Abstract
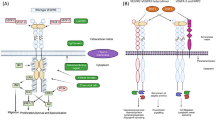
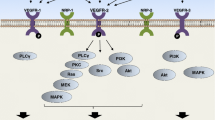
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) has been shown to be the major mediator of physiologic and pathologic angiogenesis. VEGF was initially thought to be an endothelial cell specific ligand, but recently, VEGF has been shown to mediate tumor cell function via activation of receptors on tumor cells themselves. Here, we review the expression patterns and binding profiles of the VEGF receptors and their ligands on gastrointestinal tumor cells. Furthermore, we describe the current knowledge in regards to the function of these receptors on tumor cells. Elucidating the function of VEGF receptors on tumor cells should help us to better understand the potential mechanisms of action of anti-VEGF therapies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Folkman, J., & Shing, Y. (1992). Angiogenesis. Journal of Bioliological Chemistry, 267, 10931–0934.
Hanahan, D., & Folkman, J. (1996). Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell, 86, 353–64.
Reinmuth, N., Parikh, A. A., Ahmad, S. A., Liu, W., Stoeltzing, O., Fan, F., et al. (2003). Biology of angiogenesis in tumors of the gastrointestinal tract. Microscopy Research and Technique, 60, 199–07.
Roy, H., Bhardwaj, S., & Yla-Herttuala, S. (2006). Biology of vascular endothelial growth factors. FEBS Letters, 580, 2879–887.
Yamazaki, Y., & Morita, T. (2006). Molecular and functional diversity of vascular endothelial growth factors. Molecular Diversity, 10, 515–27.
Wei, S. C., Tsao, P. N., Yu, S. C., Shun, C. T., Tsai-Wu, J. J., Wu, C. H., et al. (2005). Placenta growth factor expression is correlated with survival of patients with colorectal cancer. Gut, 54, 666–72.
Xu, L., Cochran, D. M., Tong, R. T., Winkler, F., Kashiwagi, S., Jain, R. K., et al. (2006). Placenta growth factor overexpression inhibits tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis by depleting vascular endothelial growth factor homodimers in orthotopic mouse models. Cancer Research, 66, 3971–977.
Autiero, M., Waltenberger, J., Communi, D., Kranz, A., Moons, L., Lambrechts, D., et al. (2003). Role of PlGF in the intra- and intermolecular cross talk between the VEGF receptors Flt1 and Flk1. Nature Medicine, 9, 936–43.
Ellis, L. M., Rosen, L., & Gordon, M. S. (2006). Overview of anti-VEGF therapy and angiogenesis. Part 1: Angiogenesis inhibition in solid tumor malignancies. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol 4: suppl 1–0.
Kawaguchi, M., Akagi, M., Gray, M. J., Liu, W., Fan, F., & Ellis, L. M. (2004). Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in human gastric cancer cells by interleukin-1beta. Surgery, 136, 686–92.
Karkkainen, M. J., Haiko, P., Sainio, K., Partanen, J., Taipale, J., Petrova, T. V., et al. (2004). Vascular endothelial growth factor C is required for sprouting of the first lymphatic vessels from embryonic veins [see comment]. Nature Immunology, 5, 74–0.
Ferrara, N., Gerber, H. P., & LeCouter, J. (2003). The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nature Medicine, 9, 669–76.
Nash, A. D., Baca, M., Wright, C., & Scotney, P. D. (2006). The biology of vascular endothelial growth factor-B (VEGF-B). Pulmonary Pharmacology Therapeuthics, 19, 61–9.
Olofsson, B., Jeltsch, M., Eriksson, U., & Alitalo, K. (1999). Current biology of VEGF-B and VEGF-C. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 10, 528–35.
Bellomo, D., Headrick, J. P., Silins, G. U., Paterson, C. A., Thomas, P. S., Gartside, M., et al. (2000). Mice lacking the vascular endothelial growth factor-B gene (Vegfb) have smaller hearts, dysfunctional coronary vasculature, and impaired recovery from cardiac ischemia. Circulation Research, 86, E29’E35.
Hicklin, D. J., & Ellis, L. M. (2005). Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and angiogenesis. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 23, 1011–027.
Achen, M. G., Mann, G. B., & Stacker, S. A. (2006). Targeting lymphangiogenesis to prevent tumour metastasis. British Journal of Cancer, 94, 1355–360.
Jia, H., Bagherzadeh, A., Bicknell, R., Duchen, M. R., Liu, D., & Zachary, I. (2004). Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-D and VEGF-A differentially regulate KDR-mediated signaling and biological function in vascular endothelial cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 36148–6157.
