Abstract
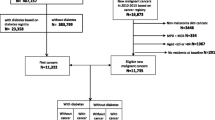
Type 2 diabetes mellitus has been associated with an increased risk of a variety of cancers in observational studies, but few have reported the relationship between diabetes and cancer risk in men and women separately. The main goal of this retrospective cohort study was to evaluate the sex-specific risk of incident overall and site-specific cancer among people with DM compared with those without, who had no reported history of cancer at the start of the follow-up in January 2000. During an average of 8 years of follow-up (SD = 2.5), we documented 1,639 and 7,945 incident cases of cancer among 16,721 people with DM and 83,874 free of DM, respectively. In women, DM was associated with an adjusted hazard ratio of 1.96 (95% CI: 1.53–2.50) and 1.41 (95% CI: 1.20–1.66) for cancers of genital organs and digestive organs, respectively. A significantly reduced HR was observed for skin cancer (0.38; 95% CI: 0.22–0.66). In men with DM, there was no significant increase in overall risk of cancer. DM was related with a 47% reduction in the risk of prostate cancer. These findings suggest that the nature of the association between DM and cancer depends on sex and specific cancer site.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roglic G, Unwin N, Bennett P, Mathers C, Tuomilehto J, Nag S et al (2005) The burden of mortality attributable to diabetes: realistic estimates for the year 2000. Diabetes Care 28:2130–2135
World Health Organization (2008) Diabetes programme. Fact sheet no 312 cited. Available from: http://www.who.int/diabetes/facts/world_figures/en/
Stamler J, Vaccaro O, Neaton J, Wentworth D (1993) Diabetes, other risk factors, and 12 years cardiovascular mortality for men screened in the multiple risk factor intervention trial. Diabetes Care 16:434–444
Adami HO, McLaughlin J, Ekbom A, Berne C, Silverman D, Hacker D et al (1996) Cancer risk in patients with diabetes mellitus. J Natl Cancer Inst 88:307–314
Shin C, Moon B, Park K, Kim S, Park S, Chung M et al (2001) Serum 8-Hydroxy-Guanine levels are increased in diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 24:733–737
Bach L, Rechler M (1992) Insulin-like growth factors and diabetes. Diabetes Metab Rev 8:229–257
Calle EE, Murphy TK, Rodriguez C, Thun MJ, Heath CW Jr (1998) Diabetes mellitus and pancreatic cancer mortality in a prospective cohort of United States adults. Cancer Causes Control 9(4):403–410
Everhart J, Wright D (1995) Diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for pancreatic cancer. A meta-analysis. JAMA 273(20):1605–1609
Gapstur S, Gann P, Lowe W, Liu K, Colangelo L, Dyer A (2000) Abnormal glucose metabolism and pancreatic cancer mortality. JAMA 283:2552–2558
Silverman DT, Schiffman M, Everhart J, Goldstein A, Lillemoe KD, Swanson GM et al (1999) Diabetes mellitus, other medical conditions and familial history of cancer as risk factors for pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer 80(11):1830–1837
Smith GD, Egger M, Shipley MJ, Marmot MG (1992) Post-challenge glucose concentration, impaired glucose tolerance, diabetes, and cancer mortality in men. Am J Epidemiol 136(9):1110–1114
Coughlin SS, Calle EE, Teras LR, Petrelli J, Thun MJ (2004) Diabetes mellitus as a predictor of cancer mortality in a large cohort of US adults. Am J Epidemiol 159(12):1160–1167
Hardell L, Fredrikson M, Axelson O (1996) Case-control study on colon cancer regarding previous disease and drug intake. Int J Oncol 8:439–444
Kune G, Kune S, Watson L (1988) Colorectal cancer risk, chronic illnesses, operations, and medications: case-control results from the Melbourne colorectal cancer study. Cancer Res 48:4399–4404
La Vecchia C, D’Avanzo B, Negri E, Franceschi S (1991) History of selected diseases and the risk of colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer 27:582–586
La Vecchia C, Negri E, Decarli A, Franceschi S (1997) Diabetes mellitus and colorectal cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 6(12):1007–1010
Will JC, Galuska DA, Vinicor F, Calle EE (1998) Colorectal cancer: another complication of diabetes mellitus? Am J Epidemiol 147(9):816–825
Adami HO, Chow WH, Nyren O, Berne C, Linet MS, Ekbom A et al (1996) Excess risk of primary liver cancer in patients with diabetes mellitus. J Natl Cancer Inst 88(20):1472–1477
Adami HO, McLaughlin J, Ekbom A, Berne C, Silverman D, Hacker D et al (1991) Cancer risk in patients with diabetes mellitus. Cancer Causes Control 2(5):307–314
