Abstract
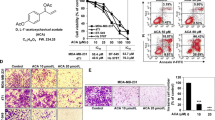
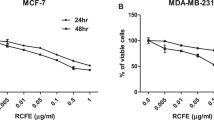
Tumor metastasis is the main cause of cancer-related deaths of patients. Breast cancer is highly malignant with considerable metastatic potential, which urges the necessity for developing novel potential drug candidate to prevent tumor metastasis. Here, we report our finding with Cucurbitacin E (CuE, α-elaterin), a tetracyclic triterpenes compound isolated from Cucurbitaceae. The potency of CuE on breast cancer metastasis inhibition was assessed in vivo and in vitro. In our animal experiments, intraperitoneal administrations of CuE significantly inhibited breast tumor metastasis to the lung without affecting apoptosis or proliferation of inoculated 4T1 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Treatment of metastatic breast tumor cells with CuE markedly blocked tumor cell migration and invasion in vitro. Subsequent studies showed that CuE impaired Arp2/3-dependent actin polymerization and suppressed Src/FAK/Rac1/MMP involved pathway. Overall, our data demonstrate that CuE blocks breast cancer metastasis by suppressing tumor cell migration and invasion. We provide first evidence of a novel role for CuE as a potential candidate for treating breast cancer metastasis.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CuE:
-
Cucurbitacin E
- FAK:
-
Focal adhesion kinase
- ARP2/3:
-
Actin-related protein 2/3
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase
- JNK:
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinases
- TIMP:
-
Tissue inhibitor of MMP
- H&E:
-
Hematoxylin and eosin
- IVIS:
-
In Vivo Imaging System
- WASP:
-
Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome Protein
References
Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O, Jemal A (2011) Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J Clin 61(4):212–236. doi:10.3322/caac.20121
Weigelt B, Peterse JL, van’t Veer LJ (2005) Breast cancer metastasis: markers and models. Nat Rev Cancer 5(8):591–602. doi:10.1038/nrc1670
Nguyen DX, Bos PD, Massague J (2009) Metastasis: from dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nat Rev Cancer 9(4):274–284. doi:10.1038/nrc2622
Steeg PS (2006) Tumor metastasis: mechanistic insights and clinical challenges. Nat Med 12(8):895–904. doi:10.1038/nm1469
Ideses Y, Brill-Karniely Y, Haviv L, Ben-Shaul A, Bernheim-Groswasser A (2008) Arp2/3 branched actin network mediates filopodia-like bundles formation in vitro. PLoS ONE 3(9):e3297. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0003297
Li Z, Kim ES, Bearer EL (2002) Arp2/3 complex is required for actin polymerization during platelet shape change. Blood 99(12):4466–4474
Yamakita Y, Oosawa F, Yamashiro S, Matsumura F (2003) Caldesmon inhibits Arp2/3-mediated actin nucleation. J Biol Chem 278(20):17937–17944. doi:10.1074/jbc.M208739200M208739200
Gabarra-Niecko V, Schaller MD, Dunty JM (2003) FAK regulates biological processes important for the pathogenesis of cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 22(4):359–374
Kessenbrock K, Plaks V, Werb Z (2010) Matrix metalloproteinases: regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell 141(1):52–67. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.015
Kunnumakkara AB, Anand P, Aggarwal BB (2008) Curcumin inhibits proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis and metastasis of different cancers through interaction with multiple cell signaling proteins. Cancer Lett 269(2):199–225. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2008.03.009
Mitra SK, Hanson DA, Schlaepfer DD (2005) Focal adhesion kinase: in command and control of cell motility. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6(1):56–68. doi:10.1038/nrm1549
Siesser PM, Hanks SK (2006) The signaling and biological implications of FAK overexpression in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 12(11 Pt 1):3233–3237. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0456
Chambliss OL, Jones CM (1966) Cucurbitacins: specific insect attractants in Cucurbitaceae. Science 153(3742):1392–1393. doi:10.1126/science.153.3742.1392
Kocyan A, Zhang LB, Schaefer H, Renner SS (2007) A multi-locus chloroplast phylogeny for the Cucurbitaceae and its implications for character evolution and classification. Mol Phylogenet Evol 44(2):553–577. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2006.12.022
Duncan KL, Duncan MD, Alley MC, Sausville EA (1996) Cucurbitacin E-induced disruption of the actin and vimentin cytoskeleton in prostate carcinoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol 52(10):1553–1560
Momma K, Masuzawa Y, Nakai N, Chujo M, Murakami A, Kioka N, Kiyama Y, Akita T, Nagao M (2008) Direct interaction of Cucurbitacin E isolated from Alsomitra macrocarpa to actin filament. Cytotechnology 56(1):33–39. doi:10.1007/s10616-007-9100-5