Wise, L. M., Ueda, N., Dryden, N. H., Fleming, S. B., Caesar, C., Roufail, S., et al. (2003). Viral vascular endothelial growth factors vary extensively in amino acid sequence, receptor-binding specificities, and the ability to induce vascular permeability yet are uniformly active mitogens. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 38004–8014.
Chen, C. N., Hsieh, F. J., Cheng, Y. M., Cheng, W. F., Su, Y. N., Chang, K. J., et al. (2004). The significance of placenta growth factor in angiogenesis and clinical outcome of human gastric cancer. Cancer Letter, 213, 73–2.
Parr, C., Watkins, G., Boulton, M., Cai, J., & Jiang, W. G. (2005). Placenta growth factor is over-expressed and has prognostic value in human breast cancer. European Journal of Cancer, 41, 2819–827.
Zhang, Z., Chen, J., Yang, K., Mansel, R. E., & Jiang, W. G. (2005). Expression of placenta growth factor (PlGF) in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and the clinical prognostic significance. World Journal of Surgical Oncology, 3, 68–9.
Cao, Y., Ji, W. R., Qi, P., Rosin, A., & Cao, Y. (1997). Placenta growth factor: Identification and characterization of a novel isoform generated by RNA alternative splicing. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 235, 493–98.
Tjwa, M., Luttun, A., Autiero, M., & Carmeliet, P. (2003). VEGF and PlGF: Two pleiotropic growth factors with distinct roles in development and homeostasis. Cell & Tissue Research, 314, 5–4.
Eriksson, A., Cao, R., Pawliuk, R., Berg, S. M., Tsang, M., Zhou, D., et al. (2002). Placenta growth factor-1 antagonizes VEGF-induced angiogenesis and tumor growth by the formation of functionally inactive PlGF-1/VEGF heterodimers. Cancer Cell, 1, 99–08.
Adini, A., Kornaga, T., Firoozbakht, F., & Benjamin, L. E. (2002). Placental growth factor is a survival factor for tumor endothelial cells and macrophages. Cancer Research, 62, 2749–752.
Li, B., Sharpe, E. E., Maupin, A. B., Teleron, A. A., Pyle, A. L., Carmeliet, P., et al. (2006). VEGF and PlGF promote adult vasculogenesis by enhancing EPC recruitment and vessel formation at the site of tumor neovascularization. FASEB Journal, 20, 1495–497.
Luttun, A., Autiero, M., Tjwa, M., & Carmeliet, P. (2004). Genetic dissection of tumor angiogenesis: Are PlGF and VEGFR-1 novel anti-cancer targets? Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1654, 79–4.
Robinson, C. J., Johnson, D. D., Chang, E. Y., Armstrong, D. M., & Wang, W. (2006). Evaluation of placenta growth factor and soluble Fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 receptor levels in mild and severe preeclampsia. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 195, 255–59.
Wey, J. S., Stoeltzing, O., & Ellis, L. M. (2004). Vascular endothelial growth factor receptors: Expression and function in solid tumors. Clinical Advances in Hematology and Oncology, 2, 37–5.
Ishida, A., Murray, J., Saito, Y., Kanthou, C., Benzakour, O., Shibuya, M., et al. (2001). Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors in smooth muscle cells. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 188, 359–68.
von Marschall, Z., Cramer, T., Hocker, M., Burde, R., Plath, T., Schirner, M., et al. (2000). De novo expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human pancreatic cancer: Evidence for an autocrine mitogenic loop. Gastroenterology, 119, 1358–372.
Buchler, P., Reber, H. A., Buchler, M. W., Friess, H., & Hines, O. J. (2002). VEGF-RII influences the prognosis of pancreatic cancer. Annals of Surgery, 236, 738–49; discussion 749.
Zhang, H., Wu, J., Meng, L., & Shou, C. C. (2002). Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors KDR and Flt-1 in gastric cancer cells. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 8, 994–98.
Tian, X., Song, S., Wu, J., Meng, L., Dong, Z., & Shou, C. (2001). Vascular endothelial growth factor: Acting as an autocrine growth factor for human gastric adenocarcinoma cell MGC803. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 286, 505–12.
Paavonen, K., Puolakkainen, P., Jussila, L., Jahkola, T., & Alitalo, K. (2000). Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 in lymphangiogenesis in wound healing. American Journal of Pathology, 156, 1499–504.
Valtola, R., Salven, P., Heikkila, P., Taipale, J., Joensuu, H., Rehn, M., et al. (1999). VEGFR-3 and its ligand VEGF-C are associated with angiogenesis in breast cancer. American Journal of Pathology, 154, 1381–390.
Ellis, L. M. (2006). The role of neuropilins in cancer. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, 5, 1099–107.
Yuan, L., Moyon, D., Pardanaud, L., Breant, C., Karkkainen, M. J., Alitalo, K., et al. (2002). Abnormal lymphatic vessel development in neuropilin 2 mutant mice. Development, 129, 4797–806.
