Abstract
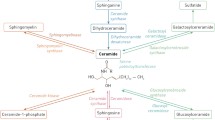
The bioactive sphingolipids including, ceramide, sphingosine, and sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) have important roles in several types of signaling and regulation of many cellular processes including cell proliferation, apoptosis, senescence, angiogenesis, and transformation. Recent accumulating evidence suggests that ceramide- and S1P-mediated pathways have been implicated in cancer development, progression, and chemotherapy. Ceramide mediates numerous cell-stress responses, such as induction of apoptosis and cell senescence, whereas S1P plays pivotal roles in cell survival, migration, and inflammation. These sphingolipids with opposing roles can be interconverted within cells, suggesting that the balance between them is related to cell fate. Importantly, these sphingolipids are metabolically related through actions of enzymes including ceramidases, ceramide synthases, sphingosine kinases, and S1P phosphatases thereby forming a network of metabolically interrelated bioactive lipid mediators whose importance in normal cellular function and diseases is gaining appreciation. In this review, we summarize involvement of sphingolipids and their related enzymes in pathogenesis and therapy of cancer and discuss future directions of sphingolipid field in cancer research.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spiegel, S., & Milstien, S. (2003). Sphingosine-1-phosphate: an enigmatic signalling lipid. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 4, 397–407.
Ogretmen, B., & Hannun, Y. A. (2004). Biologically active sphingolipids in cancer pathogenesis and treatment. Nature Reviews. Cancer, 4, 604–616.
Hannun, Y. A., & Obeid, L. M. (2008). Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: lessons from sphingolipids. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 9, 139–150.
Hannun, Y. A., & Obeid, L. M. (2002). The Ceramide-centric universe of lipid-mediated cell regulation: stress encounters of the lipid kind. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277, 25847–25850.
Linn, S. C., Kim, H. S., Keane, E. M., Andras, L. M., Wang, E., & Merrill, A. H., Jr. (2001). Regulation of de novo sphingolipid biosynthesis and the toxic consequences of its disruption. Biochemical Society Transactions, 29, 831–835.
Pewzner-Jung, Y., Ben-Dor, S., & Futerman, A. H. (2006). When do Lasses (longevity assurance genes) become CerS (ceramide synthases)?: insights into the regulation of ceramide synthesis. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281, 25001–25005.
Tafesse, F. G., Ternes, P., & Holthuis, J. C. (2006). The multigenic sphingomyelin synthase family. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281, 29421–29425.
Raas-Rothschild, A., Pankova-Kholmyansky, I., Kacher, Y., & Futerman, A. H. (2004). Glycosphingolipidoses: beyond the enzymatic defect. Glycoconjugate Journal, 21, 295–304.
Marchesini, N., & Hannun, Y. A. (2004). Acid and neutral sphingomyelinases: roles and mechanisms of regulation. Biochemistry and Cell Biology, 82, 27–44.
Hakomori, S. (2000). Traveling for the glycosphingolipid path. Glycoconjugate Journal, 17, 627–647.
Ichikawa, S., & Hirabayashi, Y. (1998). Glucosylceramide synthase and glycosphingolipid synthesis. Trends in Cell Biology, 8, 198–202.
Xu, R., Jin, J., Hu, W., Sun, W., Bielawski, J., Szulc, Z., et al. (2006). Golgi alkaline ceramidase regulates cell proliferation and survival by controlling levels of sphingosine and S1P. The FASEB Journal, 20, 1813–1825.
Galadari, S., Wu, B. X., Mao, C., Roddy, P., El Bawab, S., & Hannun, Y. A. (2006). Identification of a novel amidase motif in neutral ceramidase. Biochemical Journal, 393, 687–695.
Hait, N. C., Oskeritzian, C. A., Paugh, S. W., Milstien, S., & Spiegel, S. (2006). Sphingosine kinases, sphingosine 1-phosphate, apoptosis and diseases. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1758, 2016–2026.
