Abstract
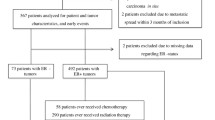
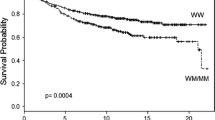
To examine the role of germline genetic variations in inflammatory pathways as modifiers of time to recurrence (TTR) in patients with early stage breast cancer (BC), DNA from 997 early stage BC patients was genotyped for 53 tagging single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in 12 genes involved in inflammation. SNPs were analyzed separately for Caucasians versus African-Americans and Hispanics. Cox proportional hazards models were used to evaluate the association between SNPs in the inflammatory genes and TTR, adjusted for clinical and pathologic covariates. In univariable analyses of Caucasian women, the homozygous genotype of 12 SNPs, including 6 NFKB1 SNPs, 4 IL4 SNPs, and 2 IL13 SNPs, were significantly associated with a decrease in TTR compared with the heterozygous and/or corresponding homozygous genotype (P < 0.05). The significant NFKB1 and IL4 SNPs were in an area of high linkage disequilibrium (D′ > 0.8). After adjusting for stage, age, and treatment, carriage of the homozygous genotypes for NFKB1 rs230532 and IL13rs1800925 were independently associated with a shorter TTR (P = 0.001 and P = 0.034, respectively). In African-American and Hispanic patients, expression of NFKB1 rs3774932, TNFrs1799964, and IL4rs3024543 SNPs were associated with a shorter TTR in univariable model. Only NFKB1 rs3774932 (P = 0.02) and IL4Rrs3024543 (P = 0.03) had independent prognostic value in the multivariable model These data support the existence of host genetic susceptibility as a component in recurrence risk mediated by pro-inflammatory and immune factors, and suggest the potential for drugs which modify immune responses and inflammatory genes to improve prognosis in early stage BC.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ (2009) Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin 59(4):225–249
Brewster AM, Hortobagyi GN, Broglio KR, Kau SW, Santa-Maria CA, Arun B et al (2008) Residual risk of breast cancer recurrence 5 years after adjuvant therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst 100(16):1179–1183
Cianfrocca M, Goldstein LJ (2004) Prognostic and predictive factors in early-stage breast cancer. Oncologist 9(6):606–616
Le Doussal V, Tubiana-Hulin M, Friedman S, Hacene K, Spyratos F, Brunet M (1989) Prognostic value of histologic grade nuclear components of Scarff–Bloom–Richardson (SBR). An improved score modification based on a multivariate analysis of 1,262 invasive ductal breast carcinomas. Cancer 64(9):1914–1921
Hess KR, Pusztai L, Buzdar AU, Hortobagyi GN (2003) Estrogen receptors and distinct patterns of breast cancer relapse. Breast Cancer Res Treat 78(1):105–118
Menard S, Fortis S, Castiglioni F, Agresti R, Balsari A (2001) HER2 as a prognostic factor in breast cancer. Oncology 61(Suppl 2):67–72
Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H et al (2001) Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(19):10869–10874
Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA et al (2000) Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 406(6797):747–752
Chang HY, Sneddon JB, Alizadeh AA, Sood R, West RB, Montgomery K et al (2004) Gene expression signature of fibroblast serum response predicts human cancer progression: similarities between tumors and wounds. PLoS Biol 2(2):E7
Teschendorff AE, Miremadi A, Pinder SE, Ellis IO, Caldas C (2007) An immune response gene expression module identifies a good prognosis subtype in estrogen receptor negative breast cancer. Genome Biol 8(8):R157
Yau C, Esserman L, Moore DH, Waldman F, Sninsky J, Benz CC (2010) A multigene predictor of metastatic outcome in early stage hormone receptor-negative and triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 12(5):R85
