Abstract
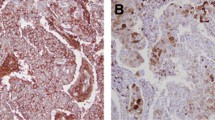
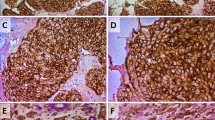
Cumulative evidence has demonstrated the presence of cancer stem cells (CSC) in breast cancer and its putative role in cancer progression. Nonetheless, the clinical significance of CSC in breast cancer remains elusive. The underlying reasons could be due to the heterogeneity of breast cancer subtypes as well as different markers used to define breast CSC. In this study, three widely used markers (aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH)1+ and CD24−CD44+) were used to define two populations of CSC in a large cohort of breast cancers. The expressions of these markers were correlated with different clinicopathological features and the molecular subtypes. ALDH1+ breast cancers were associated with basal-like and HER2-overexpressing subtypes and the characteristics histologic features were related to these two subtypes. On the other hand, CD24−CD44+ breast cancers were associated positively with the presence of extensive in situ component, the absence of lymph node involvement, and basal markers, but negatively with HER2. CD24−CD44+ breast cancers were also positively associated with luminal B cancers. As the expression of CSC markers varied among different molecular subtypes and different clinicopathological features, it appeared that each CSC population could have distinct clinical values in different subgroups of breast cancers. For improved prognostication with CSC, combining the analysis of CSC markers would be required. Within the luminal cancers, CSC appeared to identify cancers with poor outcome. The presence of CSC populations was associated with ER−PR+ cancers and tumors expressing basal markers. Basal marker expression can complement with CSC for improved indicator for poor prognosis in luminal breast cancers. For the first time, the possible contribution of CSC to these aggressive luminal cancers was demonstrated. The association of basal features and CSC in luminal cancers also raised the possibility that luminal cancer cells may acquire basal phenotype and CSC properties together during their progression.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Visvader JE, Lindeman GJ (2008) Cancer stem cells in solid tumours: accumulating evidence and unresolved questions. Nat Rev Cancer 8(10):755–768. doi:10.1038/nrc2499
Croker AK, Allan AL (2008) Cancer stem cells: implications for the progression and treatment of metastatic disease. J Cell Mol Med 12(2):374–390. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00211.x
Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF (2003) Prospective identification of tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(7):3983–3988. doi:10.1073/pnas.05302911000530291100
Sheridan C, Kishimoto H, Fuchs RK, Mehrotra S, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Turner CH, Goulet R Jr, Badve S, Nakshatri H (2006) CD44+/CD24− breast cancer cells exhibit enhanced invasive properties: an early step necessary for metastasis. Breast Cancer Res 8(5):R59. doi:10.1186/bcr1610
Ginestier C, Hur MH, Charafe-Jauffret E, Monville F, Dutcher J, Brown M, Jacquemier J, Viens P, Kleer CG, Liu S, Schott A, Hayes D, Birnbaum D, Wicha MS, Dontu G (2007) ALDH1 is a marker of normal and malignant human mammary stem cells and a predictor of poor clinical outcome. Cell Stem Cell 1(5):555–567. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2007.08.014
Morimoto K, Kim SJ, Tanei T, Shimazu K, Tanji Y, Taguchi T, Tamaki Y, Terada N, Noguchi S (2009) Stem cell marker aldehyde dehydrogenase 1-positive breast cancers are characterized by negative estrogen receptor, positive human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2, and high Ki67 expression. Cancer Sci 100(6):1062–1068. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01151.x
Neumeister V, Agarwal S, Bordeaux J, Camp RL, Rimm DL (2010) In situ identification of putative cancer stem cells by multiplexing ALDH1, CD44, and cytokeratin identifies breast cancer patients with poor prognosis. Am J Pathol 176(5):2131–2138. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2010.090712