Johnson, K. R., Johnson, K. Y., Becker, K. P., Bielawski, J., Mao, C., & Obeid, L. M. (2003). Role of human sphingosine-1-phosphate phosphatase 1 in the regulation of intra- and extracellular sphingosine-1-phosphate levels and cell viability. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 34541–34547.
Brindley, D. N. (2004). Lipid phosphate phosphatases and related proteins: signaling functions in development, cell division, and cancer. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 92, 900–912.
Sigal, Y. J., McDermott, M. I., & Morris, A. J. (2005). Integral membrane lipid phosphatases/phosphotransferases: common structure and diverse functions. Biochemical Journal, 387, 281–293.
Bandhuvula, P., & Saba, J. D. (2007). Sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase in immunity and cancer: silencing the siren. Trends in Molecular Medicine, 13, 210–217.
Obeid, L. M., Linardic, C. M., Karolak, L. A., & Hannun, Y. A. (1993). Programmed cell death induced by ceramide. Science, 259, 1769–1771.
Venable, M. E., Lee, J. Y., Smyth, M. J., Bielawska, A., & Obeid, L. M. (1995). Role of ceramide in cellular senescence. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 270, 30701–30708.
Hla, T. (2004). Physiological and pathological actions of sphingosine 1-phosphate. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology, 15, 513–520.
Liu, X., Cheng, J. C., Turner, L. S., Elojeimy, S., Beckham, T. H., Bielawska, A., et al. (2009). Acid ceramidase upregulation in prostate cancer: role in tumor development and implications for therapy. Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets, 13, 1449–1458.
Dudeja, P. K., Dahiya, R., & Brasitus, T. A. (1986). The role of sphingomyelin synthetase and sphingomyelinase in 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced lipid alterations of rat colonic plasma membranes. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 863, 309–312.
Dillehay, D. L., Webb, S. K., Schmelz, E. M., & Merrill, A. H., Jr. (1994). Dietary sphingomyelin inhibits 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced colon cancer in CF1 mice. Journal of Nutrition, 124, 615–620.
Schmelz, E. M., Dillehay, D. L., Webb, S. K., Reiter, A., Adams, J., & Merrill, A. H., Jr. (1996). Sphingomyelin consumption suppresses aberrant colonic crypt foci and increases the proportion of adenomas versus adenocarcinomas in CF1 mice treated with 1,2-dimethylhydrazine: implications for dietary sphingolipids and colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Research, 56, 4936–4941.
Schmelz, E. M., Bushnev, A. S., Dillehay, D. L., Sullards, M. C., Liotta, D. C., & Merrill, A. H., Jr. (1999). Ceramide-beta-d-glucuronide: synthesis, digestion, and suppression of early markers of colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Research, 59, 5768–5772.
Schmelz, E. M., Bushnev, A. S., Dillehay, D. L., Liotta, D. C., & Merrill, A. H., Jr. (1997). Suppression of aberrant colonic crypt foci by synthetic sphingomyelins with saturated or unsaturated sphingoid base backbones. Nutrition and Cancer, 28, 81–85.
Symolon, H., Schmelz, E. M., Dillehay, D. L., & Merrill, A. H., Jr. (2004). Dietary soy sphingolipids suppress tumorigenesis and gene expression in 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-treated CF1 mice and ApcMin/+ mice. Journal of Nutrition, 134, 1157–1161.
Schmelz, E. M., Sullards, M. C., Dillehay, D. L., & Merrill, A. H., Jr. (2000). Colonic cell proliferation and aberrant crypt foci formation are inhibited by dairy glycosphingolipids in 1, 2-dimethylhydrazine-treated CF1 mice. Journal of Nutrition, 130, 522–527.
Schmelz, E. M., Roberts, P. C., Kustin, E. M., Lemonnier, L. A., Sullards, M. C., Dillehay, D. L., et al. (2001). Modulation of intracellular beta-catenin localization and intestinal tumorigenesis in vivo and in vitro by sphingolipids. Cancer Research, 61, 6723–6729.