Bianchini G, Qi Y, Alvarez RH, Iwamoto T, Coutant C, Ibrahim NK et al (2010) Molecular anatomy of breast cancer stroma and its prognostic value in estrogen receptor-positive and -negative cancers. J Clin Oncol 28(28):4316–4323
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F (2008) Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 454(7203):436–444
Le Marchand L, Haiman CA, van den Berg D, Wilkens LR, Kolonel LN, Henderson BE (2004) T29C polymorphism in the transforming growth factor beta1 gene and postmenopausal breast cancer risk: the Multiethnic Cohort Study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 13(3):412–415
Smith KC, Bateman AC, Fussell HM, Howell WM (2004) Cytokine gene polymorphisms and breast cancer susceptibility and prognosis. Eur J Immunogenet 31(4):167–173
Balasubramanian SP, Azmy IA, Higham SE, Wilson AG, Cross SS, Cox A et al (2006) Interleukin gene polymorphisms and breast cancer: a case control study and systematic literature review. BMC Cancer 14(6):188
Kim S, Hagemann A, DeMichele A (2009) Immuno-modulatory gene polymorphisms and outcome in breast and ovarian cancer. Immunol Invest 38(3–4):324–340
Brewster AM, Do K-A, Thompson PA, Hahn KM, Sahin AA, Cao Y, Stewart MM, Murray JL, Hortobagyi GN, Bondy ML (2008) The relationship between epidemiological risk factors and breast cancer recurrence. J Clin Oncol 25(28):4438–4444
Pounds S, Morris SW (2003) Estimating the occurrence of false positive and false negatives in microarray studies by approximating and partitioning the empirical distribution of p-values. Bioinformatics 19:1236–1242
Binder H, Schumacher M (2008) Allowing for mandatory covariates in boosting estimation of sparse high-dimensional survival models. BMC Bioinformatics 9:1–10
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ (2005) Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 21(2):263–265
Ghosh S, Karin M (2002) Missing pieces in the NF-kappaB puzzle. Cell 109(Suppl):S81–S96
Nakshatri H, Goulet RJ Jr (2002) NF-kappaB and breast cancer. Curr Probl Cancer 26(5):282–309
Nelson DE, Ihekwaba AE, Elliott M, Johnson JR, Gibney CA, Foreman BE et al (2004) Oscillations in NF-kappaB signaling control the dynamics of gene expression. Science 306(5696):704–708
Barkett M, Gilmore TD (1999) Control of apoptosis by Rel/NF-kappaB transcription factors. Oncogene 18(49):6910–6924
Kurt RA, Urba WJ, Smith JW, Schoof DD (1998) Peripheral T lymphocytes from women with breast cancer exhibit abnormal protein expression of several signaling molecules. Int J Cancer 78:16–20
Baumgarten SC, Frasor J (2012) Minireview: inflammation: an instigator of more aggressive estrogen receptor (ER) positive breast cancers. Mol Endocrinol 26(3):360–371
Hageman T, Lawrence T, McNeish I, Charles KA, Kulbe H, Thompson RG, Robinson SC, Balkwill FR (2008) “Re-educating” tumor-associated macrophages by targeting NF-kB. J Exp Med 206:1261–1268
Kelly PM, Davison RS, Bliss E (1988) McGee J0. Macrophages in human breast disease: a quantitative immunohistochemical study. Br J Cancer 57:174–177
Biswas DK, Shi Q, Baily S, Strickland I, Ghosh S, Pardee AB et al (2004) NF-kappa B activation in human breast cancer specimens and its role in cell proliferation and apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(27):10137–10142
Nakshatri H, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Martin DA, Goulet RJ, Sledge GW (1997) Constitutive activation of NF-kB during progression of breast cancer to hormone-independent growth. Mol Cell Biol 17:3629–3639
de Graffenried LA, Chandrasekar B, Friedrichs WE, Donzis E, Silva J, Hidalgo M, Freeman JW, Weiss GR (2004) NF-kB inhibition markedly enhances sensitivity of resistant breast cancer tumor cells to Tamoxifen. Ann Oncol 15:885–890
Riggins RB, Zwart A, Nehra R, Clarke R (2005) The nuclear factor kB inhibitor parthenolide restores ICI 182,780 (Fasolodex, fulvestrant)-induced apoptosis in antiestrogen-resistant breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 4:33–41
