Abstract
Pathogenic germline mutations in the BRCA1 gene predispose carriers to early onset breast and ovarian cancer. Clinical genetic screening of BRCA1 often reveals variants with uncertain clinical significance, complicating patient and family management. Therefore, functional examinations are urgently needed to classify whether these uncertain variants are pathogenic or benign. In this study, we investigated 14 BRCA1 variants by in silico splicing analysis and mini-gene splicing assay. All 14 alterations were missense variants located within the BRCT domain of BRCA1 and had previously been examined by functional analysis at the protein level. Results from a validated mini-gene splicing assay indicated that nine BRCA1 variants resulted in splicing aberrations leading to truncated transcripts and thus can be considered pathogenic (c.4987A>T/p.Met1663Leu, c.4988T>A/p.Met1663Lys, c.5072C>T/p.Thr1691Ile, c.5074G>C/p.Asp1692His, c.5074G>A/p.Asp1692Asn, c.5074G>T/p.Asp1692Tyr, c.5332G>A/p.Asp1778Asn, c.5332G>T/p.Asp1778Tyr, and c.5408G>C/p.Gly1803Ala), whereas five BRCA1 variants had no effect on splicing (c.4985T>C/p.Phe1662Ser, c.5072C>A/p.Thr1691Lys, c.5153G>C/p.Trp1718Ser, c.5154G>T/p.Trp1718Cys, and c.5333A>G/p.Asp1778Gly). Eight of the variants having an effect on splicing (c.4987A>T/p.Met1663Leu, c.4988T>A/p.Met1663Lys, c.5074G>C/p.Asp1692His, c.5074G>A/p.Asp1692Asn, c.5074G>T/p.Asp1692Tyr, c.5332G>A/p.Asp1778Asn, c.5332G>T/p.Asp1778Tyr, and c.5408G>C/p.Gly1803Ala) were previously determined to have no or an uncertain effect on the protein level, whereas one variant (c.5072C>T/p.Thr1691Ile) were shown to have a strong effect on the protein level as well. In conclusion, our study emphasizes that in silico splicing prediction and mini-gene splicing analysis are important for the classification of BRCA1 missense variants located close to exon/intron boundaries.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Germline mutations in the BRCA1 (MIM 113705) tumor suppressor gene confer an increased lifetime risk of breast and ovarian cancer. The absolute risk of cancer by the age of 70 years conferred by BRCA1 mutations in female carriers is reported to be between 60 and 71 % for breast cancer and between 39 and 59 % for ovarian cancer [1–4]. Mutational screening has identified a large number of pathogenic BRCA1 mutations in women with a family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer. Unfortunately, a substantial proportion of the sequence alterations identified during routine genetic testing are in-frame deletions/insertions, missense, silent, and intronic variants of uncertain clinical significance (VUS). A number of 1273 BRCA1 VUS’s have been reported by the ENIGMA (Evidence-Based Network for the Interpretation of Germline Mutant Alleles) consortium (up until September 2010) [5]. Of these, the majority are missense variants, constituting a number of 781 unique variants. The identification of a VUS is associated with a complicated cancer risk assessment, genetic counseling, and clinical management of the patients and their families. Because most VUS occur at very low population frequencies, direct epidemiological measures, such as association studies, are often not adequately powerful to identify the variants associated with cancer predisposition [6]. A promising approach is to add functional studies to characterize the biological effect of the variants and thereby provide clinicians with a better framework for counseling and treatment. It has been shown that a large portion of BRCA1 variants induce splicing defects [7]. Ideally, RNA from a patient should be examined by RT-PCR analysis to establish if a variant has an effect on splicing. However, in many cases, RNA is not available from the patient. Alternatively, the sequence variant can be examined by mini-gene splicing analysis, which has been shown to be a valid method for investigating the impact of an alteration on the splicing pattern [8, 9]. Here, we report the functional characterization of 14 BRCA1 variants using in silico splicing analysis and a validated mini-gene splicing assay [10]. All 14 variants were located in close proximity to splice donor/acceptor sites in the highly conserved BRCT domain and had previously been investigated by protein folding, phosphopeptide-binding, and cell-based transcriptional assays [11]. The BRCT domain plays a critical role in tumor suppression and is considered to be one of two regions to contain the vast majority of cancer-associated mutations [12–16]. In summary, our study classified nine BRCA1 variants as pathogenic as these variants affect mRNA splicing leading to out-of-frame exon skipping or the use of cryptic splice sites resulting in truncated transcripts, while five BRCA1 variants were shown to have no effect on splicing.