Parikh, A. A., Fan, F., Liu, W. B., Ahmad, S. A., Stoeltzing, O., Reinmuth, N., et al. (2004). Neuropilin-1 in human colon cancer: expression, regulation, and role in induction of angiogenesis. American Journal of Pathology, 164, 2139–151.
de Paulis, A., Prevete, N., Fiorentino, I., Rossi, F. W., Staibano, S., Montuori, N., et al. (2006). Expression and functions of the vascular endothelial growth factors and their receptors in human basophils. Journal of Immunology, 177, 7322–331.
Stephenson, J. M., Banerjee, S., Saxena, N. K., Cherian, R., & Banerjee, S. K. (2002). Neuropilin-1 is differentially expressed in myoepithelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells in preneoplastic and neoplastic human breast: A possible marker for the progression of breast cancer. International Journal of Cancer, 101, 409–14.
Soker, S., Gollamudi-Payne, S., Fidder, H., Charmahelli, H., & Klagsbrun, M. (1997). Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced endothelial cell proliferation by a peptide corresponding to the exon 7-encoded domain of VEGF165. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 272, 31582–1588.
Soker, S., Takashima, S., Miao, H. Q., Neufeld, G., & Klagsbrun, M. (1998). Neuropilin-1 is expressed by endothelial and tumor cells as an isoform-specific receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor. Cell, 92, 735–45.
Miao, H. Q., Lee, P., Lin, H., Soker, S., & Klagsbrun, M. (2000). Neuropilin-1 expression by tumor cells promotes tumor angiogenesis and progression. FASEB Journal, 14, 2532–539.
Kawakami, T., Tokunaga, T., Hatanaka, H., Kijima, H., Yamazaki, H., Abe, Y., et al. (2002). Neuropilin 1 and neuropilin 2 co-expression is significantly correlated with increased vascularity and poor prognosis in nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer, 95, 2196–201.
Hansel, D. E., Wilentz, R. E., Yeo, C. J., Schulick, R. D., Montgomery, E., & Maitra, A. (2004). Expression of neuropilin-1 in high-grade dysplasia, invasive cancer, and metastases of the human gastrointestinal tract. American Journal of Surgical Pathology, 28, 347–56.
Gray, M. J., Wey, J. S., Belcheva, A., McCarty, M. F., Trevino, J. G., Evans, D. B., et al. (2005). Neuropilin-1 suppresses tumorigenic properties in a human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell line lacking neuropilin-1 coreceptors. Cancer Research, 65, 3664–670.
Fukahi, K., Fukasawa, M., Neufeld, G., Itakura, J., & Korc, M. (2004). Aberrant expression of neuropilin-1 and -2 in human pancreatic cancer cells. Clinical Cancer Research, 10, 581–90.
Fakhari, M., Pullirsch, D., Abraham, D., Paya, K., Hofbauer, R., Holzfeind, P., et al. (2002). Selective upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors neuropilin-1 and -2 in human neuroblastoma. Cancer, 94, 258–63
Cohen, T., Herzog, Y., Brodzky, A., Greenson, J. K., Eldar, S., Gluzman-Poltorak, Z., et al. (2002). Neuropilin-2 is a novel marker expressed in pancreatic islet cells and endocrine pancreatic tumours. Journal of Pathology, 198, 77–2.
Bachelder, R. E., Lipscomb, E. A., Lin, X., Wendt, M. A., Chadborn, N. H., Eickholt, B. J., et al. (2003). Competing autocrine pathways involving alternative neuropilin-1 ligands regulate chemotaxis of carcinoma cells. Cancer Research, 63, 5230–233.
Wey, J. S., Gray, M. J., Fan, F., Belcheva, A., McCarty, M. F., Stoeltzing, O., et al. (2005). Overexpression of neuropilin-1 promotes constitutive MAPK signalling and chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer cells. British Journal of Cancer, 93, 233–41.
Kusters, B., de Waal, R. M., Wesseling, P., Verrijp, K., Maass, C., Heerschap, A., et al. (2003). Differential effects of vascular endothelial growth factor A isoforms in a mouse brain metastasis model of human melanoma. Cancer Research, 63, 5408–413.
Karpanen, T., Heckman, C. A., Keskitalo, S., Jeltsch, M., Ollila, H., Neufeld, G., et al. (2006). Functional interaction of VEGF-C and VEGF-D with neuropilin receptors. FASEB Journal, 20, 1462–472.
Cai, H., & Reed, R. R. (1999). Cloning and characterization of neuropilin-1-interacting protein: A PSD-95/Dlg/ZO-1 domain-containing protein that interacts with the cytoplasmic domain of neuropilin-1. Journal Neuroscience, 19, 6519–527.
