Abstract
Introduction
To evaluate effect of different kVp, reconstruction kernels and contrast concentrations on stent luminal diameter measurements and luminal contrast attenuation values.
Methods
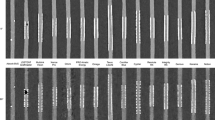
Two metallic coronary stents (2.75 mm and 3.0 mm) were deployed in silicone tubes and tubes were filled with diluted iodinated contrast (1:20 dilution of Iohexol 350 mg% to achieve an attenuation value of 550 HU at 120 kVp). The tubes were scanned at 80, 100, 120 and 140 kVp. Each scan acquisition was reconstructed using B10f, B25f, B31f, B36f, B41f, B46f, B60f, and B80f kernels. Scans were repeated using 1:35 contrast dilution (350 HU at 120 kVp). Luminal diameter was measured at mid stent level for each stent, in datasets acquired at different kVp, contrast concentrations, and reconstruction kernels. Luminal attenuation values (HU) were measured at the mid stent level and at a distance of 1 cm from the stent entrance within the tube lumen.
Results
kVp did not have a significant effect on the visualization of stent luminal diameter (P > 0.277). The change in kernel significantly affected the difference in luminal HU values at stent and non-stent levels (P < 0.001), with B46f showing the least difference in HU values. The lower contrast concentration (350 HU) showed substantially less artifactual stent stenosis compared to high contrast concentration (550 HU) (P < 0.001). There was excellent inter-observer agreement for stent luminal diameters and attenuation value measurements (r 2=0.971, P < 0.001).
Conclusions
For lower spatial resolution kernels, 120 kVp or 140 kVp provides better estimate of stent lumen. Reconstruction kernels and contrast concentration (HU) have significant effect on visualization of in-stent luminal diameter and artifactual stenosis. In clinical practice, B46f kernel and lower contrast enhancement value (∼350 HU) may be optimal for evaluating the stent lumen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama T, Moussa I, Reimers B, Ferraro M, Kobayashi Y, Blengino S, Di Francesco L, Finci L, Di Mario C, Colombo A (1998) Angiographic and clinical outcome following coronary stenting of small vessels, a comparision with coronary stenting of large vessels. J␣Am Coll Cardiol 32:1610–1618
Gaspar T, Halon DA, Lewis BS, Adawi S, Schliamser JE, Rubinshtein R, Flugelman MY, Peled N (2005) Diagnosis of coronary in-stent restenosis with multidetector row spiral computed tomography. J Am Coll Cardiol 46(8):1573–1579 (Epub 2005 Sep 12)
Kitagawa T, Fujii T, Tomohiro Y, Maeda K, Kobayashi M, Kunita E, Sekiguchi Y (2005) Noninvasive assessment of coronary stents in patients by 16-slice computed tomography. Int J Cardiol (Jul 12, Epub ahead of print)
Cury RC, Ferencik M, Achenbach S, Pomerantsev E, Nieman K, Moselewski F, Abbara S, Jang IK, Brady TJ, Hoffmann U (2006) Accuracy of 16-slice multi-detector CT to quantify the degree of coronary artery stenosis: assessment of cross-sectional and longitudinal vessel reconstructions. Eur J Radiol 57(3):345–350 (Epub 2006 Jan 25)
Stanford W (2005) Advances in cardiovascular CT imaging: CT clinical imaging. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 21:29–37
Yamada M, Jinaki M, Kuribayashi S, Sato K, Tanami Y, Yun S, Sasaki K (2005) Evaluation of coronary artery lumen diameter with 16-slice multidetector-row computed tomography. Circ J 69:1230–1232
Maintz D, Seifarth H, Raupach R, Flohr T, Rink M, Sommer T, Ozgun M, Heindel W, Fischbach R (2005) 64-slice multidetector coronary CT angiography: in vitro evaluation of 68 different stents. Eur Radiol Dec 7:1–9 (Epub ahead of print)
Seifarth H, Raupanch R, Schaller S, Fallenberg EM, Flohr T, Heindel W, Fischbach H, Maintz D (2005) Assesment of coronary artery stents using 16-slice MDCT angiography: evaluation of dedicated reconstruction kernel and a noise reduction filter. Eur Radiol 15:721–726
Nieman K, Cadermartiri F, Raaijmakers R, Pattynama P, de Feyter P (2003) Noninvasive angiographic evaluation of coronary stents with multi-slice spiral computed tomography. Herz 28:136–142
Suzuki S, Furui S, Kaminaga T, Yamauchi T, Kuwahara S, Yokoyama N, Suzuki M, Isshiki T (2005) Evaluation of coronary stents in vitro with CT angiography: effect of stent diameter, convolution kernel, and vessel orientation to the z-axis. Circ J 69(9):1124–1131
Mahnken H, Seyfarth T, Flohr T, Herzog C, Stahl J, Stanzel S, Kuettner A, Wildberger JE, Gunther RW (2005) Flat-panel detector computed tomography for the assessment of coronary artery stents. Phantom study in comparision with 16-slice spiral computed tomography. Invest Radiol 40:8–13
Seifarth H, Ozgun M, Raupach R, Flohr T, Heindel W, Fischbach R, Maintz D (2006) 64- Versus 16-slice ct angiography for coronary artery stent assessment: in vitro experience. Invest Radiol 41(1):22–27
Maintz D, Grude M, Fallenberg M, Heindel W, Fischbach R (2003) Assessment of coronary arterial stents by multislice-CT angiography. Acta Radiol 44:597–603
Mahnken AH, Buecker A, Wildberger JE, Ruebben A, Stanzel S, Vogt F, Gunther RW, Blindt R (2004) Coronary artery stents in multislice computed tomography – in vitro artifact evaluation. Invest Radiol 39:27–33
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sirineni, G.K.R., Kalra, M.K., Pottala, K. et al. Effect of Contrast Concentration, Tube Potential and Reconstruction Kernels on MDCT Evaluation of Coronary Stents: an in Vitro Study. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 23, 253–263 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-006-9107-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-006-9107-6