Lemonnier, L. A., Dillehay, D. L., Vespremi, M. J., Abrams, J., Brody, E., & Schmelz, E. M. (2003). Sphingomyelin in the suppression of colon tumors: prevention versus intervention. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 419, 129–138.
Mazzei, J. C., Zhou, H., Brayfield, B. P., Hontecillas, R., Bassaganya-Riera, J., & Schmelz, E. M. (2011). Suppression of intestinal inflammation and inflammation-driven colon cancer in mice by dietary sphingomyelin: importance of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma expression. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry (in press).
Hla, T. (2003). Signaling and biological actions of sphingosine 1-phosphate. Pharmacological Research, 47, 401–407.
Allende, M. L., & Proia, R. L. (2002). Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors and the development of the vascular system. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1582, 222–227.
Lee, M. J., Thangada, S., Claffey, K. P., Ancellin, N., Liu, C. H., Kluk, M., et al. (1999). Vascular endothelial cell adherens junction assembly and morphogenesis induced by sphingosine-1-phosphate. Cell, 99, 301–312.
Visentin, B., Vekich, J. A., Sibbald, B. J., Cavalli, A. L., Moreno, K. M., Matteo, R. G., et al. (2006). Validation of an anti-sphingosine-1-phosphate antibody as a potential therapeutic in reducing growth, invasion, and angiogenesis in multiple tumor lineages. Cancer Cell, 9, 225–238.
Kawamori, T., Osta, W., Johnson, K. R., Pettus, B. J., Bielawski, J., Tanaka, T., et al. (2006). Sphingosine kinase 1 is up-regulated in colon carcinogenesis. The FASEB Journal, 20, 386–388.
Eberhart, C. E., Coffey, R. J., Radhika, A., Giardiello, F. M., Ferrenbach, S., & DuBois, R. N. (1994). Up-regulation of cyclooxygenase 2 gene expression in human colorectal adenomas and adenocarcinomas. Gastroenterology, 107, 1183–1188.
Oshima, M., Dinchuk, J. E., Kargman, S. L., Oshima, H., Hancock, B., Kwong, E., et al. (1996). Suppression of intestinal polyposis in Apc delta716 knockout mice by inhibition of cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2). Cell, 87, 803–809.
Watanabe, K., Kawamori, T., Nakatsugi, S., Ohta, T., Ohuchida, S., Yamamoto, H., et al. (1999). Role of the prostaglandin E receptor subtype EP1 in colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Research, 59, 5093–5096.
Sonoshita, M., Takaku, K., Sasaki, N., Sugimoto, Y., Ushikubi, F., Narumiya, S., et al. (2001). Acceleration of intestinal polyposis through prostaglandin receptor EP2 in Apc(Delta 716) knockout mice. Nature Medicine, 7, 1048–1051.
Kawamori, T., Rao, C. V., Seibert, K., & Reddy, B. S. (1998). Chemopreventive activity of celecoxib, a specific cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, against colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Research, 58, 409–412.
Snider, A. J., Kawamori, T., Bradshaw, S. G., Orr, K. A., Gilkeson, G. S., Hannun, Y. A., et al. (2009). A role for sphingosine kinase 1 in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. The FASEB Journal, 23, 143–152.
Kawamori, T., Kaneshiro, T., Okumura, M., Maalouf, S., Uflacker, A., Bielawski, J., et al. (2009). Role for sphingosine kinase 1 in colon carcinogenesis. The FASEB Journal, 23, 405–414.
Kohno, M., Momoi, M., Oo, M. L., Paik, J. H., Lee, Y. M., Venkataraman, K., et al. (2006). Intracellular role for sphingosine kinase 1 in intestinal adenoma cell proliferation. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 26, 7211–7223.
Maines, L. W., Fitzpatrick, L. R., French, K. J., Zhuang, Y., Xia, Z., Keller, S. N., et al. (2008). Suppression of ulcerative colitis in mice by orally available inhibitors of sphingosine kinase. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 53, 997–1012.
