Abstract
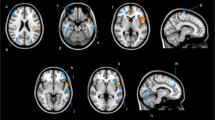
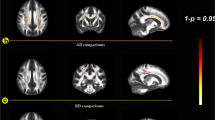
Neuroimaging studies have begun to uncover the neural substrates of cancer and treatment-related cognitive dysfunction, but the time course of these changes in the years following chemotherapy is unclear. This study analyzed multimodality 3T MRI scans to examine the structural and functional effects of chemotherapy and post-chemotherapy interval (PCI) in a cohort of breast cancer survivors (BCS; n = 24; PCI mean 6, range 3–10 y) relative to age- and education-matched healthy controls (HC; n = 23). Assessments included voxel-based morphometry for gray matter density (GMD) and fMRI for activation profile during a 3-back working memory task. The relationships between brain regions associated with PCI and neuropsychological performance, self-reported cognition, and oxidative and direct DNA damage as measured in peripheral lymphocytes were assessed in secondary analyses. PCI was positively associated with GMD and activation on fMRI in the right anterior frontal region (Brodmann Areas 9 and 10) independent of participant age. GMD in this region was also positively correlated with global neuropsychological function. Memory dysfunction, cognitive complaints, and oxidative DNA damages were increased in BCS compared with HC. Imaging results indicated lower fMRI activation in several regions in the BCS group. BCS also had lower GMD than HC in several regions, and in these regions, GMD was inversely related to oxidative DNA damage and learning and memory neuropsychological domain scores. This is the first study to show structural and functional effects of PCI and to relate oxidative DNA damage to brain alterations in BCS. The relationship between neuroimaging and cognitive function indicates the potential clinical relevance of these findings. The relationship with oxidative DNA damage provides a mechanistic clue warranting further investigation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jim HSL, Phillips KM, Chait S, Faul LA, Popa MA, Lee Y-H, Hussin MG, Jacobsen PB, Small BJ (2012) Meta-Analysis of Cognitive Functioning in Breast Cancer Survivors Previously Treated With Standard-Dose Chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 30(29):3578–3587. doi:10.1200/jco.2011.39.5640
Anderson-Hanley C, Sherman ML, Riggs R, Agocha VB, Compas BE (2003) Neuropsychological effects of treatments for adults with cancer: a meta-analysis and review of the literature. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 9(7):967–982
Correa DD, Ahles TA (2008) Neurocognitive changes in cancer survivors. Cancer J 14(6):396–400
Stewart A, Bielajew C, Collins B, Parkinson M, Tomiak E (2006) A meta-analysis of the neuropsychological effects of adjuvant chemotherapy treatment in women treated for breast cancer. Clin Neuropsychol 20(1):76–89
Jansen CE, Miaskowski C, Dodd M, Dowling G, Kramer J, Jansen CE, Miaskowski C, Dodd M, Dowling G, Kramer J (2005) A metaanalysis of studies of the effects of cancer chemotherapy on various domains of cognitive function. Cancer 104(10):2222–2233
Pullens MJ, De Vries J, Roukema JA (2010) Subjective cognitive dysfunction in breast cancer patients: a systematic review. Psychooncology 19(11):1127–1138. doi:10.1002/pon.1673
de Ruiter MB, Reneman L, Boogerd W, Veltman DJ, Caan M, Douaud G, Lavini C, Linn SC, Boven E, van Dam FSAM, Schagen SB (2011) Late effects of high-dose adjuvant chemotherapy on white and gray matter in breast cancer survivors: converging results from multimodal magnetic resonance imaging. Hum Brain Mapp. doi:10.1002/hbm.21422
Koppelmans V, de Ruiter MB, van der Lijn F, Boogerd W, Seynaeve C, van der Lugt A, Vrooman H, Niessen WJ, Breteler MM, Schagen SB (2011) Global and focal brain volume in long-term breast cancer survivors exposed to adjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat. doi:10.1007/s10549-011-1888-1
