Pacholczyk, R., & Kern, J. (2008). The T-cell receptor repertoire of regulatory T cells. Immunology, 125(4), 450–458.
Bilate, A. M., & Lafaille, J. J. (2012). Induced CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in immune tolerance. Annual Review of Immunology, 30, 733–758.
Toker, A., Engelbert, D., Garg, G., Polansky, J. K., Floess, S., Miyao, T., et al. (2013). Active demethylation of the Foxp3 locus leads to the generation of stable regulatory T cells within the thymus. Journal of Immunology, 190(7), 3180–3188.
Shalev, I., Schmelzle, M., Robson, S. C., & Levy, G. (2011). Making sense of regulatory T cell suppressive function. Seminars in Immunology, 23(4), 282–292.
Sakaguchi, S., Miyara, M., Costantino, C. M., & Hafler, D. A. (2010). Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in the human immune system. Nature Reviews Immunology, 10(7), 490–500.
Allan, S. E., Song-Zhao, G. X., Abraham, T., McMurchy, A. N., & Levings, M. K. (2008). Inducible reprogramming of human T cells into Treg cells by a conditionally active form of Foxp3. European Journal of Immunology, 38(12), 3282–3289.
Gratz, I. K., & Campbell, D. J. (2014). Organ-specific and memory treg cells: specificity, development, function, and maintenance. Frontiers in Immunology, 5, 333.
Corthay, A. (2009). How do regulatory T cells work? Scandinavian Journal of Immunology, 70(4), 326–336.
Morlacchi, S., Dal Secco, V., Soldani, C., Glaichenhaus, N., Viola, A., & Sarukhan, A. (2011). Regulatory T cells target chemokine secretion by dendritic cells independently of their capacity to regulate T cell proliferation. Journal of Immunology, 186(12), 6807–6814.
Yamaguchi, T., Wing, J. B., & Sakaguchi, S. (2011). Two modes of immune suppression by Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells under inflammatory or non-inflammatory conditions. Seminars in Immunology, 23(6), 424–430.
Wright, G. P., Notley, C. A., Xue, S. A., Bendle, G. M., Holler, A., Schumacher, T. N., et al. (2009). Adoptive therapy with redirected primary regulatory T cells results in antigen-specific suppression of arthritis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(45), 19078–19083.
Facciabene, A., Motz, G. T., & Coukos, G. (2012). T-regulatory cells: key players in tumor immune escape and angiogenesis. Cancer Research, 72(9), 2162–2171.
Mailloux, A. W., & Young, M. R. (2010). Regulatory T-cell trafficking: from thymic development to tumor-induced immune suppression. Critical Reviews in Immunology, 30(5), 435–447.
Curiel, T. J., Coukos, G., Zou, L., Alvarez, X., Cheng, P., Mottram, P., et al. (2004). Specific recruitment of regulatory T cells in ovarian carcinoma fosters immune privilege and predicts reduced survival. Nature Medicine, 10(9), 942–949.
Gobert, M., Treilleux, I., Bendriss-Vermare, N., Bachelot, T., Goddard-Leon, S., Arfi, V., et al. (2009). Regulatory T cells recruited through CCL22/CCR4 are selectively activated in lymphoid infiltrates surrounding primary breast tumors and lead to an adverse clinical outcome. Cancer Research, 69(5), 2000–2009.
Tan, W., Zhang, W., Strasner, A., Grivennikov, S., Cheng, J. Q., Hoffman, R. M., et al. (2011). Tumour-infiltrating regulatory T cells stimulate mammary cancer metastasis through RANKL-RANK signalling. Nature, 470(7335), 548–553.
Facciabene, A., Peng, X., Hagemann, I. S., Balint, K., Barchetti, A., Wang, L. P., et al. (2011). Tumour hypoxia promotes tolerance and angiogenesis via CCL28 and T(reg) cells. Nature, 475(7355), 226–230.
Wei, S., Kryczek, I., Edwards, R. P., Zou, L., Szeliga, W., Banerjee, M., et al. (2007). Interleukin-2 administration alters the CD4+Foxp3+ T-cell pool and tumor trafficking in patients with ovarian carcinoma. Cancer Research, 67(15), 7487–7494.
Liu, V. C., Wong, L. Y., Jang, T., Shah, A. H., Park, I., Yang, X., et al. (2007). Tumor evasion of the immune system by converting CD4+CD25− T cells into CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells: role of tumor-derived TGF-beta. Journal of Immunology, 178(5), 2883–2892.
Valzasina, B., Piconese, S., Guiducci, C., & Colombo, M. P. (2006). Tumor-induced expansion of regulatory T cells by conversion of CD4+CD25− lymphocytes is thymus and proliferation independent. Cancer Research, 66(8), 4488–4495.
Elkord, E., Sharma, S., Burt, D. J., & Hawkins, R. E. (2011). Expanded subpopulation of FoxP3+ T regulatory cells in renal cell carcinoma co-express Helios, indicating they could be derived from natural but not induced Tregs. Clinical Immunology, 140(3), 218–222.
