Abstract
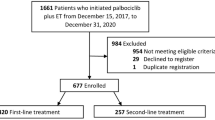
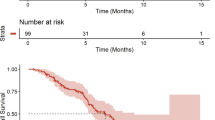
Amplified PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling is common in metastatic breast cancer (MBC). The mTOR inhibitor everolimus improves progression-free survival (PFS) when added to steroidal aromatase inhibitor therapy. This randomized phase II trial compares the efficacy of paclitaxel/bevacizumab/everolimus and paclitaxel/bevacizumab/placebo as first-line treatment for MBC. Patients with untreated HER2-negative MBC were randomized (1:1) to receive 28-day cycles of paclitaxel 90 mg/m2 IV (days 1, 8, and 15) and bevacizumab 10 mg/kg IV (days 1, 15) with either everolimus 10 mg (Arm 1) or placebo (Arm 2) daily. Treatment continued (evaluation every 8 weeks) until progression or unacceptable toxicity. Treatment of 110 patients allowed detection of an improvement in median PFS from 11 to 16 months (70 % power, α = 0.10). Between August 2009 and June 2011, 113 patients (median age 58 years; 88 % ER or PR positive) were randomized (Arm 1, 56; Arm 2, 57). Patients in both arms received a median of six treatment cycles. Median PFS (95 % CI) was 9.1 months (6.8–18.8) for Arm 1, and 7.1 months (5.6–10.8) for Arm 2 (p = 0.89). Comparisons of other efficacy endpoints were also similar in the two treatment arms. Patients receiving everolimus had more anemia, stomatitis, diarrhea, rash, and arthralgia/myalgia, although the overall incidence of severe (grade 3/4) toxicity was similar. The addition of everolimus did not improve the efficacy of weekly paclitaxel/bevacizumab as first-line treatment for patients with HER2-negative MBC. These results contrast with the demonstrated efficacy of adding everolimus to either hormonal or HER2-targeted therapy in previously treated patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A (2014) Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin 64:9–29
Miller K, Wang M, Gralow J, Dickler M, Cobleigh M, Perez EA, Shenkier T, Cella D, Davidson NE (2007) Paclitaxel plus bevacizumab versus paclitaxel alone for metastatic breast cancer. N Engl J Med 357:2666–2676
Miles DW, Chan A, Dirix LY, Cortes J, Pivot X, Tomczak P, Delozier T, Sohn JH, Provencher L, Puglisi F et al (2010) Phase III study of bevacizumab plus docetaxel compared with placebo plus docetaxel for the first-line treatment of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 28:3239–3247
Albanell J, Dalmases A, Rovira A, Rojo F (2007) mTOR signalling in human cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 9:484–493
Faivre S, Kroemer G, Raymond E (2006) Current development of mTOR inhibitors as anticancer agents. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:671–688
Zhao L, Vogt PK (2008) Class I PI3K in oncogenic cellular transformation. Oncogene 27:5486–5496
Baselga J, Campone M, Piccart M, Burris HA 3rd, Rugo HS, Sahmoud T, Noguchi S, Gnant M, Pritchard KI, Lebrun F et al (2012) Everolimus in postmenopausal hormone-receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med 366:520–529
Andre F, O’Regan R, Ozguroglu M, Toi M, Xu B, Jerusalem G, Masuda N, Wilks S, Arena F, Isaacs C et al (2014) Everolimus for women with trastuzumab-resistant, HER2-positive, advanced breast cancer (BOLERO-3): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 15:580–591
Declaration of Helsinki. www.wma.net/e/ethicsunit/helsinki.htm, World Medical Association, Ethics Unit, 2007
Eisenhauer E, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz L, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S, Mooney M et al (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumors: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45:228–247
Program, C.T.E. (2006). Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, Version 3.0. N. DCTD, NIH, DHHS, ed. (http://ctep.cancer.gov/protocolDevelopment/electronic_applications/ctc.htm#ctc_30). Accessed July 2015
Smith TJ, Khatcheressian J, Lyman GH, Ozer H, Armitage JO, Balducci L, Bennett CL, Cantor SB, Crawford J, Cross SJ et al (2006) 2006 update of recommendations for the use of white blood cell growth factors: an evidence-based clinical practice guideline. J Clin Oncol 24:3187–3205
Kaplan E, Meier P (1958) Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 53:457–481
Perren A, Weng LP, Boag AH, Ziebold U, Thakore K, Dahia PL, Komminoth P, Lees JA, Mulligan LM, Mutter GL et al (1999) Immunohistochemical evidence of loss of PTEN expression in primary ductal adenocarcinomas of the breast. Am J Pathol 155:1253–1260
Bachman KE, Argani P, Samuels Y, Silliman N, Ptak J, Szabo S, Konishi H, Karakas B, Blair BG, Lin C et al (2004) The PIK3CA gene is mutated with high frequency in human breast cancers. Cancer Biol Ther 3:772–775
