Abstract
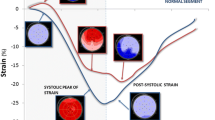
Microvascular obstruction (MVO) and transmural infarct size are prognostic factors after acute myocardial infarction (AMI). We assessed the value of myocardial deformation patterns using 3D speckle tracking imaging (3DSTI) in detecting myocardial and microvascular damage after AMI. One hundred patients with first ST-segment elevation MI from the REMI Study were prospectively included. Transthoracic echocardiography with 3DSTI and CMR were performed within 72 h after revascularization therapy. Global (3DG) and segmental (3DS) values of LV longitudinal (LS), circumferential and radial area strain were obtained. Late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) and MVO was quantified as transmural (>50 %) or non-transmural (<50 %). Predictive performance was assessed by area under the receiver operating curve characteristic (AUC). Mean LVEFCMR was 45.8 ± 9.2 % with 22.2 ± 12.7 % transmural LGE. MVO was present in 55 patients (MVO transmural extent 11.4 ± 11.8 %). In global analysis, all 3DG strain values were correlated with LVEFCMR and infarct size, with the best correlation obtained for 3DGAS (r = −0.678; p < 0.0001). All 3DG strain values, with the exception of LS, were significantly different between patients with and without MVO. In segmental analysis, all 3DS strain values were significantly lower in transmurally infarcted segments than in non-infarcted segments, and all 3DS values except 3DSRS were significantly lower in non-transmural infarcted segments than in non-infarcted segments. The best 3DS strain for detecting non-viable segments with MVO (MVO > 75 %) was 3DSAS [AUC 0.867 (0.849–0.884), 78.0 % sensitivity and 81.1 % specificity for 3DSAS = −16.1 %]. Importantly, 3DSRS and 3DSAS were associated with an increase in diagnostic accuracy of both transmural LGE and MVO over 3DSLS (all increase in AUC > 0.04, all p < 0.01). The newly developed 3DSTI, especially 3DSAS, is a sensitive and reproducible tool to predict and quantify the transmural extent of scar. This new early imaging strategy improve the prediction of MVO while enabling to assess the success of reperfusion and the risk of late systolic remodeling in STEMI.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sanz G, Castañer A, Betriu A, Magriña J, Roig E, Coll S et al (1982) Determinants of prognosis in survivors of myocardial infarction: a prospective clinical angiographic study. N Engl J Med 306(18):1065–1070
Pride YB, Appelbaum E, Lord EE, Sloan S, Cannon CP, Sabatine MS et al (2009) Relation between myocardial infarct size and ventricular tachyarrhythmia among patients with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction following fibrinolytic therapy for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol 104(4):475–479
De Waha S, Desch S, Eitel I, Fuernau G, Zachrau J, Leuschner A et al (2010) Impact of early vs. late microvascular obstruction assessed by magnetic resonance imaging on long-term outcome after ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a comparison with traditional prognostic markers. Eur Heart J 31(21):2660–2668
Schuleri KH, Centola M, Evers KS, Zviman A, Evers R, Lima JA et al (2012) Cardiovascular magnetic resonance characterization of peri-infarct zone remodeling following myocardial infarction. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 14(1):24
Products - Health United States - Tables - 2011 Complete List [Internet] (2014). http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/hus/contents2011.htm#123
Gjesdal O, Helle-Valle T, Hopp E, Lunde K, Vartdal T, Aakhus S et al (2008) Noninvasive separation of large, medium, and small myocardial infarcts in survivors of reperfused ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a comprehensive tissue Doppler and speckle-tracking echocardiography study. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 1(3):189–196 2 p following 196
Ersbøll M, Valeur N, Mogensen UM, Andersen MJ, Møller JE, Hassager C et al (2012) Relationship between left ventricular longitudinal deformation and clinical heart failure during admission for acute myocardial infarction: a two-dimensional speckle-tracking study. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 25(12):1280–1289
Altiok E, Tiemann S, Becker M, Koos R, Zwicker C, Schroeder J et al (2014) Myocardial deformation imaging by two-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography for prediction of global and segmental functional changes after acute myocardial infarction: a comparison with late gadolinium enhancement cardiac magnetic resonance. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 27(3):249–257
Seo Y, Ishizu T, Enomoto Y, Sugimori H, Yamamoto M, Machino T et al (2009) Validation of 3-dimensional speckle tracking imaging to quantify regional myocardial deformation. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 2(6):451–459
Wen H, Liang Z, Zhao Y, Yang K (2011) Feasibility of detecting early left ventricular systolic dysfunction using global area strain: a novel index derived from three-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography. Eur J Echocardiogr 12(12):910–916
Reant P, Barbot L, Touche C, Dijos M, Arsac F, Pillois X et al (2012) Evaluation of global left ventricular systolic function using three-dimensional echocardiography speckle-tracking strain parameters. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 25(1):68–79