Inagaki M, Yoshikawa E, Matsuoka Y, Sugawara Y, Nakano T, Akechi T, Wada N, Imoto S, Murakami K, Uchitomi Y, The Breast Cancer Survivors’ Brain MRIDG (2007) Smaller regional volumes of brain gray and white matter demonstrated in breast cancer survivors exposed to adjuvant chemotherapy. Cancer 109(1):146–156
Deprez S, Amant F, Yigit R, Porke K, Verhoeven J, Stock JVd, Smeets A, Christiaens M-R, Leemans A, Hecke WV, Vandenberghe J, Vandenbulcke M, Sunaert S (2011) Chemotherapy-induced structural changes in cerebral white matter and its correlation with impaired cognitive functioning in breast cancer patients. Hum Brain Mapp 32(3):480–493. doi:10.1002/hbm.21033
Abraham J, Haut MW, Moran MT, Filburn S, Lemiuex S, Kuwabara H (2008) Adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer: effects on cerebral white matter seen in diffusion tensor imaging. Clin Breast Cancer 8(1):88–91
Kesler SR, Kent JS, O’Hara R (2011) Prefrontal cortex and executive function impairments in primary breast cancer. Arch Neurol 68(11):1447–1453. doi:10.1001/archneurol.2011.245
de Ruiter MB, Reneman L, Boogerd W, Veltman DJ, van Dam FS, Nederveen AJ, Boven E, Schagen SB (2011) Cerebral hyporesponsiveness and cognitive impairment 10 years after chemotherapy for breast cancer. Hum Brain Mapp 32(8):1206–1219. doi:10.1002/hbm.21102
Deprez S, Amant F, Smeets A, Peeters R, Leemans A, Van Hecke W, Verhoeven JS, Christiaens M-R, Vandenberghe J, Vandenbulcke M, Sunaert S (2012) Longitudinal Assessment of Chemotherapy-Induced Structural Changes in Cerebral White Matter and Its Correlation With Impaired Cognitive Functioning. J Clin Oncol 30(3):274–281. doi:10.1200/jco.2011.36.8571
McDonald BC, Conroy SK, Ahles TA, West JD, Saykin AJ (2010) Gray matter reduction associated with systemic chemotherapy for breast cancer: a prospective MRI study. Breast Cancer Res Treat 123(3):819–828. doi:10.1007/s10549-010-1088-4
McDonald BC, Conroy SK, Ahles TA, West JD, Saykin AJ (2012) Alterations in Brain Activation during Working Memory Processing Associated with Breast Cancer and Treatment: A Prospective Functional MRI Study. J Clin Oncol 30(20):2500–2508. doi:JCO.2011.38.5674
Ahles TA, Saykin AJ, McDonald BC, Furstenberg CT, Cole B, Hanscom BS, Mulrooney TJ, Schwartz G, Kaufman PA (2008) Cognitive function in breast cancer patients prior to adjuvant treatment. Breast Cancer Res Treat 110:143–152
Cimprich B, Reuter-Lorenz P, Nelson J, Clark PM, Therrien B, Normolle D, Berman MG, Hayes DF, Noll DC, Peltier S, Welsh RC (2010) Prechemotherapy alterations in brain function in women with breast cancer. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 32(3):324–331. doi:10.1080/13803390903032537
Scherling C, Collins B, Mackenzie J, Bielajew C, Smith A (2011) Pre-chemotherapy differences in visuospatial working memory in breast cancer patients compared to controls: an FMRI study. Frontiers hum neurosci 5:122. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2011.00122
Ahles TA, Saykin AJ (2007) Candidate mechanisms for chemotherapy-induced cognitive changes. Nat Rev Cancer 7(3):192–201
Blasiak J, Arabski M, Krupa R, Wozniak K, Rykala J, Kolacinska A, Morawiec Z, Drzewoski J, Zadrozny M (2004) Basal, oxidative and alkylative DNA damage, DNA repair efficacy and mutagen sensitivity in breast cancer. Mutat Res 554(1–2):139–148. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2004.04.001
Unverzagt FW, Monahan PO, Moser LR, Zhao Q, Carpenter JS, Sledge GW Jr, Champion VL (2007) The Indiana University telephone-based assessment of neuropsychological status: a new method for large scale neuropsychological assessment. J Intern Neuropsychol Soc 13(5):799–806. doi:10.1017/s1355617707071020
Von Ah D, Harvison KW, Monahan PO, Moser LR, Zhao Q, Carpenter JS, Sledge GW Jr, Champion VL, Unverzagt FW (2009) Cognitive function in breast cancer survivors compared to healthy age- and education-matched women. Clin Neuropsychol 23(4):661–674. doi:10.1080/13854040802541439