Materials and methods
Variant nomenclature
All missense variants were selected from the Breast Cancer Information Core (BIC) database [17] and the literature [11] based on the close proximity to the splice acceptor and splice donor sites. The BRCA1 variants are numbered according to the guidelines from the Human Genome Variation Society (http://www.hgvs.org/mutnomen) using NCBI Reference Sequence NG_005905.2.
In silico analysis
The following five splice site prediction programs were used to predict the effect of variants on the efficiency of splicing: Splice Site Finder (http://www.interactive-biosoftware.com); GeneSplicer (http://www.cbcb.umd.edu/software/GeneSplicer); Splice Site Prediction by Neural Network (http://www.fruitfly.org/seq_tools/splice.html); MaxEntScan (http://genes.mit.edu/burgelab/maxent/Xmaxentscan_scoreseq.html); and Human Splicing Finder (http://www.umd.be/HSF/). The analysis was performed by the integrated software Alamut version 2.4 (http://www.interactive-biosoftware.com) using default settings in all predictions. A variation of more than 10 % in at least two algorithms was considered as having an effect on splicing [9].
Mini-gene splicing assay
Wild-type BRCA1 exons were cloned into the pSPL3 vector (Fig. 1) and single nucleotide substitutions were introduced by mutagenesis performed using Finnzymes’ Phusion High-Fidelity polymerase according to the accompanying instructions. Wild-type and mutant constructs were transfected in duplicate into COS-7 cells as recently described [10]. Cells were harvested after 48 h and total RNA was extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen). cDNA was synthesized using 1 µg of total RNA, M-MuLV reverse transcriptase polymerase (New England Biolabs), and 20 µM of nucleotide oligo(dT)15 primer. cDNA was amplified with Phusion DNA polymerase using the primers dUSD2 (5′-TCTGAGTCACCTGGACAACC-3′) and dUSA4 (5′-ATCTCAGTGGTATTTGTGAGC-3′). PCR products were separated by electrophoresis on a 1 % agarose gel containing ethidium bromide and quantified using Image Lab 2.0 software (Bio-Rad) (Fig. 2). Each DNA band was gel purified using GE Healthcare’s Illustra GFX PCR DNA and Gel Band Purification Kit and sequenced with the dUSD2 and dUSA4 primers.
Overview of BRCA1 constructs. The different exons were cloned into the pSPL3 vector including a minimum of 250 bp intronic sequence. The exon–intron boundary sequence is shown and the mutated nucleotide is marked in bold for each BRCA1 construct. BRCA1 constructs covering: a exon 16, b exon 17, c exon 19, d exon 21, e exon 22, and f exon 23. IVS: intervening sequence, SA: splice acceptor site, SD: splice donor site, bp: basepair
Mini-gene splicing analysis of BRCA1 variants. COS-7 cells were transfected with wild-type or mutant vectors in duplicate. Total RNA was isolated, RT-PCR analysis was performed, and PCR products were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis and visualized by ethidium bromide staining. Gel band intensities were quantified (Quant.) using the Image Lab 2.0 software. The sizes of the DNA marker (M) are indicated to the left. All PCR products were verified by Sanger sequencing. a The BRCA1 c.4985T>C/p.Phe1662Ser variant generated a strong 488-bp band corresponding to wild-type exon 16 (unaltered splicing) as well as a weak 177-bp band lacking exon 16 also present in the wild-type. b The BRCA1 c.4987A>T/p.Met1663Leu, c.4988T>A/p.Met1663Lys, c.5072C>T/p.Thr1691Ile, c.5074G>C/p.Asp1692His, c.5074G>A/p.Asp1692Asn, and c.5074G>T/p.Asp1692Tyr variants all resulted in one strong band of 177 bp lacking exon 17. Moreover, c.4988T>A/p.Met1663Lys and c.5072C>T/p.Thr1691Ile also revealed a very weak wild-type band including exon 17, while c.5074G>A/p.Asp1692Asn, c.5074G>C/p.Asp1692His, and c.5074G>T/p.Asp1692Tyr also generated a weak band comprising of 418 bp containing 153 bp of intron 17. The c.5072C>A/p.Thr1691Lys variant had no major effect on splicing compared to the wild-type exon 17 (unaltered splicing). c The BRCA1 c.5153G>C/p.Trp1718Ser and c.5154G>T/p.Trp1718Cys alterations both generated a 218-bp PCR product corresponding to wild-type exon 19 (unaltered splicing). d The BRCA1 c.5332G>A/p.Asp1778Asn and c.5332G>T/p.Asp1778Tyr variants both resulted in one strong band of 177 bp lacking exon 21. e The BRCA1 c.5333A>G/p.Asp1778Gly variant produced a 251-bp product corresponding to wild-type exon 22 (unaltered splicing). f The BRCA1 c.5408G>C/p.Gly1803Ala variant resulted in one strong band of 177 bp lacking exon 23