Nizar, S., Meyer, B., Galustian, C., Kumar, D., & Dalgleish, A. (2010). T regulatory cells, the evolution of targeted immunotherapy. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1806(1), 7–17.
Mougiakakos, D., Johansson, C. C., & Kiessling, R. (2009). Naturally occurring regulatory T cells show reduced sensitivity toward oxidative stress-induced cell death. Blood, 113(15), 3542–3545.
Carreras, J., Lopez-Guillermo, A., Fox, B. C., Colomo, L., Martinez, A., Roncador, G., et al. (2006). High numbers of tumor-infiltrating Foxp3-positive regulatory T cells are associated with improved overall survival in follicular lymphoma. Blood, 108(9), 2957–2964.
Lee, A. M., Clear, A. J., Calaminici, M., Davies, A. J., Jordan, S., MacDougall, F., et al. (2006). Number of CD4+ cells and location of forkhead box protein P3-positive cells in diagnostic follicular lymphoma tissue microarrays correlates with outcome. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 24(31), 5052–5059.
Tzankov, A., Meier, C., Hirschmann, P., Went, P., Pileri, S. A., & Dirnhofer, S. (2008). Correlation of high numbers of intratumoral Foxp3+ regulatory T cells with improved survival in germinal center-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma and classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Haematologica, 93(2), 193–200.
Polcher, M., Braun, M., Friedrichs, N., Rudlowski, C., Bercht, E., Fimmers, R., et al. (2010). Foxp3(+) cell infiltration and granzyme B(+)/Foxp3(+) cell ratio are associated with outcome in neoadjuvant chemotherapy-treated ovarian carcinoma. Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy, 59(6), 909–919.
Wolf, D., Wolf, A. M., Rumpold, H., Fiegl, H., Zeimet, A. G., Muller-Holzner, E., et al. (2005). The expression of the regulatory T cell-specific forkhead box transcription factor Foxp3 is associated with poor prognosis in ovarian cancer. Clinical Cancer Research, 11(23), 8326–8331.
Chen, K. J., Zhou, L., Xie, H. Y., Ahmed, T. E., Feng, X. W., & Zheng, S. S. (2012). Intratumoral regulatory T cells alone or in combination with cytotoxic T cells predict prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. Medical Oncology, 29(3), 1817–1826.
Gao, Q., Qiu, S. J., Fan, J., Zhou, J., Wang, X. Y., Xiao, Y. S., et al. (2007). Intratumoral balance of regulatory and cytotoxic T cells is associated with prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 25(18), 2586–2593.
Li, J. F., Chu, Y. W., Wang, G. M., Zhu, T. Y., Rong, R. M., Hou, J., et al. (2009). The prognostic value of peritumoral regulatory T cells and its correlation with intratumoral cyclooxygenase-2 expression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. BJU International, 103(3), 399–405.
Siddiqui, S. A., Frigola, X., Bonne-Annee, S., Mercader, M., Kuntz, S. M., Krambeck, A. E., et al. (2007). Tumor-infiltrating Foxp3-CD4+CD25+ T cells predict poor survival in renal cell carcinoma. Clinical Cancer Research, 13(7), 2075–2081.
Hiraoka, N., Onozato, K., Kosuge, T., & Hirohashi, S. (2006). Prevalence of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells increases during the progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its premalignant lesions. Clinical Cancer Research, 12(18), 5423–5434.
Mougiakakos, D., Johansson, C. C., Trocme, E., All-Ericsson, C., Economou, M. A., Larsson, O., et al. (2010). Intratumoral forkhead box P3-positive regulatory T cells predict poor survival in cyclooxygenase-2-positive uveal melanoma. Cancer, 116(9), 2224–2233.
Brudvik, K. W., Henjum, K., Aandahl, E. M., Bjornbeth, B. A., & Tasken, K. (2012). Regulatory T-cell-mediated inhibition of antitumor immune responses is associated with clinical outcome in patients with liver metastasis from colorectal cancer. Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy, 61(7), 1045–1053.
Shimizu, K., Nakata, M., Hirami, Y., Yukawa, T., Maeda, A., & Tanemoto, K. (2010). Tumor-infiltrating Foxp3+ regulatory T cells are correlated with cyclooxygenase-2 expression and are associated with recurrence in resected non-small cell lung cancer. Journal of Thoracic Oncology, 5(5), 585–590.
Correale, P., Rotundo, M. S., Del Vecchio, M. T., Remondo, C., Migali, C., Ginanneschi, C., et al. (2010). Regulatory (Foxp3+) T-cell tumor infiltration is a favorable prognostic factor in advanced colon cancer patients undergoing chemo or chemoimmunotherapy. Journal of Immunotherapy, 33(4), 435–441.
Ladoire, S., Martin, F., & Ghiringhelli, F. (2011). Prognostic role of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells infiltrating human carcinomas: the paradox of colorectal cancer. Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy, 60(7), 909–918.
Salama, P., Phillips, M., Grieu, F., Morris, M., Zeps, N., Joseph, D., et al. (2009). Tumor-infiltrating Foxp3+ T regulatory cells show strong prognostic significance in colorectal cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 27(2), 186–192.