La Vecchia C, Negri E, Decarli A, Franceschi S (1997) Diabetes mellitus and the risk of primary liver cancer. Int J Cancer 73(2):204–207
La Vecchia C, Negri E, Franceschi S, D’Avanzo B, Boyle P (1994) A case-control study of diabetes mellitus and cancer risk. Br J Cancer 70(5):950–953
Goodman M, Cologne J, Moriwaki H, Vaeth M, Mabuchi K (1997) Risk factors for primary breast cancer in Japan: 8 year follow-up of atomic bomb survivors. Prev Med 26:144–153
Moseson M, Koenig K, Shore R, Pasternack B (1993) The influence of medical conditions associated with hormones on the risk of breast cancer. Int J Epidemiol 22:1000–1009
O’Mara BA, Byers T, Schoenfeld E (1985) Diabetes mellitus and cancer risk: a multisite case-control study. Journal of chronic diseases 38(5):435–441
Ragozzino M, Melton L, Chu C, Palumbo P (1982) Subsequent cancer risk in the incidence cohort of Rochester, Minnesota, residents with diabetes mellitus. Journal of chronic diseases 35:13–19
Wideroff L, Gridley G, Mellemkjaer L, Chow WH, Linet M, Keehn S et al (1997) Cancer incidence in a population-based cohort of patients hospitalized with diabetes mellitus in Denmark. J Natl Cancer Inst 89(18):1360–1365
Kreiger N, Marrett L, Dodds L, Hilditch S, Darlington G (1993) Risk factors for renal cell carcinoma: results of a population-based case-control study. Cancer Causes Control 4:101–110
Mellemgaard A, Niwa S, Mehl E, Engholm G, McLaughlin J, Olsen J (1994) Risk factors for renal cell carcinoma in Denmark: role of medication and medical history. Int J Epidemiol 23:923–930
Schlehofer B, Pommer W, Mellemgaard A, Stewart J, McCredie M, Niwa S et al (1996) International renal-cell-cancer study. VI. The role of medical and family history. Int J Cancer 66:723–726
Cerhan J, Wallace R, Folsom A, Potter J, Sellers T, Zheng W et al (1997) Medical history risk factors for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in older women. J Natl Cancer Inst 89:314–318
Shoff SM, Newcomb PA (1998) Diabetes, body size, and risk of endometrial cancer. Am J Epidemiol 148(3):234–240
Weiderpass E, Persson I, Adami HO, Magnusson C, Lindgren A, Baron JA (2000) Body size in different periods of life, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and risk of postmenopausal endometrial cancer (Sweden). Cancer Causes Control 11(2):185–192
Adler AI, Weiss NS, Kamb ML, Lyon JL (1996) Is diabetes mellitus a risk factor for ovarian cancer? A case-control study in Utah and Washington (United States). Cancer Causes Control 7(4):475–478
Adami H, McLaughlin J, Ekbom A, Berne C, Silverman D, Hacker D et al (1991) Cancer risk in patients with diabetes mellitus. Cancer Causes Control 2:307–314
Adler A, Weiss N, Kamb M, Lyon J (1996) Is diabetes mellitus a risk factor for ovarian cancer? A case-control study in Utah and Washington (United States). Cancer Causes Control 7:475–478
Coughlin S, Calle E, Teras L, Petrelli J, Thun M (2004) Diabetes mellitus as a predictor of cancer mortality in a large cohort of US adults. Am J Epidemiol 159:1160–1167
Giovannucci E, Michaud D (2007) The role of obesity and related metabolic disturbances in cancers of the colon, prostate, and pancreas. Gastroenterology 132:2208–2225
Inoue M, Iwasaki M, Otani T, Sasazuki S, Noda M, Tsugane S (2006) Diabetes mellitus and the risk of cancer: results from a large-scale population-based cohort study in Japan. Arch Intern Med 166:1871–1877
Kuriki K, Hirose K, Tajima K (2007) Diabetes and cancer risk for all and specific sites among Japanese men and women. Eur J Cancer Prev 16:83–89
Nilsen T, Vatten L (2001) Prospective study of colorectal cancer risk and physical activity, diabetes, blood glucose and BMI: exploring the hyperinsulinaemia hypothesis. Br J Cancer 84:417–422
Folsom AR, Anderson KE, Sweeney C, Jacobs DR Jr (2004) Diabetes as a risk factor for death following endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol 94(3):740–745
Bendelac J (2009) Membership in sick funds 2008. Israel National Insurance Institute, Jerusalem
Chodick G, Heymann A, Shalev V, Kookia E (2003) The epidemiology of diabetes in a large Israeli HMO. Eur J Epidemiol 18:1143–1146
Heymann A, Chodick G, Halkin H, Karasik A, Shalev V, Shemer J et al (2006) The implementation of managed care for diabetes using medical informatics in a large preferred provider organization. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 71:290–298
American Diabetes Association (2002) Management of dyslipidemia in adults with diabetes. Diabetes Care 25(Suppl. 1):S74–S77
Heymann A, Chodick G, Halkin H, Kokia E, Shalev V (2007) Description of a diabetes disease register extracted from a central database. Harefuah 146:15–79
