Abstract
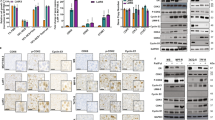
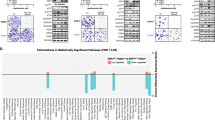
Despite significant improvement in the treatment outcome of hormone responsive postmenopausal breast cancer, some patients eventually acquire resistance to aromatase inhibitors (AIs). Using our MCF-7Ca xenograft model, we observed that although AIs such as anastrozole initially inhibit tumor growth effectively, tumors eventually began to grow. Our previous data show that anastrozole-resistant tumors upregulate growth factor receptor pathways as they adapt to grow in the low estrogen environment. Therefore, in the current study, we investigated the effect of inhibiting the growth factor receptor pathways with a MEK-1/2 inhibitor selumetinib (AZD6244, ARRY-142866). We treated the mice with anastrozole-resistant tumors with selumetinib alone or in combination with anastrozole. MCF-7Ca cells were inoculated sc into ovariectomized athymic nude mice supplemented throughout the experiment with androstenedione (100 μg/day), the substrate for aromatase conversion to estrogen. Once the tumors reached a measurable size (~300 mm3), the mice were treated with anastrozole (200 μg/day), supplemented with androstenedione (Δ4A). The tumors in the anastrozole group doubled in volume after 6 weeks, at which time the animals were regrouped to receive the following treatments: (i) anastrozole, (ii) anastrozole withdrawal (Δ4A alone), (iii) selumetinib (25 mg/kg/d, bid, po), and (iv) selumetinib + anastrozole, (n = 10 mice/group). The treatments were given for 6 weeks (till week 12) and then the mice were euthanized, the tumors were collected and analyzed. The tumors of mice treated with selumetinib + anastrozole had significantly lower growth rates than those treated with single agents (p = 0.008). Western blot analysis of the tumors showed that treatment with anastrozole resulted in upregulation of proteins in the growth factor receptor cascade such as p-mTOR, pAkt, pMEK, and pMAPK. This was accompanied by downregulation of ERα protein, consistent with previous findings. The treatment of mice with selumetinib resulted in downregulation of activated MAPK, along with p-mTOR, which likely resulted in upregulation of ERα. Our results suggest that inhibition of the growth factor receptor pathway with selumetinib can reverse anastrozole resistance.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ERα:
-
Estrogen receptor alpha
- CYP-19:
-
Aromatase
- E2 :
-
17β-Estradiol
- Δ4A:
-
3,17-Androstenedione
References
Goss PE, Muss HB, Ingle JN, Whelan TJ, Wu M (2008) Extended adjuvant endocrine therapy in breast cancer: current status and future directions. Clin breast cancer 8:411–417. doi:10.3816/CBC.2008.n.049
Swain SM (2005) Aromatase inhibitors–a triumph of translational oncology. N Engl J Med 353:2807–2809
Baum M (2002) The ATAC (Arimidex, Tamoxifen, Alone or in Combination) adjuvant breast cancer trial in postmenopausal patients: factors influencing the success of patient recruitment. Eur J Cancer 38:1984–1986
Buzdar A (2003) Anastrozole as adjuvant therapy for early-stage breast cancer: implications of the ATAC trial. Clin breast cancer 4(Suppl 1):S42–S48
Goss PE, Ingle JN, Martino S, Robert NJ, Muss HB, Piccart MJ, Castiglione M, Tu D, Shepherd LE, Pritchard KI, Livingston RB, Davidson NE, Norton L, Perez EA, Abrams JS, Cameron DA, Palmer MJ, Pater JL (2005) Randomized trial of letrozole following tamoxifen as extended adjuvant therapy in receptor-positive breast cancer: updated findings from NCIC CTG MA.17. J Natl Cancer Inst 97:1262–1271
Goss PE, Ingle JN, Martino S, Robert NJ, Muss HB, Piccart MJ, Castiglione M, Tu D, Shepherd LE, Pritchard KI, Livingston RB, Davidson NE, Norton L, Perez EA, Abrams JS, Therasse P, Palmer MJ, Pater JL (2003) A randomized trial of letrozole in postmenopausal women after five years of tamoxifen therapy for early-stage breast cancer. N Engl J Med 349:1793–1802
Mouridsen H, Gershanovich M, Sun Y, Perez-Carrion R, Boni C, Monnier A, Apffelstaedt J, Smith R, Sleeboom HP, Jaenicke F, Pluzanska A, Dank M, Becquart D, Bapsy PP, Salminen E, Snyder R, Chaudri-Ross H, Lang R, Wyld P, Bhatnagar A (2003) Phase III study of letrozole versus tamoxifen as first-line therapy of advanced breast cancer in postmenopausal women: analysis of survival and update of efficacy from the International Letrozole Breast Cancer Group. J Clin Oncol 21:2101–2109
Mouridsen H, Gershanovich M, Sun Y, Perez-Carrion R, Boni C, Monnier A, Apffelstaedt J, Smith R, Sleeboom HP, Janicke F, Pluzanska A, Dank M, Becquart D, Bapsy PP, Salminen E, Snyder R, Lassus M, Verbeek JA, Staffler B, Chaudri-Ross HA, Dugan M (2001) Superior efficacy of letrozole versus tamoxifen as first-line therapy for postmenopausal women with advanced breast cancer: results of a phase III study of the International Letrozole Breast Cancer Group. J Clin Oncol 19:2596–2606