Haas, M., Dimmler, A., Hohenberger, W., Grabenbauer, G. G., Niedobitek, G., & Distel, L. V. (2009). Stromal regulatory T-cells are associated with a favourable prognosis in gastric cancer of the cardia. BMC Gastroenterology, 9, 65.
Badoual, C., Hans, S., Rodriguez, J., Peyrard, S., Klein, C., Agueznay Nel, H., et al. (2006). Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating CD4+ T-cell subpopulations in head and neck cancers. Clinical Cancer Research, 12(2), 465–472.
Bron, L., Jandus, C., Andrejevic-Blant, S., Speiser, D. E., Monnier, P., Romero, P., et al. (2013). Prognostic value of arginase-II expression and regulatory T-cell infiltration in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. International Journal of Cancer, 132(3), E85–E93.
Strauss, L., Bergmann, C., Gooding, W., Johnson, J. T., & Whiteside, T. L. (2007). The frequency and suppressor function of CD4+CD25highFoxp3+ T cells in the circulation of patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Clinical Cancer Research, 13(21), 6301–6311.
Chaudhary, B., Abd Al Samid, M., al-Ramadi, B. K., & Elkord, E. (2014). Phenotypic alterations, clinical impact and therapeutic potential of regulatory T cells in cancer. Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy, 14(7), 931–945.
Zitvogel, L., Kepp, O., & Kroemer, G. (2011). Immune parameters affecting the efficacy of chemotherapeutic regimens. Nature Reviews. Clinical Oncology, 8(3), 151–160.
Dunn, G. P., Old, L. J., & Schreiber, R. D. (2004). The three Es of cancer immunoediting. Annual Review of Immunology, 22, 329–360.
Hori, S., Nomura, T., & Sakaguchi, S. (2003). Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science, 299(5609), 1057–1061.
Kryczek, I., Liu, R., Wang, G., Wu, K., Shu, X., Szeliga, W., et al. (2009). Foxp3 defines regulatory T cells in human tumor and autoimmune disease. Cancer Research, 69(9), 3995–4000.
Roncador, G., Brown, P. J., Maestre, L., Hue, S., Martinez-Torrecuadrada, J. L., Ling, K. L., et al. (2005). Analysis of Foxp3 protein expression in human CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells at the single-cell level. European Journal of Immunology, 35(6), 1681–1691.
Hinz, S., Pagerols-Raluy, L., Oberg, H. H., Ammerpohl, O., Grussel, S., Sipos, B., et al. (2007). Foxp3 expression in pancreatic carcinoma cells as a novel mechanism of immune evasion in cancer. Cancer Research, 67(17), 8344–8350.
Zuo, T., Wang, L., Morrison, C., Chang, X., Zhang, H., Li, W., et al. (2007). Foxp3 is an X-linked breast cancer suppressor gene and an important repressor of the HER-2/ErbB2 oncogene. Cell, 129(7), 1275–1286.
Triulzi, T., Tagliabue, E., Balsari, A., & Casalini, P. (2013). Foxp3 expression in tumor cells and implications for cancer progression. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 228(1), 30–35.
Li, W., Wang, L., Katoh, H., Liu, R., Zheng, P., & Liu, Y. (2011). Identification of a tumor suppressor relay between the Foxp3 and the Hippo pathways in breast and prostate cancers. Cancer Research, 71(6), 2162–2171.
McInnes, N., Sadlon, T. J., Brown, C. Y., Pederson, S., Beyer, M., Schultze, J. L., et al. (2012). Foxp3 and Foxp3-regulated microRNAs suppress SATB1 in breast cancer cells. Oncogene, 31(8), 1045–1054.
Dimitrakopoulos, F. I., Papadaki, H., Antonacopoulou, A. G., Kottorou, A., Gotsis, A. D., Scopa, C., et al. (2011). Association of Foxp3 expression with non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Research, 31(5), 1677–1683.
Merlo, A., Casalini, P., Carcangiu, M. L., Malventano, C., Triulzi, T., Menard, S., et al. (2009). Foxp3 expression and overall survival in breast cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 27(11), 1746–1752.
Winerdal, M. E., Marits, P., Winerdal, M., Hasan, M., Rosenblatt, R., Tolf, A., et al. (2011). Foxp3 and survival in urinary bladder cancer. BJU International, 108(10), 1672–1678.
Xue, L., Lu, H. Q., He, J., Zhao, X. W., Zhong, L., Zhang, Z. Z., et al. (2010). Expression of Foxp3 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma relating to the clinical data. Diseases of the Esophagus, 23(4), 340–346.
Miyara, M., Yoshioka, Y., Kitoh, A., Shima, T., Wing, K., Niwa, A., et al. (2009). Functional delineation and differentiation dynamics of human CD4+ T cells expressing the Foxp3 transcription factor. Immunity, 30(6), 899–911.
Rech, A. J., Mick, R., Kaplan, D. E., Chang, K. M., Domchek, S. M., & Vonderheide, R. H. (2010). Homeostasis of peripheral Foxp3(+) CD4(+) regulatory T cells in patients with early and late stage breast cancer. Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy, 59(4), 599–607.
