Abstract
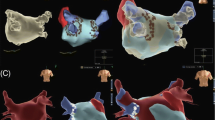
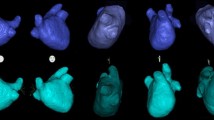
A new method in creating 3D models of the left atrium (LA) and esophagus before catheter ablation of atrial arrhythmias is 3D rotational angiography (3DRA) of the LA. The purpose of this retrospective study was to test various acquisition protocols of the 3DRA and attempt to define the parameters influencing the success of the protocols. From August 2010 to November 2014, 3DRA of the LA using the Philips Allura FD 10 X-ray system was performed in 547 consecutive patients using right atrial and left atrial protocols. Visualization of the esophagus was performed after oral administration of a contrast agent. Patients were monitored for success (creation of a useful 3D models) and evaluated for a number of parameters affecting the success of 3DRA. The success of the RA protocol was 88.89 % with and 91.91 % without esophagus imaging. The success of the LA protocol was 97.42 % with and 94.54 % without esophagus imaging. The only factor reducing the success of the RA protocol was BMI; the LA protocol was not influenced by any factor. Ventricular fibrillation induced in two patients was successfully treated with defibrillation. 3DRA of the LA is a reliable method that supports catheter ablation of complex atrial arrhythmias. The LA protocol with esophagus imaging was significantly more reliable than the RA protocol; the other protocols were comparable. The RA protocol may be negatively affected by high BMI. Simultaneous imaging of the esophagus is safe and feasible, and the LA protocol can be recommended.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calkins H, Kuck KH, Cappato R et al (2012) 2012 HRS/EHRA/ECAS expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation: recommendations for patient selection, procedural techniques, patient management and follow-up, definitions, endpoints, and research trial design. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 33:171–257
Jongbloed MR, Bax JJ, Lamb HJ, Dirksen MS, Zeppenfeld K, van der Wall EE, de Roos A, Schalij MJ (2005) Multislice computed tomography versus intracardiac echocardiography to evaluate the pulmonary veins before radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: a head-to-head comparison. J Am Coll Cardiol 45:343–350
Malchano ZJ, Neuzil P, Cury RC, Holmvang G, Weichet J, Schmidt EJ, Ruskin JN, Reddy VY (2006) Integration of cardiac CT/MR imaging with three-dimensional electroanatomical mapping to guide catheter manipulation in the left atrium: implications for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 17:1221–1229
Orlov MV, Hoffmeister P, Chaudhry GM, Almasry I, Gijsbers GH, Swack T, Haffajee CI (2007) Three-dimensional rotational angiography of the left atrium and esophagus—a virtual computed tomography scan in the electrophysiology lab? Heart Rhythm 4:37–43
Nölker G, Gutleben KJ, Marschang H, Ritscher G, Asbach S, Marrouche N, Brachmann J, Sinha AM (2008) Three-dimensional left atrial and esophagus reconstruction using cardiac C-arm computed tomography with image integration into fluoroscopic views for ablation of atrial fibrillation: accuracy of a novel modality in comparison with multislice computed tomo. Heart Rhythm 5:1651–1657
Thiagalingam A, Manzke R, D’Avila A, Ho I, Locke AH, Ruskin JN, Chan RC, Reddy VY (2008) Intraprocedural volume imaging of the left atrium and pulmonary veins with rotational X-ray angiography: implications for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 19:293–300
Li JH, Haim M, Movassaghi B, Mendel JB, Chaudhry GM, Haffajee CI, Orlov MV (2009) Segmentation and registration of three-dimensional rotational angiogram on live fluoroscopy to guide atrial fibrillation ablation: a new online imaging tool. Heart Rhythm 6:231–237
Cappato R, Calkins H, Chen SA, Davies W, Iesaka Y, Kalman J, Kim YH, Klein G, Natale A, Packer D, Skanes A, Ambrogi F, Biganzoli E (2010) Updated worldwide survey on the methods, efficacy, and safety of catheter ablation for human atrial fibrillation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 3:32–38