Brodie A, Jelovac D, Long BJ (2003) Predictions from a preclinical model: studies of aromatase inhibitors and antiestrogens. Clin Cancer Res 9:455S–459S
Brodie A, Jelovac D, Macedo L, Sabnis G, Tilghman S, Goloubeva O (2005) Therapeutic observations in MCF-7 aromatase xenografts. Clin Cancer Res 11:884s–888s
Jelovac D, Macedo L, Handratta V, Long BJ, Goloubeva OG, Ingle JN, Brodie AM (2004) Effects of exemestane and tamoxifen in a postmenopausal breast cancer model. Clin Cancer Res 10:7375–7381
Long BJ, Jelovac D, Handratta V, Thiantanawat A, MacPherson N, Ragaz J, Goloubeva OG, Brodie AM (2004) Therapeutic strategies using the aromatase inhibitor letrozole and tamoxifen in a breast cancer model. J Natl Cancer Inst 96:456–465
Brodie AH, Mouridsen HT (2003) Applicability of the intratumor aromatase preclinical model to predict clinical trial results with endocrine therapy. Am J Clin Oncol 26:S17–S26
Yue W, Brodie A (1993) MCF-7 human breast carcinomas in nude mice as a model for evaluating aromatase inhibitors. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 44:671–673
Yue W, Zhou D, Chen S, Brodie A (1994) A new nude mouse model for postmenopausal breast cancer using MCF-7 cells transfected with the human aromatase gene. Cancer Res 54:5092–5095
Jelovac D, Macedo L, Goloubeva OG, Handratta V, Brodie AM (2005) Additive antitumor effect of aromatase inhibitor letrozole and antiestrogen fulvestrant in a postmenopausal breast cancer model. Cancer Res 65:5439–5444
Macedo LF, Sabnis GJ, Goloubeva OG, Brodie A (2008) Combination of anastrozole with fulvestrant in the intratumoral aromatase xenograft model. Cancer Res 68:3516–3522
Jelovac D, Sabnis G, Long BJ, Macedo L, Goloubeva OG, Brodie AM (2005) Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase in xenografts and cells during prolonged treatment with aromatase inhibitor letrozole. Cancer Res 65:5380–5389
Sabnis G, Goloubeva O, Gilani R, Macedo L, Brodie A (2010) Sensitivity to the aromatase inhibitor letrozole is prolonged after a “break” in treatment. Mol Cancer Ther 9:46–56
Sabnis GJ, Jelovac D, Long B, Brodie A (2005) The role of growth factor receptor pathways in human breast cancer cells adapted to long-term estrogen deprivation. Cancer Res 65:3903–3910
Sabnis GJ, Kazi AA, Goloubeva O, Zhang B, Schech A, Shah P, Brodie A (2012) Effect of selumetinib and AZD8055 on the growth of anastrozole resistant tumors. AACR Meeting Abstracts Abstract 2919
Davies BR, Logie A, McKay JS, Martin P, Steele S, Jenkins R, Cockerill M, Cartlidge S, Smith PD (2007) AZD6244 (ARRY-142886), a potent inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase 1/2 kinases: mechanism of action in vivo, pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship, and potential for combination in preclinical models. Mol Cancer Ther 6:2209–2219. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0231
Huynh H, Soo KC, Chow PK, Tran E (2007) Targeted inhibition of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase pathway with AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther 6:138–146. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0436
Yeh TC, Marsh V, Bernat BA, Ballard J, Colwell H, Evans RJ, Parry J, Smith D, Brandhuber BJ, Gross S, Marlow A, Hurley B, Lyssikatos J, Lee PA, Winkler JD, Koch K, Wallace E (2007) Biological characterization of ARRY-142886 (AZD6244), a potent, highly selective mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor. Clin Cancer Res 13:1576–1583. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1150
Chung EJ, Brown AP, Asano H, Mandler M, Burgan WE, Carter D, Camphausen K, Citrin D (2009) In vitro and in vivo radiosensitization with AZD6244 (ARRY-142886), an inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 kinase. Clin Cancer Res 15:3050–3057. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2954
Zhou DJ, Pompon D, Chen SA (1990) Stable expression of human aromatase complementary DNA in mammalian cells: a useful system for aromatase inhibitor screening. Cancer Res 50:6949–6954
Macedo LF, Guo Z, Tilghman SL, Sabnis GJ, Qiu Y, Brodie A (2006) Role of androgens on MCF-7 breast cancer cell growth and on the inhibitory effect of letrozole. Cancer Res 66:7775–7782
Sabnis G, Schayowitz A, Goloubeva O, Macedo L, Brodie A (2009) Trastuzumab reverses letrozole resistance and amplifies the sensitivity of breast cancer cells to estrogen. Cancer Res 69:1416–1428
Long BJ, Tilghman SL, Yue W, Thiantanawat A, Grigoryev DN, Brodie AM (1998) The steroidal antiestrogen ICI 182,780 is an inhibitor of cellular aromatase activity. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 67:293–304