Lang RM, Badano LP, Tsang W, Adams DH, Agricola E, Buck T et al (2012) EAE/ASE recommendations for image acquisition and display using three-dimensional echocardiography. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 13(1):1–46
Cerqueira MD, Weissman NJ, Dilsizian V, Jacobs AK, Kaul S, Laskey WK et al (2002) Standardized myocardial segmentation and nomenclature for tomographic imaging of the heart. A statement for healthcare professionals from the Cardiac Imaging Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology of the American Heart Association. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 18(1):539–542
Arisha MM, Girerd N, Chauveau S, Bresson D, Scridon A, Bonnefoy E et al (2013) In-hospital heart rate turbulence and microvolt T-wave alternans abnormalities for prediction of early life-threatening ventricular arrhythmia after acute myocardial infarction. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol 18(6):530–537
Pérez de Isla L, Millán M, Lennie V, Quezada M, Guinea J, Macaya C et al (2011) Area strain: normal values for a new parameter in healthy people. Rev Esp Cardiol 64(12):1194–1197
Kleijn SA, Aly MFA, Terwee CB, van Rossum AC, Kamp O (2012) Reliability of left ventricular volumes and function measurements using three-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 13(2):159–168
Nesser H-J, Mor-Avi V, Gorissen W, Weinert L, Steringer-Mascherbauer R, Niel J et al (2009) Quantification of left ventricular volumes using three-dimensional echocardiographic speckle tracking: comparison with MRI. Eur Heart J 30(13):1565–1573
Munk K, Andersen NH, Nielsen SS, Bibby BM, Bøtker HE, Nielsen TT et al (2011) Global longitudinal strain by speckle tracking for infarct size estimation. Eur J Echocardiogr 12(2):156–165
Takeuchi M, Nishikage T, Nakai H, Kokumai M, Otani S, Lang RM (2007) The assessment of left ventricular twist in anterior wall myocardial infarction using two-dimensional speckle tracking imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 20(1):36–44
Kansal MM, Panse PM, Abe H, Caracciolo G, Wilansky S, Tajik AJ et al (2011) Relationship of contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging-derived intramural scar distribution and speckle tracking echocardiography-derived left ventricular two-dimensional strains. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 13(2):152–158
Cimino S, Canali E, Petronilli V, Cicogna F, De Luca L, Francone M et al (2013) Global and regional longitudinal strain assessed by two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography identifies early myocardial dysfunction and transmural extent of myocardial scar in patients with acute ST elevation myocardial infarction and relatively preserved LV function. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 14(8):805–811
Li Y-J, Li C, Li C-M, Zhang L, Bai W-J, Zhang X-L et al (2013) Value of three-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography and the novel area strain in detecting wall motion abnormalities of coronary artery diseases. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 44(4):651–656
Wu KC, Kim RJ, Bluemke DA, Rochitte CE, Zerhouni EA, Becker LC et al (1998) Quantification and time course of microvascular obstruction by contrast-enhanced echocardiography and magnetic resonance imaging following acute myocardial infarction and reperfusion. J Am Coll Cardiol 32(6):1756–1764
Bergerot C, Mewton N, Lacote-Roiron C, Ernande L, Ovize M, Croisille P et al (2014) Influence of microvascular obstruction on regional myocardial deformation in the acute phase of myocardial infarction: a Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography Study. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 27(1):93–100
Bière L, Donal E, Terrien G, Kervio G, Willoteaux S, Furber A et al (2014) longitudinal strain is a marker of microvascular obstruction and infarct size in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. PLoS One 9(1):e86959
Greenbaum RA, Ho SY, Gibson DG, Becker AE, Anderson RH (1981) Left ventricular fibre architecture in man. Br Heart J 45(3):248–263
Antman EM, Anbe DT, Armstrong PW, Bates ER, Green LA, Hand M et al (2004) ACC/AHA Guidelines for the management of patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction—executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Revise the 1999 Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Acute Myocardial Infarction). J Am Coll Cardiol 44(3):671–719
Wu KC (2012) CMR of microvascular obstruction and hemorrhage in myocardial infarction. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 14:68
Acknowledgments
The REMI study and the STANISLAS COHORT were supported by grants from the French Ministry of Health (Programme Hospitalier de Recherche Clinique Inter-régional 2008 and 2009) and sponsored by the CHU Nancy, F-54000, Nancy, France.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Trial registration: NCT01109225.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Figure
Study flow chart of sample selection for the global and segmental analysis of STEMI and control patients (TIFF 50 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huttin, O., Zhang, L., Lemarié, J. et al. Global and regional myocardial deformation mechanics of microvascular obstruction in acute myocardial infarction: a three dimensional speckle-tracking imaging study. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 31, 1337–1346 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-015-0690-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-015-0690-2