Greige-Gerges H, Abou Khalil R, Chahine R, Haddad C, Harb W, Ouaini N (2007) Effect of cucurbitacins on bilirubin-albumin binding in human plasma. Life Sci 80(6):579–585. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2006.10.005
Musza LL, Speight P, McElhiney S, Barrow CJ, Gillum AM, Cooper R, Killar LM (1994) Cucurbitacins, cell adhesion inhibitors from Conobea scoparioides. J Nat Prod 57(11):1498–1502
Dong Y, Lu B, Zhang X, Zhang J, Lai L, Li D, Wu Y, Song Y, Luo J, Pang X, Yi Z, Liu M (2010) Cucurbitacin E, a tetracyclic triterpenes compound from Chinese medicine, inhibits tumor angiogenesis through VEGFR2-mediated Jak2-STAT3 signaling pathway. Carcinogenesis 31(12):2097–2104. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgq167
Shan D, Chen L, Njardarson JT, Gaul C, Ma X, Danishefsky SJ, Huang XY (2005) Synthetic analogues of migrastatin that inhibit mammary tumor metastasis in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(10):3772–3776. doi:10.1073/pnas.0500658102
Chen L, Yang S, Jakoncic J, Zhang JJ, Huang XY (2010) Migrastatin analogues target fascin to block tumour metastasis. Nature 464(7291):1062–1066. doi:10.1038/nature08978
Pan X, Han H, Wang L, Yang L, Li R, Li Z, Liu J, Zhao Q, Qian M, Liu M, Du B (2011) Nitidine chloride inhibits breast cancer cells migration and invasion by suppressing c-Src/FAK associated signaling pathway. Cancer Lett 313(2):181–191. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2011.09.001
Sun CK, Man K, Ng KT, Ho JW, Lim ZX, Cheng Q, Lo CM, Poon RT, Fan ST (2008) Proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 (Pyk2) promotes proliferation and invasiveness of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through c-Src/ERK activation. Carcinogenesis 29(11):2096–2105. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgn203
Gaul C, Njardarson JT, Shan D, Dorn DC, Wu KD, Tong WP, Huang XY, Moore MA, Danishefsky SJ (2004) The migrastatin family: discovery of potent cell migration inhibitors by chemical synthesis. J Am Chem Soc 126(36):11326–11337. doi:10.1021/ja048779q
Yi ZF, Cho SG, Zhao H, Wu YY, Luo J, Li D, Yi T, Xu X, Wu Z, Liu M (2009) A novel peptide from human apolipoprotein(a) inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth by targeting c-Src phosphorylation in VEGF-induced human umbilical endothelial cells. Int J Cancer 124(4):843–852. doi:10.1002/ijc.24027
Hsia DA, Mitra SK, Hauck CR, Streblow DN, Nelson JA, Ilic D, Huang S, Li E, Nemerow GR, Leng J, Spencer KS, Cheresh DA, Schlaepfer DD (2003) Differential regulation of cell motility and invasion by FAK. J Cell Biol 160(5):753–767. doi:10.1083/jcb.200212114jcb.200212114
To C, Shilton BH, Di Guglielmo GM (2010) Synthetic triterpenoids target the Arp2/3 complex and inhibit branched actin polymerization. J Biol Chem 285(36):27944–27957. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.103036
Serrels B, Serrels A, Brunton VG, Holt M, McLean GW, Gray CH, Jones GE, Frame MC (2007) Focal adhesion kinase controls actin assembly via a FERM-mediated interaction with the Arp2/3 complex. Nat Cell Biol 9(9):1046–1056. doi:10.1038/ncb1626
Pang X, Yi T, Yi Z, Cho SG, Qu W, Pinkaew D, Fujise K, Liu M (2009) Morelloflavone, a biflavonoid, inhibits tumor angiogenesis by targeting rho GTPases and extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathways. Cancer Res 69(2):518–525. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2531
Aslakson CJ, Miller FR (1992) Selective events in the metastatic process defined by analysis of the sequential dissemination of subpopulations of a mouse mammary tumor. Cancer Res 52(6):1399–1405
Pulaski BA, Ostrand-Rosenberg S (1998) Reduction of established spontaneous mammary carcinoma metastases following immunotherapy with major histocompatibility complex class II and B7.1 cell-based tumor vaccines. Cancer Res 58(7):1486–1493
Malkas LH, Herbert BS, Abdel-Aziz W, Dobrolecki LE, Liu Y, Agarwal B, Hoelz D, Badve S, Schnaper L, Arnold RJ, Mechref Y, Novotny MV, Loehrer P, Goulet RJ, Hickey RJ (2006) A cancer-associated PCNA expressed in breast cancer has implications as a potential biomarker. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(51):19472–19477. doi:10.1073/pnas.0604614103
Blanc C, Deveraux QL, Krajewski S, Janicke RU, Porter AG, Reed JC, Jaggi R, Marti A (2000) Caspase-3 is essential for procaspase-9 processing and cisplatin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 60(16):4386–4390
Diez S, Gerisch G, Anderson K, Muller-Taubenberger A, Bretschneider T (2005) Subsecond reorganization of the actin network in cell motility and chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(21):7601–7606. doi:10.1073/pnas.0408546102
