Abstract
Background
Seroma formation is a common complication after mastectomy. This review aims to elucidate which surgical techniques are most effective in reducing the dead space and therefore seroma formation in patients undergoing mastectomy.
Methods
A literature search was performed to identify clinical studies comparing any form of flap fixation to conventional closure technique in patients undergoing mastectomy with or without axillary clearance. Studies were eligible for inclusion if outcome was described in terms of seroma formation and/or complications of seroma formation. Studies on animal research or breast reconstruction with tissue expanders or flap harvesting (latissimus dorsi) were excluded.
Results
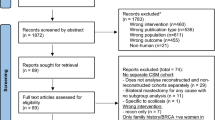
A total of nine articles were eligible for inclusion. Five were retrospective studies and four were prospective. Retrospective and prospective studies have demonstrated the higher incidence of seroma formation in patients not undergoing mechanical flap fixation. The incidence of seroma-related complications in these studies vary. Four out of the nine studies demonstrate that patients undergoing flap fixation, need significantly fewer seroma aspirations. There are very few studies on the use of tissue glues preventing seroma formation.
Conclusion
The scientific body of evidence favoring flap fixation after mastectomy is convincing. Mechanical flap fixation seems to reduce seroma formation and seroma aspiration after mastectomy. There are, however, no well-powered randomized controlled trials evaluating all aspects of seroma formation and its sequelae. Further research should elucidate whether flap fixation using sutures or tissue glue is superior.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carless PA et al (2006) Systematic review and meta-analysis of the use of fibrin sealant to prevent seroma formation after breast cancer surgery. Br J Surg 93(7):810–819
Kumar S et al (1995) Post-mastectomy seroma: a new look into the aetiology of an old problem. J R Coll Surg Edinb 40:292–294
Woodworth PA et al (2000) Seroma formation after breast cancer surgery; incidence and predicting factors. Am Surg 66(5):444–450
Tadych K et al (1987) Postmastectomy seromas and wound drainage. Surg Gynecol Obstet 165(6):483–487
Kumar S et al (1995) Post-mastectomy seroma: a new look into the aetiology of an old problem. J R Coll Surg Edinb 40:292–294
Almond LM et al (2010) Flap anchoring following primary breast cancer surgery facilitates early hospital discharge and reduces costs. Breast Care 5(2):97–101
Petrek J et al (1990) Axillary lymphadenectomy: a prospective, randomized trial of 13 factors influencing drainage, including early or delayed arm mobilization. Arch Surg 125:378–382
Hashemi E et al (2004) Seroma formation after surgery for breast cancer. World J Surg Oncol 9(2):44
Gonzalez EA et al (2003) Seroma formation following breast cancer surgery. Breast J 9(5):385–388
Porter KA et al (1998) Electrocautery as a factor in seroma formation following mastectomy. Am J Surg 176:8–11
Van Bemmel AJ et al (2011) Prevention of seroma formation after axillary dissection in breast cancer: a systematic review. Eur J Surg Oncol 37(10):829–835
Pogson CJ et al (2003) Seroma following breast cancer surgery. Eur J Surg Oncol 29:711–717
Agrawal A et al (2006) Concepts of seroma formation and prevention in breast cancer surgery. ANZ J Surg 76:1088–1095
Turner EJH et al (2014) Techniques in the prevention and management of seromas after breast surgery. Future Oncol 10(6):1049–1063
Kuroi K et al (2006) Effect of mechanical closure of dead space on seroma formation after breast surgery. Breast Cancer 13:260–265
Srivastava V et al (2012) Seroma formation after breast cancer surgery: what we have learned in the last two decades. J Breast Cancer 15(4):373–380
Liberati A et al (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLos Med 6(7):e1000100
Sakkary MA et al (2012) The value of mastectomy flap fixation in reducing fluid drainage and seroma formation in breast cancer patients. World J Surg Oncol 10:8
Ten Wolde B et al (2014) Quilting prevents seroma formation following breast cancer surgery: closing the dead space by quilting prevents seroma following axillary lymph node dissection and mastectomy. Ann Surg Oncol 21:802–807
Ouldamer L et al (2015) Quilting suture of mastectomy dead space compared with conventional closure with drain. Ann Surg Oncol 22:4233–4240
Khater A et al (2015) Evaluation of the quilting technique for reduction of postmastectomy seroma: a randomized controlled study. Int J Breast Cancer 2015:287398
Mazouni C et al (2015) Quilting sutures reduce seroma in mastectomy. Clin Breast Cancer 15(4):289–293
van Bastelaar J et al (2016) Flap fixation reduces seroma in patients undergoing mastectomy: a significant implication for clinical practice. World J Surg Oncol 8(14):66
Eichler C et al (2016) Flap adhesion and effect on postoperative complication rates using Tissuglu® in mastectomy patients. Breast Cancer 23:486–490
van Bastelaar J et al (2017) Flap fixation using tissue glue or sutures appears to reduce seroma aspiration after mastectomy for breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer 17(4):316–321
Taylor JC et al (2013) Breast cancer surgery without suction drainage: the impact of adopting a ‘no drains’ policy on symptomatic seroma formation rates. Eur J Surg Oncol 39(4):334–338
He XD et al (2011) Whether drainage should be used after surgery for breast cancer? A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Med Oncol 28(1):9010–9673
Divino CM et al (2000) Drains prevent seromas following lumpectomy with axillary dissection. Breast J 6(1):31–33
Somers RG et al (1992) The use of closed suction drainage after lumpectomy and axillary node dissection for breast cancer. Ann Surg 215(2):146–149
Zavotsky J et al (1998) Evaluation of axillary lymphadenectomy without axillary drainage for patients undergoing breast-conserving therapy. Ann Surg Oncol 5(3):227–231
Cameron AE et al (1988) Suction drainage of the axilla: a prospective randomized trial. Br J Surg 75(12):1211
Sajid MS et al (2013) Fibrin glue instillation under skin flaps to prevent seroma-related morbidity following breast and axillary surgery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 5:009557
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest and that no funding was involved.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Bastelaar, J., van Roozendaal, L., Granzier, R. et al. A systematic review of flap fixation techniques in reducing seroma formation and its sequelae after mastectomy. Breast Cancer Res Treat 167, 409–416 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-017-4540-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-017-4540-x