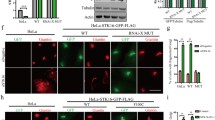
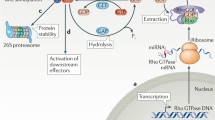
Abstract
DLC-1 was originally identified as a potential tumor suppressor. One of the key biochemical functions of DLC-1 is to serve as a GTPase activating protein (GAP) for members of the Rho family of GTPases, particularly Rho A-C and Cdc 42. Since these GTPases are critically involved in regulation of the cytoskeleton and cell migration, it seems clear that DLC-1 will also influence these processes. In this review we examine basic aspects of the actin cyoskeleton and how it relates to cell motility. We then delineate the characteristics of DLC-1 and other members of its family, and describe how they may have multiple effects on the regulation of cell polarity, actin organization, and cell migration.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang, J., & Weinberg, R. A. (2008). Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: at the crossroads of development and tumor metastasis. Developmental Cell, 14(6), 818–829.
Simpson, K. J., Selfors, L. M., Bui, J., Reynolds, A., Leake, D., Khvorova, A., et al. (2008). Identification of genes that regulate epithelial cell migration using an siRNA screening approach. Nature Cell Biology, [epub ahead of print] http://www.nature.com/ncb/journal/v10/n19/abs/ncb1762.html.
Vicente-Manzanares, M., Webb, D. J., & Horwitz, A. R. (2005). Cell migration at a glance. Journal of Cell Science, 118(Pt 21), 4917–4919.
Ridley, A. J., Schwartz, M. A., Burridge, K., Firtel, R. A., Ginsberg, M. H., Borisy, G., et al. (2003). Cell migration: integrating signals from front to back. Science, 302(5651), 1704–1709.
Berrier, A. L., & Yamada, K. M. (2007). Cell-matrix adhesion. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 213(3), 565–573.
Etienne-Manneville, S., & Hall, A. (2002). Rho GTPases in cell biology. Nature, 420(6916), 629–635.
Jaffe, A. B., & Hall, A. (2005). Rho GTPases: biochemistry and biology. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology, 21, 247–269.
Durkin, M. E., Yuan, B. Z., Zhou, X., Zimonjic, D. B., Lowy, D. R., Thorgeirsson, S. S., et al. (2007). DLC-1:a Rho GTPase-activating protein and tumour suppressor. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 11(5), 1185–1207.
Hynes, R. O. (2002). Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell, 110(6), 673–687.
Larsen, M., Artym, V. V., Green, J. A., & Yamada, K. M. (2006). The matrix reorganized: extracellular matrix remodeling and integrin signaling. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 18(5), 463–471.
Zaidel-Bar, R., Cohen, M., Addadi, L., & Geiger, B. (2004). Hierarchical assembly of cell-matrix adhesion complexes. Biochemical Society Transactions, 32(Pt3), 416–420.
Del Pozo, M. A., & Schwartz, M. A. (2007). Rac, membrane heterogeneity, caveolin and regulation of growth by integrins. Trends in Cell Biology, 17(5), 246–250.
Juliano, R. L., Reddig, P., Alahari, S., Edin, M., Howe, A., & Aplin, A. (2004). Integrin regulation of cell signalling and motility. Biochemical Society Transactions, 32(Pt3), 443–446.
Moissoglu, K., & Schwartz, M. A. (2006). Integrin signalling in directed cell migration. Biology of the Cell, 98(9), 547–555.
Ridley, A. J., & Hall, A. (2004). Snails, Swiss, and serum: the solution for Rac ‘n’ Rho. Cell, 116(2 Suppl), S23–25, 22 p following S25.
Wennerberg, K., & Der, C. J. (2004). Rho-family GTPases: it’s not only Rac and Rho (and I like it). Journal of Cell Science, 117(Pt 8), 1301–1312.
Burridge, K., & Wennerberg, K. (2004). Rho and Rac take center stage. Cell, 116(2), 167–179.
Nalbant, P., Hodgson, L., Kraynov, V., Toutchkine, A., & Hahn, K. M. (2004). Activation of endogenous Cdc42 visualized in living cells. Science, 305(5690), 1615–1619.
Pertz, O., Hodgson, L., Klemke, R. L., & Hahn, K. M. (2006). Spatiotemporal dynamics of RhoA activity in migrating cells. Nature, 440(7087), 1069–1072.
Weaver, A. M., Young, M. E., Lee, W. L., & Cooper, J. A. (2003). Integration of signals to the Arp2/3 complex. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 15(1), 23–30.
Bensenor, L. B., Kan, H. M., Wang, N., Wallrabe, H., Davidson, L. A., Cai, Y., et al. (2007). IQGAP1 regulates cell motility by linking growth factor signaling to actin assembly. Journal of Cell Science, 120(Pt 4), 658–669.