Results
Previous studies have shown that a large portion of BRCA1 variants induce splicing defects [7]. In the present study, 14 BRCA1 variants located near splice acceptor or donor sites in the conserved BRCT domain were examined using in silico splicing analysis and a validated mini-gene splicing assay [7, 10] (Table 1). The in silico splicing analysis was performed using five different splice site prediction programs which predict changes in splice site strength. The applicable threshold was a variation between the wild-type and the variant score of more than 10 % in at least two different algorithms [9]. According to this criterion, 10 BRCA1 variants (c.4987A>T/p.Met1663Leu, c.4988T>A/p.Met1663Lys, c.5072C>T/p.Thr1691Ile, c.5074G>C/p.Asp1692His, c.5074G>A/p.Asp1692Asn, c.5074G>T/p.Asp1692Tyr, c.5153G>C/p.Trp1718Ser, c.5332G>A/p.Asp1778Asn, c.5332G>T/p.Asp1778Tyr, and c.5408G>C/p.Gly1803Ala) (Table 1) were suggested to weaken the splice site strength, whereas the remaining four variants (c.4985T>C/p.Phe1662Ser, c.5072C>A/p.Thr1691Lys, c.5154G>T/p.Trp1718Cys, and c.5333A>G/p.Asp1778Gly) were not.
The functional effects of all 14 BRCA1 variants on mRNA splicing were subsequently examined by mini-gene splicing assays. Each construct was transfected into COS-7 cells in duplicate and cells were harvested. mRNA was then purified and analyzed by RT-PCR. Finally, PCR products were visualized by ethidium bromide staining of 1 % agarose gels (Fig. 2a–f) and sequenced. In line with the in silico splicing results, nine BRCA1 variants (c.4987A>T/p.Met1663Leu, c.4988T>A/p.Met1663Lys, c.5072C>T/p.Thr1691Ile, c.5074G>C/p.Asp1692His, c.5074G>A/p.Asp1692Asn, c.5074G>T/p.Asp1692Tyr, c.5332G>A/p.Asp1778Asn, c.5332G>T/p.Asp1778Tyr, and c.5408G>C/p.Gly1803Ala) revealed the presence of alternative gel bands compared to the corresponding wild-types. The wild-type BRCA1 exon 17 construct revealed the presence of one major transcript comprising the expected 265 bp containing exon 17 and a very weak band of 177 bp lacking exon 17. The c.4987A>T/p.Met1663Leu, c.4988T>A/p.Met1663Lys, c.5072C>T/p.Thr1691Ile, c.5074G>C/p.Asp1692His, c.5074G>A/p.Asp1692Asn, and c.5074G>T/p.Asp1692Tyr variants all yielded one major band of 177 bp lacking exon 17 (Fig. 2b). In addition to the 177 bp band, the c.5074G>A/p.Asp1692Asn, c.5074G>C/p.Asp1692His, and c.5074G>T/p.Asp1692Tyr alterations generated a weaker band comprising of 418 bp containing 153 bp of intron 17 by the usage of a cryptic splice donor site. Furthermore, besides the 177 bp band, the c.4988T>A/p.Met1663Lys and c.5072C>T/p.Thr1691Ile variants presented with a very weak wild-type band at 265 bp constituting 7 % and 17.5 % of the total amount of transcript, respectively (Fig. 2b). Wild-type BRCA1 exon 21 generated one transcript at the expected 232 bp, while the c.5332G>A/p.Asp1778Asn and c.5332G>T/p.Asp1778Tyr variants resulted in one strong band of 177 bp excluding exon 21 (Fig. 2d). Finally, wild-type BRCA1 exon 23 revealed a single transcript at the expected size of 238 bp, while c.5408G>C/p.Gly1803Ala resulted in one strong band of 177 bp lacking exon 23 (Fig. 2f). In contrast to the in silico splicing data, c.5153G>C/p.Trp1718Ser (Fig. 2c) did not show any splicing abnormality since both the wild-type BRCA1 exon 19 and the c.5153G>C/p.Trp1718Ser variant generated one strong band at the expected size of 218 bp containing exon 19. In accordance with the in silico splicing results, the remaining four variants (c.4985T>C/p.Phe1662Ser, c.5072C>A/p.Thr1691Lys, c.5154G>T/p.Trp1718Cys, and c.5333A>G/p.Asp1778Gly) (Fig. 2a–d) showed no difference in size or intensity of the bands between wild-type and mutant constructs.