Xu, L., Xu, W., Qiu, S., & Xiong, S. (2010). Enrichment of CCR6+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in the tumor mass correlates with impaired CD8+ T cell function and poor prognosis of breast cancer. Clinical Immunology, 135(3), 466–475.
Nishikawa, H., & Sakaguchi, S. (2014). Regulatory T cells in cancer immunotherapy. Current Opinion in Immunology, 27, 1–7.
Kryczek, I., Wu, K., Zhao, E., Wei, S., Vatan, L., Szeliga, W., et al. (2011). IL-17+ regulatory T cells in the microenvironments of chronic inflammation and cancer. Journal of Immunology, 186(7), 4388–4395.
Mandapathil, M., Hilldorfer, B., Szczepanski, M. J., Czystowska, M., Szajnik, M., Ren, J., et al. (2010). Generation and accumulation of immunosuppressive adenosine by human CD4+CD25highFoxp3+ regulatory T cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 285(10), 7176–7186.
Schuler, P. J., Schilling, B., Harasymczuk, M., Hoffmann, T. K., Johnson, J., Lang, S., et al. (2012). Phenotypic and functional characteristics of CD4+ CD39+ Foxp3+ and CD4+ CD39+ Foxp3neg T-cell subsets in cancer patients. European Journal of Immunology, 42(7), 1876–1885.
Sugiyama, D., Nishikawa, H., Maeda, Y., Nishioka, M., Tanemura, A., Katayama, I., et al. (2013). Anti-CCR4 mAb selectively depletes effector-type Foxp3+CD4+ regulatory T cells, evoking antitumor immune responses in humans. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(44), 17945–17950.
Crome, S. Q., Clive, B., Wang, A. Y., Kang, C. Y., Chow, V., Yu, J., et al. (2010). Inflammatory effects of ex vivo human Th17 cells are suppressed by regulatory T cells. Journal of Immunology, 185(6), 3199–3208.
Bates, G. J., Fox, S. B., Han, C., Leek, R. D., Garcia, J. F., Harris, A. L., et al. (2006). Quantification of regulatory T cells enables the identification of high-risk breast cancer patients and those at risk of late relapse. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 24(34), 5373–5380.
Liyanage, U. K., Moore, T. T., Joo, H. G., Tanaka, Y., Herrmann, V., Doherty, G., et al. (2002). Prevalence of regulatory T cells is increased in peripheral blood and tumor microenvironment of patients with pancreas or breast adenocarcinoma. Journal of Immunology, 169(5), 2756–2761.
Aruga, T., Suzuki, E., Saji, S., Horiguchi, S., Horiguchi, K., Sekine, S., et al. (2009). A low number of tumor-infiltrating Foxp3-positive cells during primary systemic chemotherapy correlates with favorable anti-tumor response in patients with breast cancer. Oncology Reports, 22(2), 273–278.
Liu, F., Lang, R., Zhao, J., Zhang, X., Pringle, G. A., Fan, Y., et al. (2011). CD8(+) cytotoxic T cell and Foxp3(+) regulatory T cell infiltration in relation to breast cancer survival and molecular subtypes. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment, 130(2), 645–655.
Yan, M., Jene, N., Byrne, D., Millar, E. K., O’Toole, S. A., McNeil, C. M., et al. (2011). Recruitment of regulatory T cells is correlated with hypoxia-induced CXCR4 expression, and is associated with poor prognosis in basal-like breast cancers. Breast Cancer Research, 13(2), R47.
West, N. R., Kost, S. E., Martin, S. D., Milne, K., Deleeuw, R. J., Nelson, B. H., et al. (2013). Tumour-infiltrating Foxp3(+) lymphocytes are associated with cytotoxic immune responses and good clinical outcome in oestrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. British Journal of Cancer, 108(1), 155–162.
de Kruijf, E. M., van Nes, J. G., Sajet, A., Tummers, Q. R., Putter, H., Osanto, S., et al. (2010). The predictive value of HLA class I tumor cell expression and presence of intratumoral Tregs for chemotherapy in patients with early breast cancer. Clinical Cancer Research, 16(4), 1272–1280.
Mahmoud, S. M., Paish, E. C., Powe, D. G., Macmillan, R. D., Lee, A. H., Ellis, I. O., et al. (2011). An evaluation of the clinical significance of Foxp3+ infiltrating cells in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment, 127(1), 99–108.
Ali, H. R., Provenzano, E., Dawson, S. J., Blows, F. M., Liu, B., Shah, M., et al. (2014). Association between CD8+ T-cell infiltration and breast cancer survival in 12,439 patients. Annals of Oncology, 25(8), 1536–1543.
Yang, Y., Guan, X., You, J. CLOPE: a fast and effective clustering algorithm for transactional data. In Proceedings of the eighth ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada, 2002 (pp. 682–687): ACM
Mahmoud, S. M. (2011). Inflammation and immunosurveillance in breast Cancer [PhD thesis]. Nottingham, UK: The University of Nottingham. http://etheses.nottingham.ac.uk/1827/
Ladoire, S., Arnould, L., Mignot, G., Coudert, B., Rebe, C., Chalmin, F., et al. (2011). Presence of Foxp3 expression in tumor cells predicts better survival in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment, 125(1), 65–72.
