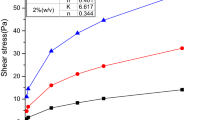
The rheological properties of water-based drilling fluids are heavily influenced by low temperatures and are some of the most important issues for permafrost natural gas hydrate drilling. In this work, we developed a polymer drilling fluid formula and studied its rheological properties at low temperatures. The rheological properties of four different drilling fluids including macro-polymers, amphoteric polymers, sulfonated polymers, and biopolymers were tested. The corresponding rheological-property/temperature response curves were drawn. The response characteristics of the rheological properties with temperature were analyzed. Based on these, a novel research idea was developed to adapt to permafrost drilling a poly-sulfonate drilling fluid system in which sulfonated lignite (SMC) and sulfonated phenolic resin (SMP) were used as the main agents while xanthan gum (XC) served as a flow-pattern modifier. According to orthogonal test results, the optimized drilling fluid formula was base mud + NaCl (20 wt. %) + NaOH (0.1) + SMP (3) + SMC (4) + XC (0.3). Moreover, the rheological-property/temperature response mechanism was analyzed using Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopic tests of the treating agents and scanning electron microscopic (SEM) tests of the mud cakes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Q. Wu, G. Jiang, and P. Zhang, Energy Convers. Manage., 51, No. 4, 783-787 (2010).
Y. Song, L. Yang, J. Zhao, et al., Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev., 31, 778-791 (2014).
L. Zhang, G. Jiang, Y. Tu, et al., J. Chin. Univ. Geosci., 17, No. 3, 276-282 (2006).
G. Jiang, F. Ning, L. Zhang, et al., J. Earth Sci., 22, No. 5, 652-657 (2011).
L. Chen, S. Wang, and C. Ye, Procedia Eng., 73, 318-325 (2014).
S. V. Kokelj, D. Riseborough, R. Coutts, et al., Cold Reg. Sci. Technol., 64, No. 1, 46-56 (2010).
M. Amani and M. J. Al-Jubouri, in: International Conference on Health, Safety and Environment in Oil and Gas Exploration and Production, Sept. 11-13, 2012, Perth, Australia, SPE-157219-MS.
M. Amani and M. Al-Jubouri, Energy Sci. Technol., 4, No. 1, 27-33 (2012).
S. Wang, L. Chen, and Y. Zhang, Nat. Gas Ind., 29, No. 6, 59-62 (2009).
Z. Lu, Y. Zhu, Y. Zhang, et al., Cold Reg. Sci. Technol., 66, No. 2, 93-104 (2011).
J. M. Davison, S. Clary, and A. Saasen, in: SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Oct. 3-6, 1999, Houston, Texas, SPE-56632-MS.
W. Halliday, D. K. Clapper, and M. Smalling, in: IADC/SPE Drilling Conference, Mar. 3-6, 1998, Dallas, Texas, SPE-39316-MS.
H. Ebeltoft, M. Yousif, and E. Soergaard, in: SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Oct. 5-8, 1997, San Antonio, Texas, SPE-38567-MS.
J. Romero and E. Touboul, in: SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, Sept. 27-30, 1998, New Orleans, Louisiana, SPE-49056-MS.
J. Yan, J. Southwest Pet. Inst., 2, 1-15 (1982).
R. L. Davidson, Handbook of Water-soluble Gums and Resins, McGraw-Hill, New York, London, 1980, 700 pp.
S. Rosalam and R. England, Enzyme Microb. Technol., 39, No. 2, 197-207 (2006).
J. Yan, Drilling Fluid Technology, 1st Ed., China University of Petroleum Press, Shangdong, 2006.
S. Hao, J. Pet. Sci. Eng., 76, No. 3-4, 109-115 (2011).
S. Faria, C. L. de Oliveira Petkowicz, et al., Carbohydr. Polym., 86, 469-476 (2011).
V. Gunasekar, K. R. Reshma, T. Greeshma, et al., Carbohydr. Polym., 102, 669-673 (2014).
N. Saqib, B. S. Tahira, T. Vincent, et al., Fuel Process. Technol., 92, No. 5, 983-991 (2011).
Y. Zhuang, Z. Zhu, H. Chao, et al., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 55, No. 7, 1063-1067 (1995).
M. Li, Y. Guo, H. He, et al., J. Chin. Univ. Pet., Ed. Nat. Sci., 34, No. 2, 145-149 (2010).
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants Nos. 41272331 and 51204027) and the State Key Laboratory of Geo-hazard Prevention and Geo-environment Protection (Grant No. SKLGP2012Z007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Khimiya i Tekhnologiya Topliv i Masel, No. 2, pp. 75 – 82, March – April, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheng, W., Chuan, Z., Chaopeng, Y. et al. Rheological Properties of Polymer Drilling Fluid Developed for Permafrost Natural Gas Hydrate Drilling. Chem Technol Fuels Oils 53, 274–285 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-017-0804-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-017-0804-8