Chumanevich, A. A., Poudyal, D., Cui, X., Davis, T., Wood, P. A., Smith, C. D., et al. (2010). Suppression of colitis-driven colon cancer in mice by a novel small molecule inhibitor of sphingosine kinase. Carcinogenesis, 31, 1787–1793.
Oskouian, B., Sooriyakumaran, P., Borowsky, A. D., Crans, A., Dillard-Telm, L., Tam, Y. Y., et al. (2006). Sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase potentiates apoptosis via p53- and p38-dependent pathways and is down-regulated in colon cancer. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103, 17384–17389.
Kimura, K., Bowen, C., Spiegel, S., & Gelmann, E. P. (1999). Tumor necrosis factor-alpha sensitizes prostate cancer cells to gamma-irradiation-induced apoptosis. Cancer Research, 59, 1606–1614.
Haimovitz-Friedman, A., Kan, C. C., Ehleiter, D., Persaud, R. S., McLoughlin, M., Fuks, Z., et al. (1994). Ionizing radiation acts on cellular membranes to generate ceramide and initiate apoptosis. The Journal of Experimental Medicine, 180, 525–535.
Chmura, S. J., Nodzenski, E., Beckett, M. A., Kufe, D. W., Quintans, J., & Weichselbaum, R. R. (1997). Loss of ceramide production confers resistance to radiation-induced apoptosis. Cancer Research, 57, 1270–1275.
Nava, V. E., Cuvillier, O., Edsall, L. C., Kimura, K., Milstien, S., Gelmann, E. P., et al. (2000). Sphingosine enhances apoptosis of radiation-resistant prostate cancer cells. Cancer Research, 60, 4468–4474.
Norris, J. S., Bielawska, A., Day, T., El-Zawahri, A., ElOjeimy, S., Hannun, Y., et al. (2006). Combined therapeutic use of AdGFPFasL and small molecule inhibitors of ceramide metabolism in prostate and head and neck cancers: a status report. Cancer Gene Therapy, 13, 1045–1051.
Seelan, R. S., Qian, C., Yokomizo, A., Bostwick, D. G., Smith, D. I., & Liu, W. (2000). Human acid ceramidase is overexpressed but not mutated in prostate cancer. Genes, Chromosomes & Cancer, 29, 137–146.
Saad, A. F., Meacham, W. D., Bai, A., Anelli, V., Elojeimy, S., Mahdy, A. E., et al. (2007). The functional effects of acid ceramidase overexpression in prostate cancer progression and resistance to chemotherapy. Cancer Biology & Therapy, 6, 1455–1460.
Mahdy, A. E., Cheng, J. C., Li, J., Elojeimy, S., Meacham, W. D., Turner, L. S., et al. (2009). Acid ceramidase upregulation in prostate cancer cells confers resistance to radiation: AC inhibition, a potential radiosensitizer. Molecular Therapy, 17, 430–438.
Spiegel, S., Cuvillier, O., Edsall, L. C., Kohama, T., Menzeleev, R., Olah, Z., et al. (1998). Sphingosine-1-phosphate in cell growth and cell death. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 845, 11–18.
Cuvillier, O., Pirianov, G., Kleuser, B., Vanek, P. G., Coso, O. A., Gutkind, S., et al. (1996). Suppression of ceramide-mediated programmed cell death by sphingosine-1-phosphate. Nature, 381, 800–803.
Sauane, M., Su, Z. Z., Dash, R., Liu, X., Norris, J. S., Sarkar, D., et al. (2010). Ceramide plays a prominent role in MDA-7/IL-24-induced cancer-specific apoptosis. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 222, 546–555.
Wang, J. D., Takahara, S., Nonomura, N., Ichimaru, N., Toki, K., Azuma, H., et al. (1999). Early induction of apoptosis in androgen-independent prostate cancer cell line by FTY720 requires caspase-3 activation. Prostate, 40, 50–55.