Zuo, T., Liu, R., Zhang, H., Chang, X., Liu, Y., Wang, L., et al. (2007). Foxp3 is a novel transcriptional repressor for the breast cancer oncogene SKP2. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 117(12), 3765–3773.
Douglass, S., Meeson, A. P., Overbeck-Zubrzycka, D., Brain, J. G., Bennett, M. R., Lamb, C. A., et al. (2014). Breast cancer metastasis: demonstration that Foxp3 regulates CXCR4 expression and the response to CXCL12. Journal of Pathology, 234 (1), 74–85.
von Minckwitz, G., Untch, M., Blohmer, J. U., Costa, S. D., Eidtmann, H., Fasching, P. A., et al. (2012). Definition and impact of pathologic complete response on prognosis after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in various intrinsic breast cancer subtypes. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 30(15), 1796–1804.
Demir, L., Yigit, S., Ellidokuz, H., Erten, C., Somali, I., Kucukzeybek, Y., et al. (2013). Predictive and prognostic factors in locally advanced breast cancer: effect of intratumoral Foxp3+ Tregs. Clinical and Experimental Metastasis, 30(8), 1047–1062.
Ladoire, S., Arnould, L., Apetoh, L., Coudert, B., Martin, F., Chauffert, B., et al. (2008). Pathologic complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy of breast carcinoma is associated with the disappearance of tumor-infiltrating Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. Clinical Cancer Research, 14(8), 2413–2420.
Verma, C., Eremin, J. M., Robins, A., Bennett, A. J., Cowley, G. P., El-Sheemy, M. A., et al. (2013). Abnormal T regulatory cells (Tregs: Foxp3+, CTLA-4+), myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs: monocytic, granulocytic) and polarised T helper cell profiles (Th1, Th2, Th17) in women with large and locally advanced breast cancers undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) and surgery: failure of abolition of abnormal Treg profile with treatment and correlation of Treg levels with pathological response to NAC. Journal of Translational Medicine, 11, 16.
Decker, T., Fischer, G., Bucke, W., Bucke, P., Stotz, F., Gruneberger, A., et al. (2012). Increased number of regulatory T cells (T-regs) in the peripheral blood of patients with HER-2/neu-positive early breast cancer. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology, 138(11), 1945–1950.
Lal, A., Chan, L., Devries, S., Chin, K., Scott, G. K., Benz, C. C., et al. (2013). Foxp3-positive regulatory T lymphocytes and epithelial Foxp3 expression in synchronous normal, ductal carcinoma in situ, and invasive cancer of the breast. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment, 139(2), 381–390.
Recchia, F., Candeloro, G., Necozione, S., Desideri, G., Cesta, A., Recchia, L., et al. (2013). Vascular endothelial growth factor expression and T-regulatory cells in premenopausal breast cancer. Oncology Letters, 5(4), 1117–1122.
Takenaka, M., Seki, N., Toh, U., Hattori, S., Kawahara, A., Yamaguchi, T., et al. (2013). Foxp3 expression in tumor cells and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes is associated with breast cancer prognosis. Molecular and Clinical Oncology, 1(4), 625–632.
Zhou, S., Xu, S., Tao, H., Zhen, Z., Chen, G., Zhang, Z., et al. (2013). CCR7 expression and intratumoral Foxp3+ regulatory T cells are correlated with overall survival and lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer. PloS One, 8(9), e74430.
Huen, N. Y., Pang, A. L., Tucker, J. A., Lee, T. L., Vergati, M., Jochems, C., et al. (2013). Up-regulation of proliferative and migratory genes in regulatory T cells from patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. International Journal of Cancer, 133(2), 373–382.
Kang, M. J., Kim, K. M., Bae, J. S., Park, H. S., Lee, H., Chung, M. J., et al. (2013). Tumor-infiltrating PD1-positive lymphocytes and Foxp3-positive regulatory T cells predict distant metastatic relapse and survival of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Translational Oncology, 6(3), 282–289.
French, J. D., Kotnis, G. R., Said, S., Raeburn, C. D., McIntyre, R. C., Jr., Klopper, J. P., et al. (2012). Programmed death-1+ T cells and regulatory T cells are enriched in tumor-involved lymph nodes and associated with aggressive features in papillary thyroid cancer. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 97(6), E934–E943.
Fu, H. Y., Li, C., Yang, W., Gai, X. D., Jia, T., Lei, Y. M., et al. (2013). Foxp3 and TLR4 protein expression are correlated in non-small cell lung cancer: implications for tumor progression and escape. Acta Histochemica, 115(2), 151–157.
Efimova, O. V., & Kelley, T. W. (2009). Induction of granzyme B expression in T-cell receptor/CD28-stimulated human regulatory T cells is suppressed by inhibitors of the PI3K-mTOR pathway. BMC Immunology, 10, 59.
Garin, M. I., Chu, C. C., Golshayan, D., Cernuda-Morollon, E., Wait, R., & Lechler, R. I. (2007). Galectin-1: a key effector of regulation mediated by CD4+CD25+ T cells. Blood, 109(5), 2058–2065.