Discussion
Genetic screening for pathogenic mutations in breast and ovarian cancer genes BRCA1 and BRCA2 is common practice for individuals from high-risk families. However, the test often results in identification of a VUS, leading to impeded cancer risk estimation and clinical management [18]. Therefore, it is important to classify all identified BRCA1/BRCA2 sequence variants [19]. It has previously been established that all variation types in BRCA1 can lead to splicing abnormalities [7]. Hence, it is important to include investigations at the RNA level when classifying a variant.
In this study, we examined 14 BRCA1 variants located in close proximity to the exon–intron boundary regarding their effect on mRNA splicing using in silico splicing analysis along with a validated mini-gene splicing assay [10]. All variants are very rare in the general population, and only two of the variants (c.4985T>C and c.5333A>G) have been reported once in the ExAC database containing data from approximately 60,000 unrelated individuals with different population origin [20].
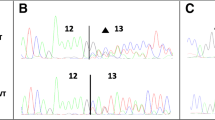
Six variants (c.4987A>T/p.Met1663Leu, c.4988T>A/p.Met1663Lys, c.5072C>T/p.Thr1691Ile, c.5074G>C/p.Asp1692His, c.5074G>A/p.Asp1692Asn, and c.5074G>T/p.Asp1692Tyr) were shown to cause out-of-frame skipping of exon 17 (Fig. 2B), a result that was in agreement with the results predicted by in silico splicing analysis (Table 1) [11]. The c.4987A>T/p.Met1663Leu, c.4988T>A/p.Met1663Lys, and c.5072C>T/p.Thr1691Ile variants are reported in the BIC database as VUS. Functional studies and in silico predictions have previously shown that the c.4987A>T/p.Met1663Leu and c.4988T>A/p.Met1663Lys missense variants had low or no functional effect on protein level [11, 21, 22]. In contrast, functional and in silico studies showed that the c.5072C>T/p.Thr1691Ile variant had a strong effect on protein function [11, 21].
The c.5074G>C/p.Asp1692His, c.5074G>A/p.Asp1692Asn, and c.5074G>T/p.Asp1692Tyr missense variants are reported in the BIC database as variants of clinical importance. Studies on the protein level classified c.5074G>C/p.Asp1692His as having an uncertain effect on protein function [11], while in silico and functional studies showed that the c.5074G>A/p.Asp1692Asn variant, previously reported as an Icelandic founder mutation [23], had low or no impact on the protein level [11, 22, 24]. The c.5074G>T/p.Asp1692Tyr variant has been predicted to have an effect on the protein level by in silico analysis [21, 22] as well as in one functional assay based on measurement of the thermodynamic stability of the BRCA1 BRCT domain [22], while other functional assays based on proteolysis, phosphopeptide-binding, and transcription assays were inconclusive [11]. In this study, the c.5074G>A/p.Asp1692Asn, c.5074G>C/p.Asp1692His, and c.5074G>T/p.Asp1692Tyr variants were shown to induce skipping of exon 17 as well as usage of a cryptic splice donor site located at c.5074 + 153 in intron 17. The use of this cryptic splice site has previously been reported for the c.5074G>C/p.Asp1692His variant using lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs) or patient blood samples [25, 26].
The two variants, c.5332G>A/p.Asp1778Asn and c.5332G>T/p.Asp1778Tyr, located in exon 21 near the exon–intron boundary also resulted in out-of-frame exon skipping (Fig. 2d) and hence are classified as pathogenic. The c.5332G>A/p.Asp1778Asn variant is reported once in the BIC database as a VUS, whereas the c.5332G>T/p.Asp1778Tyr variant has not previously been reported. Our data regarding the c.5332G>A/p.Asp1778Asn variant are in agreement with recent splicing data using RNA from patient blood samples [27]. Both the c.5332G>A/p.Asp1778Asn variant and the c.5332G>T/p.Asp1778Tyr variant have previously been shown to have no effect on protein level using functional assays and in silico analysis [11, 12, 21, 22].
