Abstract
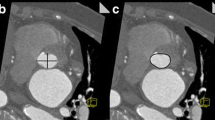
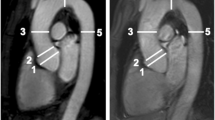
Aim To determine the variability in CT measurements of proximal thoracic aortic diameters obtained using double-oblique short axis and semiautomatic centerline analysis techniques. Institutional review board approval, with waiver of informed consent, was obtained for this HIPAA-compliant, retrospective study. Cardiac gated thoracic aortic CT scans were evaluated in 25 patients. Maximum aortic diameter measurements at the annulus, sinuses, sinotubular junction and ascending aorta were generated using double-oblique short axis and semiautomatic centerline analysis techniques. Intraobserver and interobserver variability and variability between techniques were assessed using the Wilcoxon signed rank test, Spearman’s correlation coefficients and Bland-Altman plots. Mean intraobserver diameter differences using double oblique views ranged from −0.3 to 0.6 mm. The 95 % confidence interval for difference in diameters was ±2.4 to ±5.1 mm for radiologist #1 and ±2.6 to ±5.2 mm for radiologist #2, depending on location. Mean intraobserver diameter differences using centerline analysis ranged from 0.2 to 2.3 mm, and the 95 % confidence interval for difference in diameters was ±2.0 to ±4.6 mm, depending on location. Significant interobserver differences were seen for both double oblique views and centerline analysis. Measurements obtained using the two methods were strongly correlated (r = 0.81–0.99), although they were consistently larger using centerline analysis (95 % confidence interval, ±1.8 to ±3.2 mm). Although measurement variability of the proximal thoracic aorta was generally low using double oblique and centerline analysis techniques, differences of up to approximately 5 mm in diameter occurred within the 95 % confidence interval. Neither technique was clearly more reliable than the other.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rengier F, Weber TF, Giesel FL, Bockler D, Kauczor HU, von Tengg-Kobligk H (2009) Centerline analysis of aortic CT angiographic examinations: benefits and limitations. Am J Roentgenol 192(5):W255–W263. doi:10.2214/ajr.08.1488
Mendoza DD, Kochar M, Devereux RB, Basson CT, Min JK, Holmes K, Dietz HC, Milewicz DM, LeMaire SA, Pyeritz RE, Bavaria JE, Maslen CL, Song H, Kroner BL, Eagle KA, Weinsaft JW (2011) Impact of image analysis methodology on diagnostic and surgical classification of patients with thoracic aortic aneurysms. Ann Thorac Surg 92(3):904–912. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2011.03.130
Ng ACT, Delgado V, van der Kley F, Shanks M, van de Veire NRL, Bertini M, Nucifora G, van Bommel RJ, Tops LF, de Weger A, Tavilla G, de Roos A, Kroft LJ, Leung DY, Schuijf J, Schalij MJ, Bax JJ (2009) Comparison of aortic root dimensions and geometries before and after transcatheter aortic valve implantation by 2- and 3-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography and multislice computed tomography. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 3(1):94–102. doi:10.1161/circimaging.109.885152
Rubio DM, Conde JSdLC, Alvarez-Osorio MP, Ortiz MR, Ortega MD, del Pino MdCL, Delgado FT, Saint-Gerons JS, Pineda SO, Fuertes DG, Crespín MC, Espejo S, Ysamat R (2011) Measurement of aortic valve annulus using different cardiac imaging techniques in transcatheter aortic valve implantation: agreement with finally implanted prosthesis size. Echocardiography 28(4):388–396. doi:10.1111/j.1540-8175.2010.01353.x
Messika-Zeitoun D, Serfaty J-M, Brochet E, Ducrocq G, Lepage L, Detaint D, Hyafil F, Himbert D, Pasi N, Laissy J-P, Iung B, Vahanian A (2010) Multimodal assessment of the aortic annulus diameter. J Am Coll Cardiol 55(3):186–194. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2009.06.063
Altiok E, Koos R, Schroder J, Brehmer K, Hamada S, Becker M, Mahnken AH, Almalla M, Dohmen G, Autschbach R, Marx N, Hoffmann R (2011) Comparison of two-dimensional and three-dimensional imaging techniques for measurement of aortic annulus diameters before transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Heart 97(19):1578–1584. doi:10.1136/hrt.2011.223974
Pontone G, Andreini D, Bartorelli AL, Annoni A, Mushtaq S, Bertella E, Formenti A, Cortinovis S, Alamanni F, Fusari M, Bona V, Tamborini G, Muratori M, Ballerini G, Fiorentini C, Biglioli P, Pepi M (2011) Feasibility and accuracy of a comprehensive multidetector computed tomography acquisition for patients referred for balloon-expandable transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Am Heart J 161(6):1106–1113. doi:10.1016/j.ahj.2011.03.003
Lu TLC, Rizzo E, Marques-Vidal PM, Segesser LKv, Dehmeshki J, Qanadli SD (2009) Variability of ascending aorta diameter measurements as assessed with electrocardiography-gated multidetector computerized tomography and computer assisted diagnosis software. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 10(2):217–221. doi:10.1510/icvts.2009.216275
Lin FY, Devereux RB, Roman MJ, Meng J, Jow VM, Jacobs A, Weinsaft JW, Shaw LJ, Berman DS, Gilmore A, Callister TQ, Min JK (2008) Assessment of the thoracic aorta by multidetector computed tomography: age- and sex-specific reference values in adults without evident cardiovascular disease. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr 2(5):298–308. doi:10.1016/j.jcct.2008.08.002
Mao SS, Ahmadi N, Shah B, Beckmann D, Chen A, Ngo L, Flores FR, Gao Yl, Budoff MJ (2008) Normal thoracic aorta diameter on cardiac computed tomography in healthy asymptomatic adults. Acad Radiol 15(7):827–834. doi:10.1016/j.acra.2008.02.001
Larsson E, Vishnevskaya L, Kalin B, Granath F, Swedenborg J, Hultgren R (2011) High frequency of thoracic aneurysms in patients with abdominal aortic aneurysms. Ann Surg 253(1):180–184. doi:10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181d96498
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1(8476):307–310
Hiratzka LF, Bakris GL, Beckman JA, Bersin RM, Carr VF, Casey DE, Eagle KA, Hermann LK, Isselbacher EM, Kazerooni EA, Kouchoukos NT, Lytle BW, Milewicz DM, Reich DL, Sen S, Shinn JA, Svensson LG, Williams DM (2010) 2010 ACCF/AHA/AATS/ACR/ASA/SCA/SCAI/SIR/STS/SVM guidelines for the diagnosis and management of patients with thoracic aortic disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task force on Practice Guidelines, American Association for Thoracic Surgery, American College of Radiology, American Stroke Association, Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Society of Interventional Radiology, Society of Thoracic Surgeons, and Society for Vascular Medicine. Circulation 121(13):e266–e369. doi:10.1161/CIR.0b013e3181d4739e
Rengier F, Weber TF, Partovi S, Müller-Eschner M, Böckler D, Kauczor HU, von Tengg-Kobligk H (2011) Reliability of semiautomatic centerline analysis versus manual aortic measurement techniques for TEVAR among non-experts. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 42(3):324–331. doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2011.04.019
Acknowledgments
We thank Karen Overbay for her assistance in the 3D Imaging Lab.
Conflict of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quint, L.E., Liu, P.S., Booher, A.M. et al. Proximal thoracic aortic diameter measurements at CT: repeatability and reproducibility according to measurement method. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 29, 479–488 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-012-0102-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-012-0102-9