Fan, F., Wey, J. S., McCarty, M. F., Belcheva, A., Liu, W., Bauer, T. W., et al. (2005). Expression and function of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 on human colorectal cancer cells. Oncogene, 24, 2647–653.
Lesslie, D. P., Summy, J. M., Parikh, N. U., Fan, F., Trevino, J. G., Sawyer, T. K., et al. (2006). Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 mediates migration of human colorectal carcinoma cells by activation of Src family kinases. British Journal of Cancer, 94, 1710–717.
Bates, R. C., Goldsmith, J. D., Bachelder, R. E., Brown, C., Shibuya, M., Oettgen, P., et al. (2003). Flt-1-dependent survival characterizes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of colonic organoids. Current Biology, 13, 1721–727.
Yang, A. D., Camp, E. R., Fan, F., Shen, L., Gray, M. J., Liu, W., et al. (2006). Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 activation mediates epithelial to mesenchymal transition in human pancreatic carcinoma cells. Cancer Research, 66, 46–1.
Wey, J. S., Fan, F., Gray, M. J., Bauer, T. W., McCarty, M. F., Somcio, R., et al. (2005) Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 promotes migration and invasion in pancreatic carcinoma cell lines. Cancer, 104, 427–38.
Akagi, M., Kawaguchi, M., Liu, W., McCarty, M. F., Takeda, A., Fan, F., et al. (2003). Induction of neuropilin-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor by epidermal growth factor in human gastric cancer cells. British Journal of Cancer, 88, 796–02.
Duff, S. E., Jeziorska, M., Rosa, D. D., Kumar, S., Haboubi, N., Sherlock, D., et al. (2006). Vascular endothelial growth factors and receptors in colorectal cancer: Implications for anti-angiogenic therapy. European Journal of Cancer, 42, 112–17.
Li, M., Yang, H., Chai, H., Fisher, W. E., Wang, X., Brunicardi, F. C., et al. (2004). Pancreatic carcinoma cells express neuropilins and vascular endothelial growth factor, but not vascular endothelial growth factor receptors. Cancer, 101, 2341–350.
Mulkeen, A. L., Silva, T., Yoo, P. S., Schmitz, J. C., Uchio, E., Chu, E., et al. (2006). Short interfering RNA-mediated gene silencing of vascular endothelial growth factor: Effects on cellular proliferation in colon cancer cells. Archives of Surgery, 141, 367–74; discussion 374.
Bruns, C. J., Liu, W., Davis, D. W., Shaheen, R. M., McConkey, D. J., Wilson, M. R., et al. (2000). Vascular endothelial growth factor is an in vivo survival factor for tumor endothelium in a murine model of colorectal carcinoma liver metastases. Cancer, 89, 488–99.
Miao, H. Q., & Klagsbrun, M. (2000). Neuropilin is a mediator of angiogenesis. Cancer Metastasis Reviews, 19, 29–7.
Soker, S., Miao, H. Q., Nomi, M., Takashima, S., & Klagsbrun, M. (2002). VEGF165 mediates formation of complexes containing VEGFR-2 and neuropilin-1 that enhance VEGF165-receptor binding. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 85, 357–68.
Chung, G. G., Yoon, H. H., Zerkowski, M. P., Ghosh, S., Thomas, L., Harigopal, M., et al. (2006). Vascular endothelial growth factor, FLT-1, and FLK-1 analysis in a pancreatic cancer tissue microarray. Cancer, 106, 1677–684.
Parikh, A. A., Liu, W. B., Fan, F., Stoeltzing, O., Reinmuth, N., Bruns, C. J., et al. (2003). Expression and regulation of the novel vascular endothelial growth factor receptor neuropilin-1 by epidermal growth factor in human pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer, 98, 720–29.
Maeda, K., Chung, Y. S., Ogawa, Y., Takatsuka, S., Kang, S. M., Ogawa, M., et al. (1996). Prognostic value of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in gastric carcinoma. Cancer, 77, 858–63.
Kido, S., Kitadai, Y., Hattori, N., Haruma, K., Kido, T., Ohta, M., et al. (2001). Interleukin 8 and vascular endothelial growth factor—prognostic factors in human gastric carcinomas? European Journal of Cancer, 37, 1482–487.
Terris, B., Scoazec, J. Y., Rubbia, L., Bregeaud, L., Pepper, M. S., Ruszniewski, P., et al. (1998). Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in digestive neuroendocrine tumours. Histopathology, 32, 133–38.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dallas, N.A., Fan, F., Gray, M.J. et al. Functional significance of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors on gastrointestinal cancer cells. Cancer Metastasis Rev 26, 433–441 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-007-9070-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-007-9070-2