Saal LH, Holm K, Maurer M, Memeo L, Su T, Wang X, Yu JS, Malmstrom PO, Mansukhani M, Enoksson J et al (2005) PIK3CA mutations correlate with hormone receptors, node metastasis, and ERBB2, and are mutually exclusive with PTEN loss in human breast carcinoma. Cancer Res 65:2554–2559
Ghayad SE, Vendrell JA, Ben Larbi S, Dumontet C, Bieche I, Cohen PA (2010) Endocrine resistance associated with activated ErbB system in breast cancer cells is reversed by inhibiting MAPK or PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Int J Cancer 126:545–562
Pandolfi PP (2004) Breast cancer–loss of PTEN predicts resistance to treatment. N Engl J Med 351:2337–2338
Stemke-Hale K, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Lluch A, Neve RM, Kuo WL, Davies M, Carey M, Hu Z, Guan Y, Sahin A et al (2008) An integrative genomic and proteomic analysis of PIK3CA, PTEN, and AKT mutations in breast cancer. Cancer Res 68:6084–6091
Lopez-Knowles E, O’Toole SA, McNeil CM, Millar EK, Qiu MR, Crea P, Daly RJ, Musgrove EA, Sutherland RL (2010) PI3K pathway activation in breast cancer is associated with the basal-like phenotype and cancer-specific mortality. Int J Cancer 126:1121–1131
Hurvitz SA, Andre F, Jiang Z, et al: Phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo- controlled mutlicenter trial of daily everolimus plus weekly trastuzumab and paclitaxel as first- line therapy in women with HER2+ advanced breast cancer: BOLERO-1. San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, 2014, Abstract # S6-01
Meric-Bernstam F, Gonzalez-Angulo AM (2009) Targeting the mTOR signaling network for cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol 27:2278–2287
Campbell RA, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Patel NM, Constantinidou D, Ali S, Nakshatri H (2001) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT-mediated activation of estrogen receptor alpha: a new model for anti-estrogen resistance. J Biol Chem 276:9817–9824
Simoncini T, Hafezi-Moghadam A, Brazil DP, Ley K, Chin WW, Liao JK (2000) Interaction of oestrogen receptor with the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase. Nature 407:538–541
deGraffenried LA, Friedrichs WE, Russell DH, Donzis EJ, Middleton AK, Silva JM, Roth RA, Hidalgo M (2004) Inhibition of mTOR activity restores tamoxifen response in breast cancer cells with aberrant Akt Activity. Clin Cancer Res 10:8059–8067
Creighton CJ, Fu X, Hennessy BT, Casa AJ, Zhang Y, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Lluch A, Gray JW, Brown PH, Hilsenbeck SG et al (2010) Proteomic and transcriptomic profiling reveals a link between the PI3K pathway and lower estrogen-receptor (ER) levels and activity in ER+ breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 12:R40
Wolff AC, Lazar AA, Bondarenko I, Garin AM, Brincat S, Chow L, Sun Y, Neskovic-Konstantinovic Z, Guimaraes RC, Fumoleau P et al (2013) Randomized phase III placebo-controlled trial of letrozole plus oral temsirolimus as first-line endocrine therapy in postmenopausal women with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 31:195–202
Dupont Jensen J, Laenkholm AV, Knoop A, Ewertz M, Bandaru R, Liu W, Hackl W, Barrett JC, Gardner H (2011) PIK3CA mutations may be discordant between primary and corresponding metastatic disease in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 17:667–677
Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Ferrer-Lozano J, Stemke-Hale K, Sahin A, Liu S, Barrera JA, Burgues O, Lluch AM, Chen H, Hortobagyi GN et al (2011) PI3K pathway mutations and PTEN levels in primary and metastatic breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 10:1093–1101
Bachelot T, Bourgier C, Cropet C, Guastalla J-P, Ferrero J-M, Leger-Falandry C, Soulie P, Eymard J-C, Debled M, Spaeth D et al (2011) Abstract S1-6: TAMRAD: A GINECO randomized phase II trial of everolimus in combination with tamoxifen versus tamoxifen alone in patients (pts) with hormone-receptor positive, HER2 negative metastatic breast cancer (MBC) with prior exposure to aromatase inhibitors (AI). Cancer Res 70:S1–S6
Acknowledgments
Supported in part by a grant from Novartis
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
DAY is a consultant for Novartis. LDB is a consultant for Genentech and GSK. JAO is a consultant for Novartis. All other authors declare they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
http://www.ClinicalTrials.gov. Identifier: NCT00915603.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yardley, D.A., Bosserman, L.D., O’Shaughnessy, J.A. et al. Paclitaxel, bevacizumab, and everolimus/placebo as first-line treatment for patients with metastatic HER2-negative breast cancer: a randomized placebo-controlled phase II trial of the Sarah Cannon Research Institute. Breast Cancer Res Treat 154, 89–97 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-015-3599-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-015-3599-5