Abstract
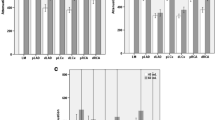
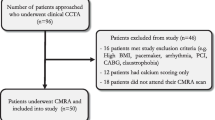
Purpose: Assess the effect of heart rate on diagnostic accuracy for the detection of significant coronary artery stenosis using 16-row multislice computed tomography (MSCT). Material and methods: About 120 patients (105 males; 59±11 years) with suspected coronary artery disease who underwent conventional coronary angiography (CA) and MSCT-CA were retrospectively enrolled for the study. Patients underwent a MSCT-CA (Sensation 16, Siemens, Germany), with the following protocol: collimation 16×0.75 mm, gantry rotation time 420 ms, feed/rotation 3.0 mm, kV 120, mAs 400–500. The protocol for contrast material administration was 100 ml of Iodixanol (Visipaque 320 mg l/ml, Amersham, UK) at 4 ml/s and the delay was defined with a bolus tracking technique. In all patients the mean heart rate (HR) during the scan was used as a criteria to divide the population in two groups of 60 patients each. In one group (Low HR) the 60 patients with lower heart rates, and in the other group (High HR) the patients with higher heart rates. In the two groups diagnostic accuracy (per coronary segment) for the detection of significant stenosis (≥50% lumen reduction) was evaluated in vessels ≥2 mm of diameter using quantitative CA as reference standard. The difference in diagnostic accuracy were compared with a Chi2 test and a p<0.05 was considered significant. Results: There was no significant difference between the two groups regarding age, gender, weight, mean intravascular attenuation, and calcium score. Overall 1310 (652 for Low HR and 658 for High HR) segments with 219 (105 for Low HR and 114 for High HR) significant lesions were available for the analysis. The average heart rate was 52±4HU and 63±5HU for Low HR and High HR, respectively (p<0.001). The sensitivity and specificity were 92 and 96% for Low HR and 90 and 92% for High HR (p<0.05). There were 22 vs. 44 false positives, and 8 vs. 12 false negatives in the Low HR and High HR, respectively. Conclusion: Increasing HR significantly deteriorates diagnostic accuracy in MSCT-CA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
1. Nieman K, Cademartiri F, Lemos PA, Raaijmakers R, Pattynama PM, de Feyter PJ. (2002). Reliable noninvasive coronary angiography with fast submillimeter multislice spiral computed tomography. Circulation 106:2051–4
2. Ropers D, Baum U, Pohle K, et al. (2003). Detection of coronary artery stenoses with thin-slice multi-detector row spiral computed tomography and multiplanar reconstruction. Circulation 107:664–6
3. Mollet NR, Cademartiri F, Nieman K, et al. (2004). Multislice spiral computed tomography coronary angiography in patients with stable angina pectoris. J Am Coll Cardiol 43:2265–70
4. Nieman K, Rensing BJ, van Geuns RJ, et al. (2002). Non-invasive coronary angiography with multislice spiral computed tomography: impact of heart rate. Heart 88:470–4
5. Schroeder S, Kopp AF, Kuettner A, et al. (2002). Influence of heart rate on vessel visibility in noninvasive coronary angiography using new multislice computed tomography: experience in 94 patients. Clin Imaging 26:106–11
6. Austen WG, Edwards JE, Frye RL, et al. (1975). A reporting system on patients evaluated for coronary artery disease. Report of the Ad Hoc Committee for Grading of Coronary Artery Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Surgery, American Heart Association. Circulation 51:5–40
7. Hoffman U, Moselewski F, Cury RC, et al. (2004). Predictive value of 16-slice multidetector spiral computed tomography to detect significant obstructive coronary artery disease in patients at high risk for coronary artery disease: patient-versus segment-based analysis. Circulation 110(17):2638–43
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Address for correspondence: Filippo Cademartiri, MD, Department of Radiology, Erasmus Medical Center, Dr Molenwaterplein 40, 3015GD Rotterdam, The Netherlands. Tel.: 0031-(0)-10-463-4127; Fax: 0031-(0)-10-463-4033; E-mail: filippocademartiri@hotmail.com
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cademartiri, F., Mollet, N.R., Runza, G. et al. Diagnostic accuracy of multislice computed tomography coronary angiography is improved at low heart rates. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 22, 101–105 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-005-9010-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-005-9010-6