Buess M, Rajski M, Vogel-Durrer BM, Herrmann R, Rochlitz C (2009) Tumor-endothelial interaction links the CD44(+)/CD24(−) phenotype with poor prognosis in early-stage breast cancer. Neoplasia 11(10):987–1002
Ricardo S, Vieira AF, Gerhard R, Leitao D, Pinto R, Cameselle-Teijeiro JF, Milanezi F, Schmitt F, Paredes J (2011) Breast cancer stem cell markers CD44, CD24 and ALDH1: expression distribution within intrinsic molecular subtype. J Clin Pathol 64(11):937–946. doi:10.1136/jcp.2011.090456
Abraham BK, Fritz P, McClellan M, Hauptvogel P, Athelogou M, Brauch H (2005) Prevalence of CD44+/CD24−/low cells in breast cancer may not be associated with clinical outcome but may favor distant metastasis. Clin Cancer Res 11(3):1154–1159
Ahmed MA, Aleskandarany MA, Rakha EA, Moustafa RZ, Benhasouna A, Nolan C, Green AR, Ilyas M, Ellis IO (2011) A CD44(−)/CD24 (+) phenotype is a poor prognostic marker in early invasive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. doi:10.1007/s10549-011-1865-8
Mylona E, Giannopoulou I, Fasomytakis E, Nomikos A, Magkou C, Bakarakos P, Nakopoulou L (2008) The clinicopathologic and prognostic significance of CD44+/CD24(−/low) and CD44−/CD24+ tumor cells in invasive breast carcinomas. Hum Pathol 39(7):1096–1102. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2007.12.003
Hwang-Verslues WW, Kuo WH, Chang PH, Pan CC, Wang HH, Tsai ST, Jeng YM, Shew JY, Kung JT, Chen CH, Lee EY, Chang KJ, Lee WH (2009) Multiple lineages of human breast cancer stem/progenitor cells identified by profiling with stem cell markers. PLoS ONE 4(12):e8377. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008377
Elston CW, Ellis IO (1991) Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological grade in breast cancer: experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology 19(5):403–410
Lakhani SR, Ellis IO, Schnitee SJ, Tan PH, van de Vijver MJ (eds) (2012) World Health Organisation classification of tumors of the breast, 4th edn. IARC Press, Lyon
Hammond ME, Hayes DF, Dowsett M, Allred DC, Hagerty KL, Badve S, Fitzgibbons PL, Francis G, Goldstein NS, Hayes M, Hicks DG, Lester S, Love R, Mangu PB, McShane L, Miller K, Osborne CK, Paik S, Perlmutter J, Rhodes A, Sasano H, Schwartz JN, Sweep FC, Taube S, Torlakovic EE, Valenstein P, Viale G, Visscher D, Wheeler T, Williams RB, Wittliff JL, Wolff AC (2010) American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 28(16):2784–2795. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.25.6529
Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Schwartz JN, Hagerty KL, Allred DC, Cote RJ, Dowsett M, Fitzgibbons PL, Hanna WM, Langer A, McShane LM, Paik S, Pegram MD, Perez EA, Press MF, Rhodes A, Sturgeon C, Taube SE, Tubbs R, Vance GH, van de Vijver M, Wheeler TM, Hayes DF (2007) American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 25(1):118–145. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.09.2775
Ali HR, Dawson SJ, Blows FM, Provenzano E, Pharoah PD, Caldas C (2011) Cancer stem cell markers in breast cancer: pathological, clinical and prognostic significance. Breast Cancer Res 13(6):R118. doi:10.1186/bcr3061
Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Thurlimann B, Senn HJ (2011) Strategies for subtypes-dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann Oncol 22(8):1736–1747. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdr304
Nielsen TO, Hsu FD, Jensen K, Cheang M, Karaca G, Hu Z, Hernandez-Boussard T, Livasy C, Cowan D, Dressler L, Akslen LA, Ragaz J, Gown AM, Gilks CB, van de Rijn M, Perou CM (2004) Immunohistochemical and clinical characterization of the basal-like subtype of invasive breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 10(16):5367–5374. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-022010/16/5367
Honeth G, Bendahl PO, Ringner M, Saal LH, Gruvberger-Saal SK, Lovgren K, Grabau D, Ferno M, Borg A, Hegardt C (2008) The CD44+/CD24− phenotype is enriched in basal-like breast tumors. Breast Cancer Res 10(3):R53. doi:10.1186/bcr2108