Van Dyke AL, Cote ML, Wenzlaff AS, Land S, Schwartz AG (2009) Cytokine SNPs: comparison of allele frequencies by race and implications for future studies. Cytokine 46(2):236–244
Erdei E, Kang H, Meisner A, White K, Pickett G, Baca C, Royce M, Berwick M (2010) Polymorphisms in cytokine genes and serum cytokine levels among New Mexican Women with and without breast cancer. Cytokine 51:18–24
De Nardo DG, Coussens LM (2007) Inflammation and breast cancer. Balancing immune response: crosstalk between adaptive and innate immune cells during breast cancer progression. Breast Cancer Res 2(4):212
Schoof N, von Bonin F, Zeynalova S, Ziepert M, Jung W, Loeffler M, Pfreundschuh M, Trumper L, Kube D (2009) Favorable impact of the interleukin-4 receptor allelic variant I75 on the survival of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients demonstrated in a large prospective clinical trial. Ann Oncol 20(9):1548–1554
Aspord C, Pedroza-Gonzalez A, Gallegos M, Tindle S, Burton EC, Su D et al (2007) Breast cancer instructs dendritic cells to prime interleukin 13-secreting CD4+ T cells that facilitate tumor development. J Exp Med 204(5):1037–1047
Martin AM, Athanasiadis G, Greshock JD, Fisher J, Lux MP, Calzone K et al (2003) Population frequencies of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in immuno-modulatory genes. Hum Hered 55(4):171–178
Haukim N, Bidwell JL, Smith AJ, Keen LJ, Gallagher G, Kimberly R et al (2002) Cytokine gene polymorphism in human disease: on-line databases, supplement 2. Genes Immun 3(6):313–330
Guida E, Stewart A (1998) Influence of hypoxia and glucose deprivation on tumour necrosis factor-alpha and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor expression in human cultured monocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem 8(1–2):75–88
Miles DW, Happerfield LC, Naylor MS, Bobrow LG, Rubens RD, Balkwill FR (1994) Expression of tumour necrosis factor (TNF alpha) and its receptors in benign and malignant breast tissue. Int J Cancer 56(6):777–782
Jung JH, Chae YS, Moon JH, Kang BW, Kim JG, Sohn SK, Park JY, Lee MH, Park HY (2010) TNF superfamily gene polymorphism as prognostic factor in early breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136(5):685–694
Mestiri S, Bouaouina N, Ahmed SB, Khedhaier A, Jrad BB, Remadi S et al (2001) Genetic variation in the tumor necrosis factor-alpha promoter region and in the stress protein hsp70-2: susceptibility and prognostic implications in breast carcinoma. Cancer 91(4):672–678
Pusztai L, Mendoza TR, Reuben JM, Martinez MM, Willey JS, Lara J, Syed A, Fritsche HA, Bruera E, Booser D, Valero V, Arun B, Ibrahim N, Rivera E, Royce M, Cleeland CS, Hortobagyi GN (2004) Changes in plasma levels of inflammatory cytokines in response to paclitaxel chemotherapy. Cytokine 25(3):94–102
Demaria S, Pikarsky E, Karin M, Coussens LM, Chen YC, El-Omar EM et al (2010) Cancer and inflammation: promise for biologic therapy. J Immunother 33(4):335–351
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge Ricardo Mottu and Katharina Alvarez for manuscript preparation. Supported by Grants R03 CA123553 (A.M.B.), Susan Komen Disparities Career Award (A.M.B), R01 CA089608 (M.L.B., P.T.), K07 CA160753 (M.P.), and CA16672 (MD Anderson Cancer Center) from the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services.
Conflict of interest
The authors indicated no potential conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murray, J.L., Thompson, P., Yoo, S.Y. et al. Prognostic value of single nucleotide polymorphisms of candidate genes associated with inflammation in early stage breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 138, 917–924 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2445-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2445-x