Huang, T. Y., DerMardirossian, C., & Bokoch, G. M. (2006). Cofilin phosphatases and regulation of actin dynamics. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 18(1), 26–31.
Yamaguchi, H., & Condeelis, J. (2007). Regulation of the actin cytoskeleton in cancer cell migration and invasion. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1773(5), 642–652.
Kumar, R., Gururaj, A. E., & Barnes, C. J. (2006). p21-activated kinases in cancer. Nature Reviews Cancer, 6(6), 459–471.
Cai, L., Marshall, T. W., Uetrecht, A. C., Schafer, D. A., & Bear, J. E. (2007). Coronin 1B coordinates Arp2/3 complex and cofilin activities at the leading edge. Cell, 128(5), 915–929.
Krause, M., Dent, E. W., Bear, J. E., Loureiro, J. J., & Gertler, F. B. (2003). Ena/VASP proteins: regulators of the actin cytoskeleton and cell migration. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology, 19, 541–564.
Fukata, Y., Amano, M., & Kaibuchi, K. (2001). Rho-Rho-kinase pathway in smooth muscle contraction and cytoskeletal reorganization of non-muscle cells. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 22(1), 32–39.
Pellegrin, S., & Mellor, H. (2007). Actin stress fibres. Journal of Cell Science, 120(Pt 20), 3491–3499.
Watanabe, N., & Higashida, C. (2004). Formins: processive cappers of growing actin filaments. Experimental Cell Research, 301(1), 16–22.
Nayal, A., Webb, D. J., Brown, C. M., Schaefer, E. M., Vicente-Manzanares, M., & Horwitz, A. R. (2006). Paxillin phosphorylation at Ser273 localizes a GIT1-PIX-PAK complex and regulates adhesion and protrusion dynamics. Journal of Cell Biology, 173(4), 587–589.
Nishiya, N., Kiosses, W. B., Han, J., & Ginsberg, M. H. (2005). An alpha4 integrin-paxillin-Arf-GAP complex restricts Rac activation to the leading edge of migrating cells. Nature Cell Biology, 7(4), 343–352.
Dow, L. E., & Humbert, P. O. (2007). Polarity regulators and the control of epithelial architecture, cell migration, and tumorigenesis. International Review of Cytology, 262, 253–302.
Myers, K. R., & Casanova, J. E. (2008). Regulation of actin cytoskeleton dynamics by Arf-family GTPases. Trends in Cell Biology, 18(4), 184–192.
Balasubramanian, N., Scott, D. W., Castle, J. D., Casanova, J. E., & Schwartz, M. A. (2007). Arf6 and microtubules in adhesion-dependent trafficking of lipid rafts. Nature Cell Biology, 9(12), 1381–1391.
Palamidessi, A., Frittoli, E., Garre, M., Faretta, M., Mione, M., Testa, I., et al. (2008). Endocytic trafficking of Rac is required for the spatial restriction of signaling in cell migration. Cell, 134(1), 135–147.
Bos, J. L., Rehmann, H., & Wittinghofer, A. (2007). GEFs and GAPs: critical elements in the control of small G proteins. Cell, 129(5), 865–877.
Rossman, K. L., Der, C. J., & Sondek, J. (2005). GEF means go: turning on RHO GTPases with guanine nucleotide-exchange factors. Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology, 6(2), 167–180.
Bernards, A., & Settleman, J. (2004). GAP control: regulating the regulators of small GTPases. Trends in Cell Biology, 14(7), 377–385.
Tcherkezian, J., & Lamarche-Vane, N. (2007). Current knowledge of the large RhoGAP family of proteins. Biology of the Cell, 99(2), 67–86.
Kandpal, R. P. (2006). Rho GTPase activating proteins in cancer phenotypes. Current Protein & Peptide Science, 7(4), 355–365.
Chang, J. H., Gill, S., Settleman, J., & Parsons, S. J. (1995). c-Src regulates the simultaneous rearrangement of actin cytoskeleton, p190RhoGAP, and p120RasGAP following epidermal growth factor stimulation. Journal of Cell Biology, 130(2), 355–368.
Xue, W., Krasnitz, A., Lucito, R., Sordella, R., Vanaelst, L., Cordon-Cardo, C., et al. (2008). DLC1 is a chromosome 8p tumor suppressor whose loss promotes hepatocellular carcinoma. Genes & Development, 22(11), 1439–1444.
Sjoblom, T., Jones, S., Wood, L. D., Parsons, D. W., Lin, J., Barber, T. D., et al. (2006). The consensus coding sequences of human breast and colorectal cancers. Science, 314(5797), 268–274.