McDonald BC, Conroy SK, Smith DJ, West JD, Saykin AJ (2012) Frontal gray matter reduction after breast cancer chemotherapy and association with executive symptoms: a replication and extension Study. Brain Behav Immun. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2012.05.007
Ferguson RJ, McDonald BC, Saykin AJ, Ahles TA (2007) Brain structure and function differences in monozygotic twins: possible effects of breast cancer chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 25(25):3866–3870
Ashburner J, Friston KF (2000) Voxel-based morphometry—the methods. Neuroimage 11(6 Pt 1):805–821
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2001) Why voxel-based morphometry should be used. Neuroimage 14(6):1238–1243
Good CD, Johnsrude IS, Ashburner J, Henson RN, Friston KJ, Frackowiak RS (2001) A voxel-based morphometric study of ageing in 465 normal adult human brains. Neuroimage 14(1 Pt 1):21–36
Risacher SL, Saykin AJ, West JD, Shen L, Firpi HA, McDonald BC, Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging I (2009) Baseline MRI predictors of conversion from MCI to probable AD in the ADNI cohort. Curr Alzheimer Res 6(4):347–361
Saykin AJ, Wishart HA, Rabin LA, Santulli RB, Flashman LA, West JD, McHugh TL, Mamourian AC (2006) Older adults with cognitive complaints show brain atrophy similar to that of amnestic MCI. Neurology 67(5):834–842. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000234032.77541.a2
Wishart HA, Saykin AJ, McAllister TW, Rabin LA, McDonald BC, Flashman LA, Roth RM, Mamourian AC, Tsongalis GJ, Rhodes CH (2006) Regional brain atrophy in cognitively intact adults with a single APOE epsilon4 allele. Neurology 67(7):1221–1224. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000238079.00472.3a
Lezak MD, Howieson DB, Loring DW (2004) Neuropsychological assessment. Oxford University Press, New York
Strauss E, Sherman EMS, Spreen O (2006) A compendium of neuropsychological tests: administration, norms, and commentary. Oxford University Press, New York
Craft S, Newcomer J, Kanne S, Dagogo-Jack S, Cryer P, Sheline Y, Luby J, Dagogo-Jack A, Alderson A (1996) Memory improvement following induced hyperinsulinemia in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 17(1):123–130
Brown FC, Roth RM, Saykin AJ, Beverly-Gibson G (2007) A new measure of visual location learning and memory: development and psychometric properties for the Brown Location Test (BLT). Clin Neuropsychol 21(5):811–825. doi:10.1080/13854040600878777
The Psychological Corporation (1997) WAIS-III Wechsler memory scale, 3rd edn. WMS Wechsler memory scale, 3rd edn., Updated technical manual. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
Fischer JS, Jak AJ, Kniker JE, Rudick RA (2001) Administration and scoring manual for the multiple sclerosis functional composite measure (MSFC). National Multiple Sclerosis Society
Wilkinson GS, Robertson GJ (2006) WRAT4 wide range achievement test professional manual. Psychological Assessment Resources, Inc, Lutz
The Psychological Corporation (1999) Wechsler abbreviated scale of intelligence. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
Delis DC, Kaplan E, Kramer JH (2001) The Delis-Kaplan executive function system. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
Smith A (1982) Symbol digit modalities test. Western Psychological Services, Los Angeles
Lafayette Instrument (1989) Grooved pegboard: instruction/owner’s manual. Lafayette Instrument, Lafayette
Seidenberg M, Haltiner A, Taylor MA, Hermann BB, Wyler A (1994) Development and validation of a Multiple Ability Self-Report Questionnaire. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 16(1):93–104. doi:10.1080/01688639408402620
