Abstract
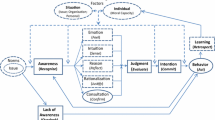
This study used structural equation modeling to verify the performance of the ethical decision-making models developed by Jones and by Kelley and Elm. A comparison showed that the Kelley and Elm decision model yielded the optimal degree of fit. The investigations conducted in this study indicated that moral intensities are not an objective, existing concept but rather the product of subjective perception influenced by organizational factors. In addition to directly influencing ethical decisions, organizational factors indirectly influence ethical decisions through moral intensities.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaah, I. P. (1992). Social inclusion as a marketing ethics correlate. Journal of Business Ethics, 11(8), 599–608.
Akaike, H. (1987). Factor analysis and AIC. Psychometrika, 52(3), 317–332.
Bandura, A. (1986). Social foundations of thought and action: A social cognitive theory. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall.
Barnett, T. (2001). Dimensions of morla intensity and ethical decision making: An empirical study. Joural of Applied Social Psychology, 31(5), 1038–1057.
Bauman, Z. (1995). Life in fragments: Essays in postmodern morality. Malden: Wiley-Blackwell.
Bentler, P. M. (1980). Multivariate analysis with latent variables: Causal modeling. Annual Review of Psychology, 31(1), 419–456.
Bentler, P. M., & Bonett, D. G. (1980). Significance tests and goodness of fit in the analysis of covariance structures. Psychological Bulletin, 88, 588–606.
Berman, B. J. (1990). Perfecting the machine: Instrumental rationality and the bureaucratic ideologies of the state. World Futures: Journal of General Evolution, 28(1–4), 141–161.
Chao, G. T., O Leary-Kelly, A. M., Klein, H. J., & Garnder, P. D. (1994). Organizational socialization: Its contents and consequences. Journal of Applied Psychology, 79(5), 730–743.
Chia, A., & Lim, S. M. (2000). The effects of issue characteristics on the recognition of moral issues. Journal of Business Ethics, 27(3), 255–269.
Cooper, T. L. (1987). Hierarchy, virtue, and the practice of public administration: A perspective for normative ethics. Public Administration Review, 474, 320–328.
Cooper, T. L. (2001). The responsible administrator: An approach to ethics for administrative role (4th ed.). San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Cudeck, R., & Browne, M. W. (1983). Cross-validation of covariance structures. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 18(2), 147–167.
Darley, J., & Latane, B. (1968). Bystander intervention in emergencies: Diffusion of responsibility. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 8(4), 377–383.
Dubinsky, A. J., & Loken, B. (1989). Analyzing ethical decision making in marketing. Journal of Business Research, 19(2), 83–107.
Ferrell, O. C., & Gresham, L. G. (1985). A contingency framework for understanding ethical decision making in marketing. The Journal of Marketing, 49(3), 87–96.
Ferrell, O. C., & Skinner, S. J. (1988). Ethical behavior and bureaucratic structure in marketing research organizations. Journal of Marketing Research, 25(1), 103–109.
Ford, R., & Richardson, W. (1994). Ethical decision making: A review of the empirical literature. Journal of Business Ethics, 13(3), 205–221.
Fraboni, M., & Cooper, D. (1989). Further validation of three short forms of the Marlowe-Crowne scale of social desirability. Psychological Reports, 65, 595–600.
Hofstede, G., & Hofstede, G. J. (2005). Cultures in organizations. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Hu, L., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 6(1), 1–55.
Hunt, S. D., & Vitell, S. J. (1986). A general theory of marketing ethics. Journal of macromarketing, 6(1), 5–16.
Janis, I. L. (1972). Victims of groupthink: A psychological study of foreign-policy decisions and fiascoes. New York: Houghton Mifflin.
Jones, T. M. (1991). Ethical decision making by individuals in organizations: An issue-contingent model. Academy of Management Review, 16(2), 366–395.
Kelley, P. C., & Elm, D. R. (2003). The effect of context on moral intensity of ethical issues: Revising Jones’s Issue-Contingent model. Journal of Business Ethics, 48(2), 139–154.
Kelman, H. C. (1973). Violence without moral restraint: Reflections on the dehumanization of victims and victimizers. Journal of Social Issues, 29(4), 25–61.
Kish-Gephart, J. J., Harrison, D. A., & Trevino, L. K. (2010). Bad apples, bad cases, and bad barrels: Meta-analytic evidence about sources of unethical decisions at work. Journal of Applied Psychology, 95(1), 1–31. doi:10.1037/a0017103.
Lo, H. H., Chen, C. H., & Chen, H. C. (2004). The relationship among leader types, follower types and leadership effectiveness: The members of military as sample. Journal National Defense Management, 22(5), 51–60.
Loe, T., Ferrell, L., & Mansfield, P. (2000). A review of empirical studies assessing ethical decision making in business. Journal of Business Ethics, 25(3), 185–204.
Lu, Z. J. (2002). The study on the relationships among elementary school teachers’ professional moral reasoning ego-strength and professional moral behavior. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, National Ping Tung University of Education, Taiwan.
Messick, D. M., & Bazerman, M. H. (1996). Ethical leadership and the psychology of decision making. Sloan Management Review, 37, 9–22.
Milgram, S. (1974). Obedience to authority: An experimental view. New York: Harper & Row.
O’Fallon, M. J., & Butterfield, K. D. (2005). A review of the empirical ethical decision-making literature: 1996–2003. Journal of Business Ethics, 59(4), 375–413.
Paolillo, J. G. P., & Vitell, S. J. (2002). An empirical investigation of the influence of selected personal, organizational and moral intensity factors on ethical decision making. Journal of Business Ethics, 35(1), 65–74.
Park, W.-W. (1989). Team players and teamwork: The new competitive business strategy. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Rest, J. (1986). Moral development: Advances in theory and research. New York: Praeger.
Smith, H. R., & Carroll, A. B. (1984). Organizational ethics: A stacked deck. Journal of Business Ethics, 3(2), 95–100.
Steiger, J. H. (1990). Structural model evaluation and modification: An interval estimation approach. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 25(2), 173–180.
Trevino, L. K. (1986). Ethical decision making in organizations: A person-situation interactionist model. The Academy of Management Review, 11(3), 601–627.
Wasieleski, D. M., & Hayibor, S. (2008). Breaking the rules: Examining the facilitation effects of moral intensity characteristics on the recognition of rule violations. Journal of Business Ethics, 78(1), 275–289.
Weber, J. (1990). Managers’ moral reasoning: Assessing their responses to three moral dilemmas. Human Relations, 43(7), 687–702.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, YM. Comparative Analysis of Jones’ and Kelley’s Ethical Decision-Making Models. J Bus Ethics 130, 573–583 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-014-2245-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-014-2245-1