Borsellino, G., Kleinewietfeld, M., Di Mitri, D., Sternjak, A., Diamantini, A., Giometto, R., et al. (2007). Expression of ectonucleotidase CD39 by Foxp3+ Treg cells: hydrolysis of extracellular ATP and immune suppression. Blood, 110(4), 1225–1232.
Spranger, S., Spaapen, R. M., Zha, Y., Williams, J., Meng, Y., Ha, T. T., et al. (2013). Up-regulation of PD-L1, IDO, and T(regs) in the melanoma tumor microenvironment is driven by CD8(+) T cells. Science Translational Medicine, 5(200), 200ra116.
Wing, K., Onishi, Y., Prieto-Martin, P., Yamaguchi, T., Miyara, M., Fehervari, Z., et al. (2008). CTLA-4 control over Foxp3+ regulatory T cell function. Science, 322(5899), 271–275.
Bos, P. D., Plitas, G., Rudra, D., Lee, S. Y., & Rudensky, A. Y. (2013). Transient regulatory T cell ablation deters oncogene-driven breast cancer and enhances radiotherapy. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 210(11), 2435–2466.
Camisaschi, C., Casati, C., Rini, F., Perego, M., De Filippo, A., Triebel, F., et al. (2010). LAG-3 expression defines a subset of CD4(+)CD25(high)Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells that are expanded at tumor sites. Journal of Immunology, 184(11), 6545–6551.
Delgoffe, G. M., Woo, S. R., Turnis, M. E., Gravano, D. M., Guy, C., Overacre, A. E., et al. (2013). Stability and function of regulatory T cells is maintained by a neuropilin-1-semaphorin-4a axis. Nature, 501(7466), 252–256.
Facciabene, A., Santoro, S., & Coukos, G. (2012). Know thy enemy: why are tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells so deleterious? Oncoimmunology, 1(4), 575–577.
Whiteside, T. L. (2008). The tumor microenvironment and its role in promoting tumor growth. Oncogene, 27(45), 5904–5912.
Karavitis, J., Hix, L. M., Shi, Y. H., Schultz, R. F., Khazaie, K., & Zhang, M. (2012). Regulation of COX2 expression in mouse mammary tumor cells controls bone metastasis and PGE2-induction of regulatory T cell migration. PloS One, 7(9), e46342.
Kudo-Saito, C., Shirako, H., Ohike, M., Tsukamoto, N., & Kawakami, Y. (2013). CCL2 is critical for immunosuppression to promote cancer metastasis. Clinical and Experimental Metastasis, 30(4), 393–405.
Hansen, W., Hutzler, M., Abel, S., Alter, C., Stockmann, C., Kliche, S., et al. (2012). Neuropilin 1 deficiency on CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells impairs mouse melanoma growth. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 209(11), 2001–2016.
Wada, J., Suzuki, H., Fuchino, R., Yamasaki, A., Nagai, S., Yanai, K., et al. (2009). The contribution of vascular endothelial growth factor to the induction of regulatory T-cells in malignant effusions. Anticancer Research, 29(3), 881–888.
Gupta, S., Joshi, K., Wig, J. D., & Arora, S. K. (2007). Intratumoral Foxp3 expression in infiltrating breast carcinoma: its association with clinicopathologic parameters and angiogenesis. Acta Oncologica, 46(6), 792–797.
Boyce, B. F., & Xing, L. (2007). Biology of RANK, RANKL, and osteoprotegerin. Arthritis Research and Therapy, 9(Suppl 1), S1.
Faghih, Z., Erfani, N., Haghshenas, M. R., Safaei, A., Talei, A. R., & Ghaderi, A. (2014). Immune profiles of CD4+ lymphocyte subsets in breast cancer tumor draining lymph nodes. Immunology Letters, 158(1–2), 57–65.
Kashimura, S., Saze, Z., Terashima, M., Soeta, N., Ohtani, S., Osuka, F., et al. (2012). CD83(+) dendritic cells and Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells in primary lesions and regional lymph nodes are inversely correlated with prognosis of gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer, 15(2), 144–153.
Mansfield, A. S., Heikkila, P. S., Vaara, A. T., von Smitten, K. A., Vakkila, J. M., & Leidenius, M. H. (2009). Simultaneous Foxp3 and IDO expression is associated with sentinel lymph node metastases in breast cancer. BMC Cancer, 9, 231.
Tsiatas, M. L., Gyftaki, R., Liacos, C., Politi, E., Rodolakis, A., Dimopoulos, M. A., et al. (2009). Study of T lymphocytes infiltrating peritoneal metastases in advanced ovarian cancer: associations with vascular endothelial growth factor levels and prognosis in patients receiving platinum-based chemotherapy. International Journal of Gynecological Cancer, 19(8), 1329–1334.
Abadi, Y. M., Jeon, H., Ohaegbulam, K. C., Scandiuzzi, L., Ghosh, K., Hofmeyer, K. A., et al. (2013). Host b7x promotes pulmonary metastasis of breast cancer. Journal of Immunology, 190(7), 3806–3814.