Cella DF, Tulsky DS, Gray G, Sarafian B, Linn E, Bonomi A, Silberman M, Yellen SB, Winicour P, Brannon J (1993) The Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy scale: development and validation of the general measure. J Clin Oncol 11(3):570–579
Radloff LS (1977) The CES-D Scale: A self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Appl Psychol Meas 1(3):385–401
Spielberger CD (1983) State-trait anxiety inventory. Consulting Psychologists Press, Inc, Palo Alto
Pu X, Kamendulis LM, Klaunig JE (2009) Acrylonitrile-induced oxidative stress and oxidative DNA damage in male Sprague-Dawley rats. Toxicol Sci 111(1):64–71. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfp133
Ahles TA, Saykin AJ, McDonald BC, Li Y, Furstenberg CT, Hanscom BS, Mulrooney TJ, Schwartz GN, Kaufman PA (2010) Longitudinal Assessment of Cognitive Changes Associated With Adjuvant Treatment for Breast Cancer: impact of Age and Cognitive Reserve. J Clin Oncol 28(29):4434–4440. doi:10.1200/jco.2009.27.0827
Silverman DH, Dy CJ, Castellon SA, Lai J, Pio BS, Abraham L, Waddell K, Petersen L, Phelps ME, Ganz PA (2007) Altered frontocortical, cerebellar, and basal ganglia activity in adjuvant-treated breast cancer survivors 5–10 years after chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat 103(3):303–311
Chen Y, Jungsuwadee P, Vore M, Butterfield DA, St Clair DK (2007) Collateral damage in cancer chemotherapy: oxidative stress in nontargeted tissues. Mol Interven 7(3):147–156
Migliore L, Petrozzi L, Lucetti C, Gambaccini G, Bernardini S, Scarpato R, Trippi F, Barale R, Frenzilli G, Rodilla V, Bonuccelli U (2002) Oxidative damage and cytogenetic analysis in leukocytes of Parkinson’s disease patients. Neurology 58(12):1809–1815
Migliore L, Fontana I, Trippi F, Colognato R, Coppede F, Tognoni G, Nucciarone B, Siciliano G (2005) Oxidative DNA damage in peripheral leukocytes of mild cognitive impairment and AD patients. Neurobiol Aging 26(5):567–573. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2004.07.016
Castellon SA, Ganz PA, Bower JE, Petersen L, Abraham L, Greendale GA, Castellon SA, Ganz PA, Bower JE, Petersen L, Abraham L, Greendale GA (2004) Neurocognitive performance in breast cancer survivors exposed to adjuvant chemotherapy and tamoxifen. J Clin & Exp Neuropsychol 26(7):955–969
Shilling V, Jenkins V, Fallowfield L, Howell T, Shilling V, Jenkins V, Fallowfield L, Howell T (2003) The effects of hormone therapy on cognition in breast cancer.[erratum appears in J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2005 Jun;96(1):93]. J Steroid Biochem & Mol Biol 86 (3–5):405–412
Jenkins V, Shilling V, Fallowfield L, Howell A, Hutton S (2004) Does hormone therapy for the treatment of breast cancer have a detrimental effect on memory and cognition? A pilot study. Psychooncology 13(1):61–66. doi:10.1002/pon.709
Barona A, Reynolds CR, Chastain R (1984) A demographically based index of pre-morbid intelligence for the WAIS-R. J Consult Clin Psychol 52(5):885–887
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute (R01CA101318, PI:AJS; R25CA117865, PI: VLC), the American Cancer Society (ACS RSGBP-04-089-01-PBP, PI: VLC), The Indiana University Melvin and Bren Simon Cancer Center Translational Research Acceleration Collaboration (PI: FWU), The National Institutes of Health, National Institute on Aging (F30 AG039959, PI: SKC), and the Indiana University Medical Scientist Training Program (National Institute of General Medical Sciences GM077229-02).
Disclosures
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Conroy, S.K., McDonald, B.C., Smith, D.J. et al. Alterations in brain structure and function in breast cancer survivors: effect of post-chemotherapy interval and relation to oxidative DNA damage. Breast Cancer Res Treat 137, 493–502 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2385-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2385-x