Permpongkosol, S., Wang, J. D., Takahara, S., Matsumiya, K., Nonomura, N., Nishimura, K., et al. (2002). Anticarcinogenic effect of FTY720 in human prostate carcinoma DU145 cells: modulation of mitogenic signaling, FAK, cell-cycle entry and apoptosis. International Journal of Cancer, 98, 167–172.
Chua, C. W., Lee, D. T., Ling, M. T., Zhou, C., Man, K., Ho, J., et al. (2005). FTY720, a fungus metabolite, inhibits in vivo growth of androgen-independent prostate cancer. International Journal of Cancer, 117, 1039–1048.
Akao, Y., Banno, Y., Nakagawa, Y., Hasegawa, N., Kim, T. J., Murate, T., et al. (2006). High expression of sphingosine kinase 1 and S1P receptors in chemotherapy-resistant prostate cancer PC3 cells and their camptothecin-induced up-regulation. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 342, 1284–1290.
Pchejetski, D., Doumerc, N., Golzio, M., Naymark, M., Teissie, J., Kohama, T., et al. (2008). Chemosensitizing effects of sphingosine kinase-1 inhibition in prostate cancer cell and animal models. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, 7, 1836–1845.
Mulders, A. C., Nau, S., Li, Y., & Michel, M. C. (2007). Effects of sphingosine-1-phosphate and sphingosylphosphorylcholine on intracellular Ca2+ and cell death in prostate cancer cell lines. Autonomic & Autacoid Pharmacology, 27, 173–179.
Lucci, A., Cho, W. I., Han, T. Y., Giuliano, A. E., Morton, D. L., & Cabot, M. C. (1998). Glucosylceramide: a marker for multiple-drug resistant cancers. Anticancer Research, 18, 475–480.
Lavie, Y., Cao, H., Bursten, S. L., Giuliano, A. E., & Cabot, M. C. (1996). Accumulation of glucosylceramides in multidrug-resistant cancer cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 271, 19530–19536.
Liu, Y. Y., Han, T. Y., Giuliano, A. E., & Cabot, M. C. (2001). Ceramide glycosylation potentiates cellular multidrug resistance. The FASEB Journal, 15, 719–730.
Liu, Y. Y., Han, T. Y., Yu, J. Y., Bitterman, A., Le, A., Giuliano, A. E., et al. (2004). Oligonucleotides blocking glucosylceramide synthase expression selectively reverse drug resistance in cancer cells. Journal of Lipid Research, 45, 933–940.
Gouaze, V., Yu, J. Y., Bleicher, R. J., Han, T. Y., Liu, Y. Y., Wang, H., et al. (2004). Overexpression of glucosylceramide synthase and P-glycoprotein in cancer cells selected for resistance to natural product chemotherapy. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, 3, 633–639.
Liu, Y. Y., Gupta, V., Patwardhan, G. A., Bhinge, K., Zhao, Y., Bao, J., et al. (2010). Glucosylceramide synthase upregulates MDR1 expression in the regulation of cancer drug resistance through cSrc and beta-catenin signaling. Molecular Cancer, 9, 145.
Ruckhaberle, E., Karn, T., Hanker, L., Gatje, R., Metzler, D., Holtrich, U., et al. (2009). Prognostic relevance of glucosylceramide synthase (GCS) expression in breast cancer. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology, 135, 81–90.
Gouaze, V., Liu, Y. Y., Prickett, C. S., Yu, J. Y., Giuliano, A. E., & Cabot, M. C. (2005). Glucosylceramide synthase blockade down-regulates P-glycoprotein and resensitizes multidrug-resistant breast cancer cells to anticancer drugs. Cancer Research, 65, 3861–3867.
Ogretmen, B. (2006). Sphingolipids in cancer: regulation of pathogenesis and therapy. FEBS Letters, 580, 5467–5476.
Schiffmann, S., Sandner, J., Birod, K., Wobst, I., Angioni, C., Ruckhaberle, E., et al. (2009). Ceramide synthases and ceramide levels are increased in breast cancer tissue. Carcinogenesis, 30, 745–752.