Biragyn, A., Bodogai, M., Olkhanud, P. B., Denny-Brown, S. R., Puri, N., Ayukawa, K., et al. (2013). Inhibition of lung metastasis by chemokine CCL17-mediated in vivo silencing of genes in CCR4+ Tregs. Journal of Immunotherapy, 36(4), 258–267.
Chopra, M., Riedel, S. S., Biehl, M., Krieger, S., von Krosigk, V., Bauerlein, C. A., et al. (2013). Tumor necrosis factor receptor 2-dependent homeostasis of regulatory T cells as a player in TNF-induced experimental metastasis. Carcinogenesis, 34(6), 1296–1303.
Dalotto-Moreno, T., Croci, D. O., Cerliani, J. P., Martinez-Allo, V. C., Dergan-Dylon, S., Mendez-Huergo, S. P., et al. (2013). Targeting galectin-1 overcomes breast cancer-associated immunosuppression and prevents metastatic disease. Cancer Research, 73(3), 1107–1117.
Ghochikyan, A., Davtyan, A., Hovakimyan, A., Davtyan, H., Poghosyan, A., Bagaev, A., et al. (2014). Primary 4T1 tumor resection provides critical “window of opportunity” for immunotherapy. Clinical and Experimental Metastasis, 31(2), 185–198.
Kim, P. S., Jochems, C., Grenga, I., Donahue, R. N., Tsang, K. Y., Gulley, J. L., et al. (2014). Pan-Bcl-2 inhibitor, GX15-070 (obatoclax), decreases human T regulatory lymphocytes while preserving effector T lymphocytes: a rationale for its use in combination immunotherapy. Journal of Immunology, 192(6), 2622–2633.
Mandl, S. J., Rountree, R. B., Dalpozzo, K., Do, L., Lombardo, J. R., Schoonmaker, P. L., et al. (2012). Immunotherapy with MVA-BN(R)-HER2 induces HER-2-specific Th1 immunity and alters the intratumoral balance of effector and regulatory T cells. Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy, 61(1), 19–29.
Olkhanud, P. B., Baatar, D., Bodogai, M., Hakim, F., Gress, R., Anderson, R. L., et al. (2009). Breast cancer lung metastasis requires expression of chemokine receptor CCR4 and regulatory T cells. Cancer Research, 69(14), 5996–6004.
Olkhanud, P. B., Damdinsuren, B., Bodogai, M., Gress, R. E., Sen, R., Wejksza, K., et al. (2011). Tumor-evoked regulatory B cells promote breast cancer metastasis by converting resting CD4(+) T cells to T-regulatory cells. Cancer Research, 71(10), 3505–3515.
Tanikawa, T., Wilke, C. M., Kryczek, I., Chen, G. Y., Kao, J., Nunez, G., et al. (2012). Interleukin-10 ablation promotes tumor development, growth, and metastasis. Cancer Research, 72(2), 420–429.
Lee-Chang, C., Bodogai, M., Martin-Montalvo, A., Wejksza, K., Sanghvi, M., Moaddel, R., et al. (2013). Inhibition of breast cancer metastasis by resveratrol-mediated inactivation of tumor-evoked regulatory B cells. Journal of Immunology, 191(8), 4141–4151.
Vadrevu, S. K., Chintala, N. K., Sharma, S. K., Sharma, P., Cleveland, C., Riediger, L., et al. (2014). Complement C5a receptor facilitates cancer metastasis by altering T-cell responses in the metastatic niche. Cancer Research, 74(13), 3454–3465.
Weiss, J. M., Subleski, J. J., Back, T., Chen, X., Watkins, S. K., Yagita, H., et al. (2014). Regulatory T cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the tumor microenvironment undergo Fas-dependent cell death during IL-2/alphaCD40 therapy. Journal of Immunology, 192(12), 5821–5829.
Kim, R., Emi, M., & Tanabe, K. (2007). Cancer immunoediting from immune surveillance to immune escape. Immunology, 121(1), 1–14.
Spranger, S., Koblish, H. K., Horton, B., Scherle, P. A., Newton, R., & Gajewski, T. F. (2014). Mechanism of tumor rejection with doublets of CTLA-4, PD-1/PD-L1, or IDO blockade involves restored IL-2 production and proliferation of CD8(+) T cells directly within the tumor microenvironment. Journal of Immunotherapy of Cancer, 2, 3.
Byrne, W. L., Mills, K. H., Lederer, J. A., & O’Sullivan, G. C. (2011). Targeting regulatory T cells in cancer. Cancer Research, 71(22), 6915–6920.
von Boehmer, H., & Daniel, C. (2013). Therapeutic opportunities for manipulating T(Reg) cells in autoimmunity and cancer. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 12(1), 51–63.
Kozawa, E., Sugiura, H., Wasa, J., Kohyama, K., Yamada, K., Nishioka, A., et al. (2010). Suppression of tumour metastasis in a murine osteosarcoma model with anti-CD25 monoclonal antibody treatment. Anticancer Research, 30(12), 5019–5022.
Allard, B., Pommey, S., Smyth, M. J., & Stagg, J. (2013). Targeting CD73 enhances the antitumor activity of anti-PD-1 and anti-CTLA-4 mAbs. Clinical Cancer Research, 19(20), 5626–5635.