Park SY, Lee HE, Li H, Shipitsin M, Gelman R, Polyak K (2010) Heterogeneity for stem cell-related markers according to tumor subtype and histologic stage in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 16(3):876–887. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1532
Korkaya H, Paulson A, Iovino F, Wicha MS (2008) HER2 regulates the mammary stem/progenitor cell population driving tumorigenesis and invasion. Oncogene 27(47):6120–6130. doi:10.1038/onc.2008.207
Higgins MJ, Stearns V (2009) Understanding resistance to tamoxifen in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Clin Chem 55(8):1453–1455. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2009.125377
Rakha EA, El-Sayed ME, Green AR, Paish EC, Powe DG, Gee J, Nicholson RI, Lee AH, Robertson JF, Ellis IO (2007) Biologic and clinical characteristics of breast cancer with single hormone receptor positive phenotype. J Clin Oncol 25(30):4772–4778. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.12.2747
Fernandez-Valdivia R, Mukherjee A, Mulac-Jericevic B, Conneely OM, DeMayo FJ, Amato P, Lydon JP (2005) Revealing progesterone’s role in uterine and mammary gland biology: insights from the mouse. Semin Reprod Med 23(1):22–37. doi:10.1055/s-2005-864031
Hilton HN, Graham JD, Kantimm S, Santucci N, Cloosterman D, Huschtscha LI, Mote PA, Clarke CL (2012) Progesterone and estrogen receptors segregate into different cell subpopulations in the normal human breast. Mol Cell Endocrinol. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2012.04.010
Horwitz KB, Dye WW, Harrell JC, Kabos P, Sartorius CA (2008) Rare steroid receptor-negative basal-like tumorigenic cells in luminal subtype human breast cancer xenografts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(15):5774–5779. doi:10.1073/pnas.0706216105
Joshi PA, Jackson HW, Beristain AG, Di Grappa MA, Mote PA, Clarke CL, Stingl J, Waterhouse PD, Khokha R (2010) Progesterone induces adult mammary stem cell expansion. Nature 465(7299):803–807. doi:10.1038/nature09091
Simoes BM, Piva M, Iriondo O, Comaills V, Lopez-Ruiz JA, Zabalza I, Mieza JA, Acinas O, Vivanco MD (2011) Effects of estrogen on the proportion of stem cells in the breast. Breast Cancer Res Treat 129(1):23–35. doi:10.1007/s10549-010-1169-4
Stuart-Harris R, Shadbolt B, Palmqvist C, Chaudri Ross HA (2009) The prognostic significance of single hormone receptor positive metastatic breast cancer: an analysis of three randomised phase III trials of aromatase inhibitors. Breast 18(6):351–355. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2009.09.002
Dunnwald LK, Rossing MA, Li CI (2007) Hormone receptor status, tumor characteristics, and prognosis: a prospective cohort of breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res 9(1):R6. doi:10.1186/bcr1639
Cheang MC, Voduc D, Bajdik C, Leung S, McKinney S, Chia SK, Perou CM, Nielsen TO (2008) Basal-like breast cancer defined by five biomarkers has superior prognostic value than triple-negative phenotype. Clin Cancer Res 14(5):1368–1376. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1658
Abd El-Rehim DM, Pinder SE, Paish CE, Bell J, Blamey RW, Robertson JF, Nicholson RI, Ellis IO (2004) Expression of luminal and basal cytokeratins in human breast carcinoma. J Pathol 203(2):661–671. doi:10.1002/path.1559
Kabos P, Haughian JM, Wang X, Dye WW, Finlayson C, Elias A, Horwitz KB, Sartorius CA (2011) Cytokeratin 5 positive cells represent a steroid receptor negative and therapy resistant subpopulation in luminal breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res Treat 128(1):45–55. doi:10.1007/s10549-010-1078-6
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsang, J.Y.S., Huang, YH., Luo, MH. et al. Cancer stem cell markers are associated with adverse biomarker profiles and molecular subtypes of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 136, 407–417 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2271-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2271-6