Jones, S., Zhang, X., Parsons, D. W., Lin, J. C., Leary, R. J., Angenendt, P., et al. (2008). Core signaling pathways in human pancreatic cancers revealed by global genomic analyses. Science, 321(5897), 1801–1806.
Yuan, B. Z., Jefferson, A. M., Baldwin, K. T., Thorgeirsson, S. S., Popescu, N. C., & Reynolds, S. H. (2004). DLC-1 operates as a tumor suppressor gene in human non-small cell lung carcinomas. Oncogene, 23(7), 1405–1411.
Yuan, B. Z., Zhou, X., Durkin, M. E., Zimonjic, D. B., Gumundsdottir, K., Eyfjord, J. E., et al. (2003). DLC-1 gene inhibits human breast cancer cell growth and in vivo tumorigenicity. Oncogene, 22(3), 445–450.
Zhou, X., Thorgeirsson, S. S., & Popescu, N. C. (2004). Restoration of DLC-1 gene expression induces apoptosis and inhibits both cell growth and tumorigenicity in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncogene, 23(6), 1308–1313.
Healy, K. D., Hodgson, L., Kim, T. Y., Shutes, A., Maddileti, S., Juliano, R. L., et al. (2008). DLC-1 suppresses non-small cell lung cancer growth and invasion by RhoGAP-dependent and independent mechanisms. Molecular Carcinogenesis, 47(5), 326–337.
Li, H., Fung, K. L., Jin, D. Y., Chung, S. S., Ching, Y. P., Ng, I. O., et al. (2007). Solution structures, dynamics, and lipid-binding of the sterile alpha-motif domain of the deleted in liver cancer 2. Proteins, 67(4), 1154–1166.
Kim, T. Y., Healy, K. D., Der, C. J., Sciaky, N., Bang, Y. J., Juliano, R. L. (2008). Effects of structure of Rho GTPase-activating protein DLC-1 on cell morphology and migration. Journal of Biological Chemistry, [epub ahead of print] http://www.jbc.org/cgi/reprint/M800617200v800617201.
Liao, Y. C., Si, L., deVere White, R. W., & Lo, S. H. (2007). The phosphotyrosine-independent interaction of DLC-1 and the SH2 domain of cten regulates focal adhesion localization and growth suppression activity of DLC-1. Journal of Cell Biology, 176(1), 43–49.
Qian, X., Li, G., Asmussen, H. K., Asnaghi, L., Vass, W. C., Braverman, R., et al. (2007). Oncogenic inhibition by a deleted in liver cancer gene requires cooperation between tensin binding and Rho-specific GTPase-activating protein activities. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104(21), 9012–9017.
Gay, N. J., & Keith, F. J. (1991). Drosophila Toll and IL-1 receptor. Nature, 351(6325), 355–356.
Zhou, X., Zimonjic, D. B., Park, S. W., Yang, X. Y., Durkin, M. E., & Popescu, N. C. (2008). DLC1 suppresses distant dissemination of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells in nude mice through reduction of RhoA GTPase activity, actin cytoskeletal disruption and down-regulation of genes involved in metastasis. International Journal of Oncology, 32(6), 1285–1291.
Kang, Y., Siegel, P. M., Shu, W., Drobnjak, M., Kakonen, S. M., Cordon-Cardo, C., et al. (2003). A multigenic program mediating breast cancer metastasis to bone. Cancer Cell, 3(6), 537–549.
Kim, T. Y., Lee, J. W., Kim, H. P., Jong, H. S., Kim, T. Y., Jung, M., et al. (2007). DLC-1, a GTPase-activating protein for Rho, is associated with cell proliferation, morphology, and migration in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 355(1), 72–77.
Syed, V., Mukherjee, K., Lyons-Weiler, J., Lau, K. M., Mashima, T., Tsuruo, T., et al. (2005). Identification of ATF-3, caveolin-1, DLC-1, and NM23-H2 as putative antitumorigenic, progesterone-regulated genes for ovarian cancer cells by gene profiling. Oncogene, 24(10), 1774–1787.
Wong, C. M., Yam, J. W., Ching, Y. P., Yau, T. O., Leung, T. H., Jin, D. Y., et al. (2005). Rho GTPase-activating protein deleted in liver cancer suppresses cell proliferation and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Research, 65(19), 8861–8868.
Euer, N., Schwirzke, M., Evtimova, V., Burtscher, H., Jarsch, M., Tarin, D., et al. (2002). Identification of genes associated with metastasis of mammary carcinoma in metastatic versus non-metastatic cell lines. Anticancer Research, 22(2A), 733–740.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, T.Y., Vigil, D., Der, C.J. et al. Role of DLC-1, a tumor suppressor protein with RhoGAP activity, in regulation of the cytoskeleton and cell motility. Cancer Metastasis Rev 28, 77–83 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-008-9167-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-008-9167-2