Abstract
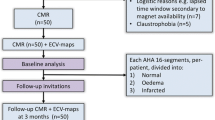
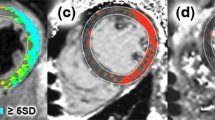
Left ventricular ballooning syndrome (LVBS), also known as Takotsubo cardiomyopathy, is characterized by regional left ventricular dysfunction associated with severe psychological stress. T2 weighted cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) can identify myocardial edema due to ischemia or other insults. A standard clinical CMR scan with double inversion recovery fast spin echo T2 weighted sequences was performed on consecutive patients with LVBS. T2 signal was compared in myocardial segments with normal and impaired function based on systolic wall thickening (SWT). Eight LVBS patients were identified, all female, with a median age of 61 years and median left ventricular ejection fraction of 52%. Four patients had apical ballooning and four had mid-wall or basal ballooning. In severely dysfunctional segments (those with SWT < 25%), the median percentage of high T2 signal was 85 compared with 35 in those with SWT > 25% (P < 0.001). When the segments were categorized into tertiles based on SWT, the percentage of high T2 signal was greatest in segments with the worst function (68% vs. 43% vs. 31%, P = 0.005). In the five patients who returned for follow up, there was a significant reduction in high T2 signal compared with baseline in those segments that were initially severely dysfunctional (85% vs. 35%, P < 0.001). In conclusion, we describe elevated T2 signal consistent with myocardial edema in patients with LVBS. The T2 signal is highest in myocardium with the most impaired function and resolves over time.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gianni M, Dentali F, Grandi AM et al (2006) Apical ballooning syndrome or takotsubo cardiomyopathy: a systematic review. Eur Heart J 27:1523–1529
Bybee KA, Kara T, Prasad A et al (2004) Systematic review: transient left ventricular apical ballooning: a syndrome that mimics ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Ann Intern Med 141:858–865
Mitchell JH, Hadden TB, Wilson JM et al (2007) Clinical features and usefulness of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in assessing myocardial viability and prognosis in Takotsubo cardiomyopathy (transient left ventricular apical ballooning syndrome). Am J Cardiol 100:296–301
Sharkey SW (2008) Electrocardiogram mimics of acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: insights from cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in patients with tako-tsubo (stress) cardiomyopathy. J Electrocardiol 41:621–625
Deetjen AG, Conradi G, Mollmann S et al (2006) Value of gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in patients with Tako-Tsubo-like left ventricular dysfunction. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 8:367–372
Valles E, Pujadas S, Guindo J et al (2007) Delayed-contrast enhancement cardioresonance in transient left ventricular apical ballooning. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 23:243–247
Aletras AH, Tilak GS, Natanzon A et al (2006) Retrospective determination of the area at risk for reperfused acute myocardial infarction with T2-weighted cardiac magnetic resonance imaging: histopathological and displacement encoding with stimulated echoes (DENSE) functional validations. Circulation 113:1865–1870
Simonetti OP, Finn JP, White RD et al (1996) “Black blood” T2-weighted inversion-recovery MR imaging of the heart. Radiology 199:49–57
Abdel-Aty H, Cocker M, Friedrich MG (2009) Myocardial edema is a feature of Tako-Tsubo cardiomyopathy and is related to the severity of systolic dysfunction: insights from T2-weighted cardiovascular magnetic resonance. Int J Cardiol 132:291–293
Cerqueira MD, Weissman NJ, Dilsizian V et al (2002) Standardized myocardial segmentation and nomenclature for tomographic imaging of the heart: a statement for healthcare professionals from the Cardiac Imaging Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology of the American Heart Association. Circulation 105:539–542
Holman ER, Buller VG, de Roos A et al (1997) Detection and quantification of dysfunctional myocardium by magnetic resonance imaging. A new three-dimensional method for quantitative wall-thickening analysis. Circulation 95:924–931
Abdel-Aty H, Zagrosek A, Schulz-Menger J et al (2004) Delayed enhancement and T2-weighted cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging differentiate acute from chronic myocardial infarction. Circulation 109:2411–2416
Vultaggio A, Matucci A, Del Pace S et al (2007) Tako-Tsubo-like syndrome during anaphylactic reaction. Eur J Heart Fail 9:209–211
Sharkey SW, Lesser JR, Zenovich AG et al (2005) Acute and reversible cardiomyopathy provoked by stress in women from the United States. Circulation 111:472–479
Lee VH, Connolly HM, Fulgham JR et al (2006) Tako-tsubo cardiomyopathy in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: an underappreciated ventricular dysfunction. J Neurosurg 105:264–270
Lentschener C, Vignaux O, Spaulding C et al (2006) Early postoperative tako-tsubo-like left ventricular dysfunction: transient left ventricular apical ballooning syndrome. Anesth Analg 103:580–582
Spes C, Knape A, Mudra H (2006) Recurrent tako-tsubo-like left ventricular dysfunction (apical ballooning) in a patient with pheochromocytoma—a case report. Clin Res Cardiol 95:307–311
Wedekind H, Moller K, Scholz KH (2006) Tako-tsubo cardiomyopathy. Incidence in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Herz 31:339–346
Bybee KA, Prasad A, Barsness GW et al (2004) Clinical characteristics and thrombolysis in myocardial infarction frame counts in women with transient left ventricular apical ballooning syndrome. Am J Cardiol 94:343–346
Pilliere R, Mansencal N, Digne F et al (2006) Prevalence of tako-tsubo syndrome in a large urban agglomeration. Am J Cardiol 98:662–665
Kurowski V, Kaiser A, von Hof K et al (2007) Apical and midventricular transient left ventricular dysfunction syndrome (tako-tsubo cardiomyopathy): frequency, mechanisms, and prognosis. Chest 132:809–816
Hurst RT, Askew JW, Reuss CS et al (2006) Transient midventricular ballooning syndrome: a new variant. J Am Coll Cardiol 48:579–583
Pennell D (2006) Myocardial salvage: retrospection, resolution, and radio waves. Circulation 113:1821–1823
Karolle BL, Carlson RE, Aisen AM et al (1991) Transmural distribution of myocardial edema by NMR relaxometry following myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Am Heart J 122:655–664
Willerson JT, Scales F, Mukherjee A et al (1977) Abnormal myocardial fluid retention as an early manifestation of ischemic injury. Am J Pathol 87:159–188
Garcia-Dorado D, Oliveras J, Gili J et al (1993) Analysis of myocardial oedema by magnetic resonance imaging early after coronary artery occlusion with or without reperfusion. Cardiovasc Res 27:1462–1469
Wisenberg G, Prato FS, Carroll SE et al (1988) Serial nuclear magnetic resonance imaging of acute myocardial infarction with and without reperfusion. Am Heart J 115:510–518
Abdel-Aty H, Boye P, Zagrosek A et al (2005) Diagnostic performance of cardiovascular magnetic resonance in patients with suspected acute myocarditis: comparison of different approaches. J Am Coll Cardiol 45:1815–1822
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Medis Medical Imaging Systems (Leiden, The Netherlands) for QMASS software.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joshi, S.B., Chao, T., Herzka, D.A. et al. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance T2 signal abnormalities in left ventricular ballooning syndrome. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 26, 227–232 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-009-9515-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-009-9515-5