The final variant that showed aberrant splicing using the mini-gene splicing assay was c.5408G>C/p.Gly1803Ala (Fig. 2f). This variant caused out-of-frame skipping of exon 23 of BRCA1. The c.5408G>C/p.Gly1803Ala variant has been reported three times in the BIC database as a VUS and functional studies as well as in silico analysis showed that the variant had an uncertain or no effect on the protein level [11, 21].
The following five variants—c.4985T>C/p.Phe1662Ser, c.5072C>A/p.Thr1691Lys, c.5153G>C/p.Trp1718Ser, c.5154G>T/p.Trp1718Cys, and c.5333A>G/p.Asp1778Gly—did not show any splicing abnormality when investigated by the mini-gene splicing assay (Fig. 2a–c, e). This result was in accordance with the in silico splicing prediction except for the c.5153G>C/p.Trp1718Ser variant which was suggested to affect splicing by all the programs used (Table 1). All five variants are reported in the BIC database as VUS. Three variants (c.5072C>A/p.Thr1691Lys, c.5153G>C/p.Trp1718Ser, and c.5154G>T/p.Trp1718Cys) have been shown to have a strong functional effect on the protein level [11]. In addition, structural examination of c.5072C>A/p.Thr1691Lys showed that the alteration significantly disturbed the surface of the binding pocket interacting with the BACH1 phosphorylated peptide [28–30]. Both c.4985T>C/p.Phe1662Ser and c.5333A>G/p.Asp1778Gly missense variants have been reported to have a low functional effect on the protein level [11]. In addition, the c.4985T>C/p.Phe1662Ser variant has previously been classified as a variant of no clinical significance based on in silico analysis [31]. Finally, the c.5333A>G/p.Asp1778Gly variant has previously been tested for its effect on mRNA splicing using LCLs or patient blood samples [25, 32], and the results are in agreement with the result shown in Fig. 2e.
The mini-gene assay used in this study has recently been validated and showed a 100 % concordance with results using patient blood samples [10]. However, there are limitations using a mini-gene assay, since the assay examine the expression of an artificial transcript usually containing one exon and varying amounts of flanking intron sequences, compared to assessing the natural endogenous expression of BRCA1 transcripts. The use of mini-gene constructs containing only one exon will moreover miss more complex changes (e.g. skipping of more exons). Finally, the COS-7 cell line used in the mini-gene assay may not fully reflect the splicing machinery used in breast tissue. However, since BRCA1 alternative splicing is similar in breast tissue and blood samples [33], and the use of COS-7 cells showed a 100 % concordance with results using patient blood samples [10], we infer that the basal splicing machinery necessary for correct BRCA1 splicing is present in COS-7 cells.
Another caveat is the finding that natural occurring BRCA1 isoforms lacking exons 17, 21, and 23 exist [33]. However, since other BRCA1 variants inducing exon 17, 21, and 23 skipping are classified as pathogenic in the BIC database (c.4987-1G>A, c.5074 + 1G>T, c.5074 + 1G>A, c.5074 + 2T>C, c.5278-1G>T, c.5332 + 1G>A, c.5407-1G>A, c.5407-2A>T, c.5467 + 1G>A, and c.5467 + 2T>C), we classify BRCA1 exon 17, 21, and 23 missense variants inducing skipping as pathogenic (class 5) even though minor amounts of naturally occurring transcripts lacking these exons exist.