Struckhoff, A. P., Bittman, R., Burow, M. E., Clejan, S., Elliott, S., Hammond, T., et al. (2004). Novel ceramide analogs as potential chemotherapeutic agents in breast cancer. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 309, 523–532.
Antoon, J. W., Liu, J., Gestaut, M. M., Burow, M. E., Beckman, B. S., & Foroozesh, M. (2009). Design, synthesis, and biological activity of a family of novel ceramide analogues in chemoresistant breast cancer cells. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 52, 5748–5752.
Antoon, J. W., Liu, J., Ponnapakkam, A. P., Gestaut, M. M., Foroozesh, M., & Beckman, B. S. (2010). Novel d-erythro N-octanoyl sphingosine analogs as chemo- and endocrine-resistant breast cancer therapeutics. Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology, 65, 1191–1195.
Goetzl, E. J., Dolezalova, H., Kong, Y., & Zeng, L. (1999). Dual mechanisms for lysophospholipid induction of proliferation of human breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Research, 59, 4732–4737.
Wang, F., Nohara, K., Olivera, A., Thompson, E. W., & Spiegel, S. (1999). Involvement of focal adhesion kinase in inhibition of motility of human breast cancer cells by sphingosine 1-phosphate. Experimental Cell Research, 247, 17–28.
Nava, V. E., Hobson, J. P., Murthy, S., Milstien, S., & Spiegel, S. (2002). Sphingosine kinase type 1 promotes estrogen-dependent tumorigenesis of breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Experimental Cell Research, 281, 115–127.
Spiegel, S., Olivera, A., Zhang, H., Thompson, E. W., Su, Y., & Berger, A. (1994). Sphingosine-1-phosphate, a novel second messenger involved in cell growth regulation and signal transduction, affects growth and invasiveness of human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment, 31, 337–348.
French, K. J., Schrecengost, R. S., Lee, B. D., Zhuang, Y., Smith, S. N., Eberly, J. L., et al. (2003). Discovery and evaluation of inhibitors of human sphingosine kinase. Cancer Research, 63, 5962–5969.
Sukocheva, O., Wadham, C., & Xia, P. (2009). Role of sphingolipids in the cytoplasmic signaling of estrogens. Steroids, 74, 562–567.
Sukocheva, O. A., Wang, L., Albanese, N., Pitson, S. M., Vadas, M. A., & Xia, P. (2003). Sphingosine kinase transmits estrogen signaling in human breast cancer cells. Molecular Endocrinology, 17, 2002–2012.
Sukocheva, O., Wadham, C., Holmes, A., Albanese, N., Verrier, E., Feng, F., et al. (2006). Estrogen transactivates EGFR via the sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor Edg-3: the role of sphingosine kinase-1. The Journal of Cell Biology, 173, 301–310.
Takabe, K., Kim, R. H., Allegood, J. C., Mitra, P., Ramachandran, S., Nagahashi, M., et al. (2010). Estradiol induces export of sphingosine 1-phosphate from breast cancer cells via ABCC1 and ABCG2. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 285, 10477–10486.
Wakita, H., Tokura, Y., Yagi, H., Nishimura, K., Furukawa, F., & Takigawa, M. (1994). Keratinocyte differentiation is induced by cell-permeant ceramides and its proliferation is promoted by sphingosine. Archives for Dermatological Research, 286, 350–354.
Rodriguez-Lafrasse, C., Alphonse, G., Broquet, P., Aloy, M. T., Louisot, P., & Rousson, R. (2001). Temporal relationships between ceramide production, caspase activation and mitochondrial dysfunction in cell lines with varying sensitivity to anti-Fas-induced apoptosis. Biochemical Journal, 357, 407–416.
Chmura, S. J., Mauceri, H. J., Advani, S., Heimann, R., Beckett, M. A., Nodzenski, E., et al. (1997). Decreasing the apoptotic threshold of tumor cells through protein kinase C inhibition and sphingomyelinase activation increases tumor killing by ionizing radiation. Cancer Research, 57, 4340–4347.