Ge, Y., Domschke, C., Stoiber, N., Schott, S., Heil, J., Rom, J., et al. (2012). Metronomic cyclophosphamide treatment in metastasized breast cancer patients: immunological effects and clinical outcome. Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy, 61(3), 353–362.
Kaji, W., Tanaka, S., Tsukimoto, M., & Kojima, S. (2014). Adenosine A(2B) receptor antagonist PSB603 suppresses tumor growth and metastasis by inhibiting induction of regulatory T cells. Journal of Toxicological Sciences, 39(2), 191–198.
Li, C. X., Wong, B. L., Ling, C. C., Ma, Y. Y., Shao, Y., Geng, W., et al. (2014). A novel oxygen carrier “YQ23” suppresses the liver tumor metastasis by decreasing circulating endothelial progenitor cells and regulatory T cells. BMC Cancer, 14(1), 293.
Pohla, H., Buchner, A., Stadlbauer, B., Frankenberger, B., Stevanovic, S., Walter, S., et al. (2012). High immune response rates and decreased frequencies of regulatory T cells in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients after tumor cell vaccination. Molecular Medicine, 18, 1499–1508.
Shahabi, V., Seavey, M. M., Maciag, P. C., Rivera, S., & Wallecha, A. (2011). Development of a live and highly attenuated Listeria monocytogenes-based vaccine for the treatment of HER2/neu-overexpressing cancers in human. Cancer Gene Therapy, 18(1), 53–62.
Maciag, P. C., Radulovic, S., & Rothman, J. (2009). The first clinical use of a live-attenuated Listeria monocytogenes vaccine: a phase I safety study of Lm-LLO-E7 in patients with advanced carcinoma of the cervix. Vaccine, 27(30), 3975–3983.
Wallecha, A., Singh, R., & Malinina, I. (2013). Listeria monocytogenes (Lm)-LLO immunotherapies reduce the immunosuppressive activity of myeloid-derived suppressor cells and regulatory T cells in the tumor microenvironment. Journal of Immunotherapy, 36(9), 468–476.
Audia, S., Nicolas, A., Cathelin, D., Larmonier, N., Ferrand, C., Foucher, P., et al. (2007). Increase of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in the peripheral blood of patients with metastatic carcinoma: a phase I clinical trial using cyclophosphamide and immunotherapy to eliminate CD4+CD25+ T lymphocytes. Clinical and Experimental Immunology, 150(3), 523–530.
Emmenegger, U., Francia, G., Chow, A., Shaked, Y., Kouri, A., Man, S., et al. (2011). Tumors that acquire resistance to low-dose metronomic cyclophosphamide retain sensitivity to maximum tolerated dose cyclophosphamide. Neoplasia, 13(1), 40–48.
Simpson, T. R., Li, F., Montalvo-Ortiz, W., Sepulveda, M. A., Bergerhoff, K., Arce, F., et al. (2013). Fc-dependent depletion of tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells co-defines the efficacy of anti-CTLA-4 therapy against melanoma. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 210(9), 1695–1710.
Galon, J., Pages, F., Marincola, F. M., Angell, H. K., Thurin, M., Lugli, A., et al. (2012). Cancer classification using the immunoscore: a worldwide task force. Journal of Translational Medicine, 10, 205.
Galon, J., Mlecnik, B., Bindea, G., Angell, H. K., Berger, A., Lagorce, C., et al. (2014). Towards the introduction of the ‘immunoscore’ in the classification of malignant tumours. Journal of Pathology, 232(2), 199–209.
Gonzalez, L., Strbo, N., & Podack, E. R. (2013). Humanized mice: novel model for studying mechanisms of human immune-based therapies. Immunologic Research, 57(1–3), 326–334.
Budiu, R. A., Elishaev, E., Brozick, J., Lee, M., Edwards, R. P., Kalinski, P., et al. (2013). Immunobiology of human mucin 1 in a preclinical ovarian tumor model. Oncogene, 32(32), 3664–3675.
Drennan, S., Stafford, N. D., Greenman, J., & Green, V. L. (2013). Increased frequency and suppressive activity of CD127(low/-) regulatory T cells in the peripheral circulation of patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma are associated with advanced stage and nodal involvement. Immunology, 140(3), 335–343.
Schneider, T., Kimpfler, S., Warth, A., Schnabel, P. A., Dienemann, H., Schadendorf, D., et al. (2011). Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells and natural killer cells distinctly infiltrate primary tumors and draining lymph nodes in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. Journal of Thoracic Oncology, 6(3), 432–438.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (Grant MOP-126138) and the BC Cancer Foundation. E.C.H. is supported by a Frederick Banting and Charles Best Canada Graduate Scholarship from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and by a 4-year doctoral fellowship from the University of British Columbia. K.L.B. is a Michael Smith Foundation for Health Research Biomedical Research scholar.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Halvorsen, E.C., Mahmoud, S.M. & Bennewith, K.L. Emerging roles of regulatory T cells in tumour progression and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 33, 1025–1041 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-014-9529-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-014-9529-x