In conclusion, using in silico splicing prediction and a validated mini-gene splicing assay, we classified nine BRCA1 variants as pathogenic (c.4987A>T/p.Met1663Leu, c.4988T>A/p.Met1663Lys, c.5072C>T/p.Thr1691Ile, c.5074G>C/p.Asp1692His, c.5074G>A/p.Asp1692Asn, c.5074G>T/p.Asp1692Tyr, c.5332G>A/p.Asp1778Asn, c.5332G>T/p.Asp1778Tyr, and c.5408G>C/p.Gly1803Ala), since the variants affected mRNA splicing leading to out-of-frame exon skipping or the use of cryptic splice sites resulting in truncated transcripts. All nine variants had previously been investigated at the protein level but only one of the variants (c.5072C>T/p.Thr1691Ile) showed a strong functional effect [11, 21]. The remaining five BRCA1 variants (c.4985T>C/p.Phe1662Ser, c.5072C>A/p.Thr1691Lys, c.5153G>C/p.Trp1718Ser, c.5154G>T/p.Trp1718Cys, and c.5333A>G/p.Asp1778Gly) had no effect on splicing when examined by the mini-gene splicing assay. However, three of these variants (c.5072C>A/p.Thr1691Lys, c.5153G>C/p.Trp1718Ser, and c.5154G>T/p.Trp1718Cys) had previously been shown to have a strong functional effect on the protein level [11]. Our results clearly demonstrate the relevance of assessing missense variants for possible splicing defects before final classification. However, the splicing data should, when possibly, be combined with multifactorial likelihood analysis, based on co-segregation, family history, tumor pathology, and co-occurrence with a pathogenic BRCA1 mutation to support the conclusions before the findings are used in the clinic.
References
Antoniou A, Pharoah PD, Narod S et al (2003) Average risks of breast and ovarian cancer associated with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations detected in case Series unselected for family history: a combined analysis of 22 studies. Am J Hum Genet 72(5):1117–1130
King MC, Marks JH, Mandell JB (2003) Breast and ovarian cancer risks due to inherited mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2. Science 302(5645):643–646
van der Kolk DM, de Bock GH, Leegte BK et al (2010) Penetrance of breast cancer, ovarian cancer and contralateral breast cancer in BRCA1 and BRCA2 families: high cancer incidence at older age. Breast Cancer Res Treat 124(3):643–651
Mavaddat N, Peock S, Frost D et al (2013) Cancer risks for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers: results from prospective analysis of EMBRACE. J Natl Cancer Inst 105(11):812–822
Spurdle AB, Healey S, Devereau A et al (2012) ENIGMA–evidence-based network for the interpretation of germline mutant alleles: an international initiative to evaluate risk and clinical significance associated with sequence variation in BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. Hum Mutat 33(1):2–7
Goldgar DE, Easton DF, Deffenbaugh AM, Monteiro AN, Tavtigian SV, Couch FJ (2004) Integrated evaluation of DNA sequence variants of unknown clinical significance: application to BRCA1 and BRCA2. Am J Hum Genet 75(4):535–544
Sanz DJ, Acedo A, Infante M et al (2010) A high proportion of DNA variants of BRCA1 and BRCA2 is associated with aberrant splicing in breast/ovarian cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 16(6):1957–1967
Bonnet C, Krieger S, Vezain M et al (2008) Screening BRCA1 and BRCA2 unclassified variants for splicing mutations using reverse transcription PCR on patient RNA and an ex vivo assay based on a splicing reporter minigene. J Med Genet 45(7):438–446
Thery JC, Krieger S, Gaildrat P et al (2011) Contribution of bioinformatics predictions and functional splicing assays to the interpretation of unclassified variants of the BRCA genes. Eur J Hum Genet 19(10):1052–1058
Steffensen AY, Dandanell M, Jonson L et al (2014) Functional characterization of BRCA1 gene variants by mini-gene splicing assay. Eur J Hum Genet 22(12):1362–1368
Lee MS, Green R, Marsillac SM et al (2010) Comprehensive analysis of missense variations in the BRCT domain of BRCA1 by structural and functional assays. Cancer Res 70(12):4880–4890
Abkevich V, Zharkikh A, Deffenbaugh AM et al (2004) Analysis of missense variation in human BRCA1 in the context of interspecific sequence variation. J Med Genet 41(7):492–507
Chasman D, Adams RM (2001) Predicting the functional consequences of non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms: structure-based assessment of amino acid variation. J Mol Biol 307(2):683–706
Chenevix-Trench G, Healey S, Lakhani S et al (2006) Genetic and histopathologic evaluation of BRCA1 and BRCA2 DNA sequence variants of unknown clinical significance. Cancer Res 66(4):2019–2027