Israel Center for Disease Control (1999) Health status in Israel 1999. Tel-Hashomer: Israel ministry of health. Report no.: 209
Israel Central Bureau of Statistics (1998) 1995 Census of population and housing Jerusalem
Cox DR (1972) Regression models and life tables (with discussion). J R Stat Soc B 32:187–220
Larsson S, Orsini N, Wolk A (2005) Diabetes mellitus and risk of colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst 97:1679–1687
Hu F, Manson J, Liu S, Hunter D, Colditz G, Michels K (1999) Prospective study of adult onset diabetes mellitus (type 2) and risk of colorectal cancer in women. J Natl Cancer Inst 91:542–547
Huxley R, Ansary-Moghaddam A, Berrington de González A, Barzi F, Woodward M (2005) Type-II diabetes and pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis of 36 studies. Br J Cancer 92:2076–2083
Le Marchand L, Wilkens L, Kolonel L, Hankin J, Lyu L (1997) Associations of sedentary lifestyle, obesity, smoking, alcohol use, and diabetes with the risk of colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 57:4787–4794
Limburg P, Anderson K, Johnson T, Jacobs D Jr, Lazovich D, Hong C (2005) Diabetes mellitus and subsite-specific colorectal cancer risks in the Iowa Women’s Health Study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14:133–137
O’Mara B, Byers T, Schoenfeld E (1985) Diabetes mellitus and cancer risk: a multisite case-control study. J Chronic Dis 38:435–441
Wei E, Ma J, Pollak M, Rifai N, Fuchs C, Hankinson S et al (2005) A prospective study of C-Peptide, insulin-like growth Factor-I, insulin-like growth factor binding Protein-1, and the risk of colorectal cancer in women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14:850–855
Khaw K, Wareham N, Bingham S, Luben R, Welch A, Day N (2004) Preliminary communication: glycated hemoglobin, diabetes, and incident colorectal cancer in men and women: a prospective analysis from the European prospective investigation into cancer-Norfolk study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 13:915–919
Kasper J, Liu Y, Giovannucci E (2009) Diabetes mellitus and risk of prostate cancer in the health professionals follow-up study. Int J Cancer 124:1398–1403
Waters K, Henderson B, Stram D, Wan P (2009) LN. K, Haiman C. Association of Diabetes With Prostate Cancer Risk in the Multiethnic Cohort. Am J Epidemiol. 169:937–945
Weissmann A, Linn S, Weltfriend S, Friedman-Birnbaum R (2000) Epidemiological study of classic Kaposi’s sarcoma: a retrospective review of 125 cases from northern Israel. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 14:91–95
Anderson L, Lauria C, Romano N, Brown E, Whitby D, Graubard B et al (2008) Risk factors for classical Kaposi sarcoma in a population-based case-control study in Sicily. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 17:3435–3443
Scott T, Carroll M, Cogliano F, Smith B, Lamorte W (1999) A case-control assessment of risk factors for gallbladder carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci 44:1619–1625
Strom B, Soloway R, Rios-Dalenz J, Rodriguez-Martinez H, West S, Kinman J et al (1995) Risk factors for gallbladder cancer. An international collaborative case-control study. Cancer 76:1747–1756
Yagyu K, Lin Y, Obata Y, Kikuchi S, Ishibashi T, Kurosawa M et al (2004) Bowel movement frequency, medical history and the risk of gallbladder cancer death: a cohort study in Japan. Cancer Sci 95:674–678
Zatonski W, Lowenfels A, Boyle P, Maisonneuve P, Bueno de Mesquita H, Ghadirian P et al (1997) Epidemiologic aspects of gallbladder cancer: a case-control study of the SEARCH program of the international agency for research on cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 89:1132–1138
Xue F, Michels K (2007) Diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and breast cancer: a review of the current evidence. Am J Clin Nutr 86:s823–s835
Iezzoni L (1997) Assessing quality using administrative data. Ann Intern Med 127:666–674
Szklo M, Javier Nieto F (2007) Epidemiology: beyond the basics Sudbury, mass. Aspen, Gaithersburg, MD
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Gabriel Chodick had full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chodick, G., Heymann, A.D., Rosenmann, L. et al. Diabetes and risk of incident cancer: a large population-based cohort study in Israel. Cancer Causes Control 21, 879–887 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-010-9515-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-010-9515-8