Carpen M, Matkins J, Syros G, Gorev MV, Alikhani Z, Wylie JV, Natan SR, Griben A, Hicks A, Armstrong J, Orlov MV (2013) First experience of 3D rotational angiography fusion with NavX electroanatomical mapping to guide catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 10:422–427
Einstein AJ, Moser KW, Thompson RC, Cerqueira MD, Henzlova MJ (2007) Radiation dose to patients from cardiac diagnostic imaging. Circulation 116:1290–1305
Tang M, Kriatselis C, Ye G, Nedios S, Roser M, Solowjowa N, Fleck E, Gerds-Li JH (2009) Reconstructing and registering three-dimensional rotational angiogram of left atrium during ablation of atrial fibrillation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 32:1407–1416
Kriatselis C, Tang M, Nedios S, Roser M, Gerds-Li H, Fleck E (2009) Intraprocedural reconstruction of the left atrium and pulmonary veins as a single navigation tool for ablation of atrial fibrillation: a feasibility, efficacy, and safety study. Heart Rhythm 6:733–741
Dong J, Calkins H, Solomon SB, Lai S, Dalal D, Lardo AC, Brem E, Preiss A, Berger RD, Halperin H, Dickfeld T (2006) Integrated electroanatomic mapping with three-dimensional computed tomographic images for real-time guided ablations. Circulation 113:186–194
Kriatselis C, Tang M, Roser M, Fleck E, Gerds-Li H (2009) A new approach for contrast-enhanced X-ray imaging of the left atrium and pulmonary veins for atrial fibrillation ablation: rotational angiography during adenosine-induced asystole. Europace 11:35–41
Kriatselis C, Nedios S, Akrivakis S, Tang M, Roser M, Gerds-Li JH, Fleck E, Orlov M (2011) Intraprocedural imaging of left atrium and pulmonary veins: a comparison study between rotational angiography and cardiac computed tomography. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 34:315–322
Thorning C, Hamady M, Liaw JV, Juli C, Lim PB, Dhawan R, Peters NS, Davies DW, Kanagaratnam P, O’Neill MD, Wright AR (2011) CT evaluation of pulmonary venous anatomy variation in patients undergoing catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. Clin Imaging 35:1–9
Yang L, Xu L, Yan Z, Yu W, Fan Z, Lv B, Zhang Z (2012) Low dose 320-row CT for left atrium and pulmonary veins imaging–the feasibility study. Eur J Radiol 81:1549–1554
Lehar F, Starek Z, Jez J, Novak M, Wolf J, Stepanova R, Kruzliak P, Kulik T, Zbankova A, Jancar R, Vitovec J (2015) Comparison of clinical outcomes and safety of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation supported by data from CT scan or three-dimensional rotational angiogram of left atrium and pulmonary veins. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub 159:622–628
Knecht S, Wright M, Akrivakis S, Nault I, Matsuo S, Chaudhry GM, Haffajee C, Sacher F, Lellouche N, Miyazaki S, Forclaz A, Jadidi AS, Hocini M, Ritter P, Clementy J, Haïssaguerre M, Orlov M, Jaïs P (2010) Prospective randomized comparison between the conventional electroanatomical system and three-dimensional rotational angiography during catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 7:459–465
Funding
This study was funded by a Grant of the European Regional Development Fund—Project FNUSA-ICRC (No. CZ.1.05/1.1.00/02.0123) and Masaryk University, Faculty of Medicine, Kamenice 5, 625 00 Brno, Czech Republic.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This retrospective study received approval from the ethics committee of our institution. Informed consent was not necessary because the current study was retrospective in nature and retrospectively processed common clinical data.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Starek, Z., Lehar, F., Jez, J. et al. Periprocedural 3D imaging of the left atrium and esophagus: comparison of different protocols of 3D rotational angiography of the left atrium and esophagus in group of 547 consecutive patients undergoing catheter ablation of the complex atrial arrhythmias. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 32, 1011–1019 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-016-0888-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-016-0888-y