Lovelock PK, Healey S, Au W et al (2006) Genetic, functional, and histopathological evaluation of two C-terminal BRCA1 missense variants. J Med Genet 43(1):74–83
Miki Y, Swensen J, Shattuck-Eidens D et al (1994) A strong candidate for the breast and ovarian cancer susceptibility gene BRCA1. Science 266(5182):66–71
Szabo C, Masiello A, Ryan JF, Brody LC (2000) The breast cancer information core: database design, structure, and scope. Hum Mutat 16(2):123–131
Frank TS, Deffenbaugh AM, Reid JE et al (2002) Clinical characteristics of individuals with germline mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2: analysis of 10,000 individuals. J Clin Oncol 20(6):1480–1490
Baralle D, Lucassen A, Buratti E (2009) Missed threads. The impact of pre-mRNA splicing defects on clinical practice. EMBO Rep 10(8):810–816
Exome Aggregation Consortium (ExAC), Cambridge http://exac.broadinstitute.org
Karchin R, Monteiro AN, Tavtigian SV, Carvalho MA, Sali A (2007) Functional impact of missense variants in BRCA1 predicted by supervised learning. PLoS Comput Biol 3(2):e26
Rowling PJ, Cook R, Itzhaki LS (2010) Toward classification of BRCA1 missense variants using a biophysical approach. J Biol Chem 285(26):20080–20087
Bergthorsson JT, Jonasdottir A, Johannesdottir G et al (1998) Identification of a novel splice-site mutation of the BRCA1 gene in two breast cancer families: screening reveals low frequency in Icelandic breast cancer patients. Hum Mutat Suppl 1:S195–S197
Vallon-Christersson J, Cayanan C, Haraldsson K et al (2001) Functional analysis of BRCA1 C-terminal missense mutations identified in breast and ovarian cancer families. Hum Mol Genet 10(4):353–360
Thomassen M, Blanco A, Montagna M et al (2012) Characterization of BRCA1 and BRCA2 splicing variants: a collaborative report by ENIGMA consortium members. Breast Cancer Res Treat 132(3):1009–1023
Wappenschmidt B, Becker AA, Hauke J et al (2012) Analysis of 30 putative BRCA1 splicing mutations in hereditary breast and ovarian cancer families identifies exonic splice site mutations that escape in silico prediction. PLoS One 7(12):e50800
Houdayer C, Caux-Moncoutier V, Krieger S et al (2012) Guidelines for splicing analysis in molecular diagnosis derived from a set of 327 combined in silico/in vitro studies on BRCA1 and BRCA2 variants. Hum Mutat 33(8):1228–1238
Gough CA, Gojobori T, Imanishi T (2007) Cancer-related mutations in BRCA1-BRCT cause long-range structural changes in protein-protein binding sites: a molecular dynamics study. Proteins 66(1):69–86
Kuo WH, Lin PH, Huang AC et al (2012) Multimodel assessment of BRCA1 mutations in Taiwanese (ethnic Chinese) women with early-onset, bilateral or familial breast cancer. J Hum Genet 57(2):130–138
Williams RS, Lee MS, Hau DD, Glover JN (2004) Structural basis of phosphopeptide recognition by the BRCT domain of BRCA1. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11(6):519–525
Easton DF, Deffenbaugh AM, Pruss D et al (2007) A systematic genetic assessment of 1,433 sequence variants of unknown clinical significance in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 breast cancer-predisposition genes. Am J Hum Genet 81(5):873–883
Colombo M, De Vecchi G, Caleca L et al (2013) Comparative in vitro and in silico analyses of variants in splicing regions of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes and characterization of novel pathogenic mutations. PLoS One 8(2):e57173
Colombo M, Blok MJ, Whiley P et al (2014) Comprehensive annotation of splice junctions supports pervasive alternative splicing at the BRCA1 locus: a report from the ENIGMA consortium. Hum Mol Genet 23(14):3666–3680
Spurdle AB, Couch FJ, Hogervorst FB, Radice P, Sinilnikova OM (2008) Prediction and assessment of splicing alterations: implications for clinical testing. Hum Mutat 29(11):1304–1313
Walker LC, Whiley PJ, Houdayer C et al (2013) Evaluation of a 5-tier scheme proposed for classification of sequence variants using bioinformatic and splicing assay data: inter-reviewer variability and promotion of minimum reporting guidelines. Hum Mutat 34(10):1424–1431
Acknowledgments
We thank Stine Østergaard for technical assistance. This study was supported by the Familien Hede Nielsens Foundation.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
About this article
Cite this article
Ahlborn, L.B., Dandanell, M., Steffensen, A.Y. et al. Splicing analysis of 14 BRCA1 missense variants classifies nine variants as pathogenic. Breast Cancer Res Treat 150, 289–298 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-015-3313-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-015-3313-7