Otto AM, Muller CS, Huff T, Hannappel E (2002) Chemotherapeutic drugs change actin skeleton organization and the expression of beta-thymosins in human breast cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 128(5):247–256. doi:10.1007/s00432-002-0332-7
Machesky LM, Insall RH (1998) Scar1 and the related Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein, WASP, regulate the actin cytoskeleton through the Arp2/3 complex. Curr Biol 8(25):1347–1356
Robinson RC, Turbedsky K, Kaiser DA, Marchand JB, Higgs HN, Choe S, Pollard TD (2001) Crystal structure of Arp2/3 complex. Science 294(5547):1679–1684. doi:10.1126/science.1066333294/5547/1679
Kelleher JF, Atkinson SJ, Pollard TD (1995) Sequences, structural models, and cellular localization of the actin-related proteins Arp2 and Arp3 from Acanthamoeba. J Cell Biol 131(2):385–397
Wu X, Gan B, Yoo Y, Guan JL (2005) FAK-mediated src phosphorylation of endophilin A2 inhibits endocytosis of MT1-MMP and promotes ECM degradation. Dev Cell 9(2):185–196. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2005.06.006
Visse R, Nagase H (2003) Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: structure, function, and biochemistry. Circ Res 92(8):827–839. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000070112.80711.3D92/8/827
Ogier C, Bernard A, Chollet AM, Le Diguardher T, Hanessian S, Charton G, Khrestchatisky M, Rivera S (2006) Matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) regulates astrocyte motility in connection with the actin cytoskeleton and integrins. Glia 54(4):272–284. doi:10.1002/glia.20349
Sadzuka Y, Hatakeyama H, Daimon T, Sonobe T (2008) Screening of biochemical modulator by tumor cell permeability of doxorubicin. Int J Pharm 354(1–2):63–69. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2007.10.015
Friedl P, Wolf K (2003) Tumour-cell invasion and migration: diversity and escape mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer 3(5):362–374. doi:10.1038/nrc1075nrc1075
Sun C, Zhang M, Shan X, Zhou X, Yang J, Wang Y, Li-Ling J, Deng Y (2010) Inhibitory effect of cucurbitacin E on pancreatic cancer cells growth via STAT3 signaling. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136(4):603–610. doi:10.1007/s00432-009-0698-x
Burridge K, Wennerberg K (2004) Rho and Rac take center stage. Cell 116(2):167–179
Sein TT, Thant AA, Hiraiwa Y, Amin AR, Sohara Y, Liu Y, Matsuda S, Yamamoto T, Hamaguchi M (2000) A role for FAK in the Concanavalin A-dependent secretion of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9. Oncogene 19(48):5539–5542. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203932
Chen JS, Huang XH, Wang Q, Chen XL, Fu XH, Tan HX, Zhang LJ, Li W, Bi J (2010) FAK is involved in invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Exp Metastasis 27(2):71–82. doi:10.1007/s10585-010-9306-3
Lu J, Guo H, Treekitkarnmongkol W, Li P, Zhang J, Shi B, Ling C, Zhou X, Chen T, Chiao PJ, Feng X, Seewaldt VL, Muller WJ, Sahin A, Hung MC, Yu D (2009) 14-3-3zeta Cooperates with ErbB2 to promote ductal carcinoma in situ progression to invasive breast cancer by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Cell 16(3):195–207. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2009.08.010
Liotta LA, Tryggvason K, Garbisa S, Hart I, Foltz CM, Shafie S (1980) Metastatic potential correlates with enzymatic degradation of basement membrane collagen. Nature 284(5751):67–68
Curran S, Murray GI (1999) Matrix metalloproteinases in tumour invasion and metastasis. J Pathol 189(3):300–308. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199911)189:3<300:AID-PATH456>3.0.CO;2-C
Karavasilis V, Malamou-Mitsi V, Briasoulis E, Tsanou E, Kitsou E, Kalofonos H, Fountzilas G, Fotsis T, Pavlidis N (2005) Matrix metalloproteinases in carcinoma of unknown primary. Cancer 104(10):2282–2287. doi:10.1002/cncr.21454
Acknowledgments
This study was partially sponsored by the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (2012CB910400, 2009CB918402), National Natural Science Foundation of China (30930055, 30971523, and 81071807) and The Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (11DZ2260300 and 12XD1406100). We thank all members in Dr. Mingyao Liu’s lab in Institute of Biomedical Sciences and School of Life Sciences, East China Normal University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Tao Zhang and Jingjie Li contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, T., Li, J., Dong, Y. et al. Cucurbitacin E inhibits breast tumor metastasis by suppressing cell migration and invasion. Breast Cancer Res Treat 135, 445–458 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2175-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2175-5