Sabnis GJ, Macedo LF, Goloubeva O, Schayowitz A, Brodie AM (2008) Stopping treatment can reverse acquired resistance to letrozole. Cancer Res 68:4518–4524
Sabnis GJ, Macedo L, Goloubeva O, Schayowitz A, Zhu Y, Brodie A (2008) Toremifene-atamestane; alone or in combination: predictions from the preclinical intratumoral aromatase model. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 108:1–7
Osborne CK, Shou J, Massarweh S, Schiff R (2005) Crosstalk between estrogen receptor and growth factor receptor pathways as a cause for endocrine therapy resistance in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11:865s–870s
Santen RJ, Song RX, McPherson R, Kumar R, Adam L, Jeng MH, Yue W (2002) The role of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase in breast cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 80:239–256
Santen RJ, Song RX, Zhang Z, Kumar R, Jeng MH, Masamura S, Lawrence J Jr, MacMahon LP, Yue W, Berstein L (2005) Adaptive hypersensitivity to estrogen: mechanisms and clinical relevance to aromatase inhibitor therapy in breast cancer treatment. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 95:155–165
Yue W, Wang JP, Conaway MR, Li Y, Santen RJ (2003) Adaptive hypersensitivity following long-term estrogen deprivation: involvement of multiple signal pathways. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 86:265–274
Smith CL (1998) Cross-talk between peptide growth factor and estrogen receptor signaling pathways. Biol Reprod 58:627–632
Miller TW, Hennessy BT, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Fox EM, Mills GB, Chen H, Higham C, Garcia-Echeverria C, Shyr Y, Arteaga CL (2010) Hyperactivation of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase promotes escape from hormone dependence in estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer. J Clin Investig 120:2406–2413. doi:10.1172/JCI41680
Santen RJ, Song RX, Masamura S, Yue W, Fan P, Sogon T, Hayashi S, Nakachi K, Eguchi H (2008) Adaptation to estradiol deprivation causes up-regulation of growth factor pathways and hypersensitivity to estradiol in breast cancer cells. Adv Exp Med Biol 630:19–34
Sabnis G, Goloubeva O, Jelovac D, Schayowitz A, Brodie A (2007) Inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/akt pathway improves response of long-term estrogen-deprived breast cancer xenografts to antiestrogens. Clin Cancer Res 13:2751–2757
Kinkade CW, Castillo-Martin M, Puzio-Kuter A, Yan J, Foster TH, Gao H, Sun Y, Ouyang X, Gerald WL, Cordon-Cardo C, Abate-Shen C (2008) Targeting AKT/mTOR and ERK MAPK signaling inhibits hormone-refractory prostate cancer in a preclinical mouse model. J Clin Investig 118:3051–3064. doi:10.1172/JCI34764
Serra V, Scaltriti M, Prudkin L, Eichhorn PJ, Ibrahim YH, Chandarlapaty S, Markman B, Rodriguez O, Guzman M, Rodriguez S, Gili M, Russillo M, Parra JL, Singh S, Arribas J, Rosen N, Baselga J (2011) PI3 K inhibition results in enhanced HER signaling and acquired ERK dependency in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer. Oncogene 30:2547–2557. doi:10.1038/onc.2010.626
(2012) Everolimus Approved for HR-Positive Breast Cancer. Cancer discovery 2:756. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-NB2012-083
Beaver JA, Park BH (2012) The BOLERO-2 trial: the addition of everolimus to exemestane in the treatment of postmenopausal hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. Future oncology 8:651–657. doi:10.2217/fon.12.49
Gupta M, Ansell SM, Novak AJ, Kumar S, Kaufmann SH, Witzig TE (2009) Inhibition of histone deacetylase overcomes rapamycin-mediated resistance in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by inhibiting Akt signaling through mTORC2. Blood 114:2926–2935. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-05-220889
O’Reilly KE, Rojo F, She QB, Solit D, Mills GB, Smith D, Lane H, Hofmann F, Hicklin DJ, Ludwig DL, Baselga J, Rosen N (2006) mTOR inhibition induces upstream receptor tyrosine kinase signaling and activates Akt. Cancer Res 66:1500–1508. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2925
Wan X, Harkavy B, Shen N, Grohar P, Helman LJ (2007) Rapamycin induces feedback activation of Akt signaling through an IGF-1R-dependent mechanism. Oncogene 26:1932–1940. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209990
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants to G Sabnis (KG10037 from Susan G Komen) and to A. Brodie (CA-62483 from NCI/NIH and SAC100010 from Susan G Komen). Astra-Zeneca also provided financial support for the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabnis, G.J., Kazi, A., Golubeva, O. et al. Effect of selumetinib on the growth of anastrozole-resistant tumors. Breast Cancer Res Treat 138, 699–708 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2474-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2474-5