Alphonse, G., Bionda, C., Aloy, M. T., Ardail, D., Rousson, R., & Rodriguez-Lafrasse, C. (2004). Overcoming resistance to gamma-rays in squamous carcinoma cells by poly-drug elevation of ceramide levels. Oncogene, 23, 2703–2715.
Separovic, D., Bielawski, J., Pierce, J. S., Merchant, S., Tarca, A. L., Ogretmen, B., et al. (2009). Increased tumour dihydroceramide production after Photofrin-PDT alone and improved tumour response after the combination with the ceramide analogue LCL29. Evidence from mouse squamous cell carcinomas. British Journal of Cancer, 100, 626–632.
Mehta, S., Blackinton, D., Omar, I., Kouttab, N., Myrick, D., Klostergaard, J., et al. (2000). Combined cytotoxic action of paclitaxel and ceramide against the human Tu138 head and neck squamous carcinoma cell line. Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology, 46, 85–92.
Senkal, C. E., Ponnusamy, S., Rossi, M. J., Sundararaj, K., Szulc, Z., Bielawski, J., et al. (2006). Potent antitumor activity of a novel cationic pyridinium-ceramide alone or in combination with gemcitabine against human head and neck squamous cell carcinomas in vitro and in vivo. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 317, 1188–1199.
Rossi, M. J., Sundararaj, K., Koybasi, S., Phillips, M. S., Szulc, Z. M., Bielawska, A., et al. (2005). Inhibition of growth and telomerase activity by novel cationic ceramide analogs with high solubility in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery, 132, 55–62.
Fujiwara, K., Kitatani, K., Fukushima, K., Yazama, H., Umehara, H., Kikuchi, M., et al. (2011). Inhibitory effects of dietary glucosylceramides on squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck in NOD/SCID mice. International Journal of Clinical Oncology, 16, 133–140.
Koybasi, S., Senkal, C. E., Sundararaj, K., Spassieva, S., Bielawski, J., Osta, W., et al. (2004). Defects in cell growth regulation by C18:0-ceramide and longevity assurance gene 1 in human head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 44311–44319.
Karahatay, S., Thomas, K., Koybasi, S., Senkal, C. E., Elojeimy, S., Liu, X., et al. (2007). Clinical relevance of ceramide metabolism in the pathogenesis of human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC): attenuation of C(18)-ceramide in HNSCC tumors correlates with lymphovascular invasion and nodal metastasis. Cancer Letters, 256, 101–111.
Senkal, C. E., Ponnusamy, S., Rossi, M. J., Bialewski, J., Sinha, D., Jiang, J. C., et al. (2007). Role of human longevity assurance gene 1 and C18-ceramide in chemotherapy-induced cell death in human head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, 6, 712–722.
Senkal, C. E., Ponnusamy, S., Bielawski, J., Hannun, Y. A., & Ogretmen, B. (2010). Antiapoptotic roles of ceramide-synthase-6-generated C16-ceramide via selective regulation of the ATF6/CHOP arm of ER-stress-response pathways. The FASEB Journal, 24, 296–308.
Shirai, K., Kaneshiro, T., Wada, M., Furuya, H., Bielawski, J., Hannun, Y. A., et al. (2011). A role of sphingosine kinase 1 in head and neck carcinogenesis. Cancer Prevention Research (Philadelphia, Pa.), 4, 454–462.
Kim, M. Y., Linardic, C., Obeid, L., & Hannun, Y. (1991). Identification of sphingomyelin turnover as an effector mechanism for the action of tumor necrosis factor alpha and gamma-interferon. Specific role in cell differentiation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 266, 484–489.
Baran, Y., Salas, A., Senkal, C. E., Gunduz, U., Bielawski, J., Obeid, L. M., et al. (2007). Alterations of ceramide/sphingosine 1-phosphate rheostat involved in the regulation of resistance to imatinib-induced apoptosis in K562 human chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 282, 10922–10934.
Li, Q. F., Wu, C. T., Guo, Q., Wang, H., & Wang, L. S. (2008). Sphingosine 1-phosphate induces Mcl-1 upregulation and protects multiple myeloma cells against apoptosis. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 371, 159–162.
Paugh, S. W., Paugh, B. S., Rahmani, M., Kapitonov, D., Almenara, J. A., Kordula, T., et al. (2008). A selective sphingosine kinase 1 inhibitor integrates multiple molecular therapeutic targets in human leukemia. Blood, 112, 1382–1391.
Prinetti, A., Basso, L., Appierto, V., Villani, M. G., Valsecchi, M., Loberto, N., et al. (2003). Altered sphingolipid metabolism in N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-retinamide-resistant A2780 human ovarian carcinoma cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 5574–5583.
Prinetti, A., Millimaggi, D., D’Ascenzo, S., Clarkson, M., Bettiga, A., Chigorno, V., et al. (2006). Lack of ceramide generation and altered sphingolipid composition are associated with drug resistance in human ovarian carcinoma cells. Biochemical Journal, 395, 311–318.
Devine, K. M., Smicun, Y., Hope, J. M., & Fishman, D. A. (2008). S1P induced changes in epithelial ovarian cancer proteolysis, invasion, and attachment are mediated by Gi and Rac. Gynecologic Oncology, 110, 237–245.
Smicun, Y., Reierstad, S., Wang, F. Q., Lee, C., & Fishman, D. A. (2006). S1P regulation of ovarian carcinoma invasiveness. Gynecologic Oncology, 103, 952–959.
Cakir, Z., Saydam, G., Sahin, F., & Baran, Y. (2011). The roles of bioactive sphingolipids in resveratrol-induced apoptosis in HL60: acute myeloid leukemia cells. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology, 137, 279–286.
Kurinna, S. M., Tsao, C. C., Nica, A. F., Jiffar, T., & Ruvolo, P. P. (2004). Ceramide promotes apoptosis in lung cancer-derived A549 cells by a mechanism involving c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase. Cancer Research, 64, 7852–7856.
Johnson, K. R., Johnson, K. Y., Crellin, H. G., Ogretmen, B., Boylan, A. M., Harley, R. A., et al. (2005). Immunohistochemical distribution of sphingosine kinase 1 in normal and tumor lung tissue. Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry, 53, 1159–1166.
Shida, D., Kitayama, J., Yamaguchi, H., Yamashita, H., Mori, K., Watanabe, T., et al. (2004). Sphingosine 1-phosphate transactivates c-Met as well as epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in human gastric cancer cells. FEBS Letters, 577, 333–338.
Van Brocklyn, J. R., Jackson, C. A., Pearl, D. K., Kotur, M. S., Snyder, P. J., & Prior, T. W. (2005). Sphingosine kinase-1 expression correlates with poor survival of patients with glioblastoma multiforme: roles of sphingosine kinase isoforms in growth of glioblastoma cell lines. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology, 64, 695–705.
Wu, W., Shu, X., Hovsepyan, H., Mosteller, R. D., & Broek, D. (2003). VEGF receptor expression and signaling in human bladder tumors. Oncogene, 22, 3361–3370.
Qiu, L., Zhou, C., Sun, Y., Di, W., Scheffler, E., Healey, S., et al. (2006). Paclitaxel and ceramide synergistically induce cell death with transient activation of EGFR and ERK pathway in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncology Reports, 16, 907–913.
Guillermet-Guibert, J., Davenne, L., Pchejetski, D., Saint-Laurent, N., Brizuela, L., Guilbeau-Frugier, C., et al. (2009). Targeting the sphingolipid metabolism to defeat pancreatic cancer cell resistance to the chemotherapeutic gemcitabine drug. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, 8, 809–820.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grants P01CA97132 and R01CA124687. We regret being unable to cite other important studies because of space limitations.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Furuya, H., Shimizu, Y. & Kawamori, T. Sphingolipids in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 30, 567–576 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-011-9304-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-011-9304-1