Abstract
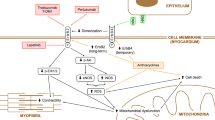
The ErbB2 receptor is a proto-oncogene associated with a poor prognosis in breast cancer. Herceptin, the only humanized anti-ErbB2 antibody currently in clinical use, has proven to be an essential tool in the immunotherapy of breast carcinoma, but induces cardiotoxicity. ErbB2 is involved in the growth and survival pathway of adult cardiomyocytes; however, its levels in the adult heart are much lower than those found in breast cancer cells, the intended targets of anti-ErbB2 antibodies. Furthermore, clinical trials have shown relatively low cardiotoxicity for Lapatinib, a dual kinase inhibitor of EGFR and ErbB2, and Pertuzumab, a new anti-ErbB2 monoclonal antibody currently in clinical trials, which recognizes an epitope distant from that of Herceptin. A novel human antitumor compact anti-ErbB2 antibody, Erb-hcAb, selectively cytotoxic for ErbB2-positive cancer cells in vitro and vivo, recognizes an epitope different from that of Herceptin, and does not show cardiotoxic effects both in vitro on rat and human cardiomyocytes and in vivo on a mouse model. We investigated the molecular basis of the different cardiotoxic effects among the ErbB2 inhibitors by testing their effects on the formation of the Neuregulin 1β (NRG-1)/ErbB2/ErbB4 complex and on the activation of its downstream signaling. We report herein that Erb-hcAb at difference with Herceptin, 2C4 (Pertuzumab) and Lapatinib, does not affect the ErbB2–ErbB4 signaling pathway activated by NRG-1 in cardiac cells. These findings may have important implications for the mechanism and treatment of anti-ErbB2-induced cardiotoxicity.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HFC:
-
Human fetal cardiomyocytes
- scFv:
-
Single chain fragment variable
- Erb-hcAb:
-
Erbicin-human-compact antibody
- NRG-1:
-
Neuregulin 1β
References
Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ, Ullrich A, McGuire WL (1987) Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/Neu oncogene. Science 235(4785):177–182
Baselga J, Albanell J, Molina MA, Arribas J (2001) Mechanism of action of trastuzumab and scientific update. Semin Oncol 28:4–11
Slamon DJ, Leyland-Jones B, Shak S, Fuchs H, Paton V, Bajamonde A, Fleming T, Eiermann W, Wolter J, Pegram M, Baselga J, Norton L (2001) Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N Engl J Med 344:783–792
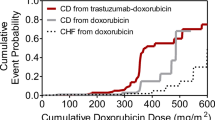
Sparano JA (2001) Cardiac toxicity of trastuzumab (herceptin): implications for the design of adjuvant trials. Semin Oncol 28:20–27. doi:10.1053/sonc.2001.22813
Chien KR (2000) Myocyte survival pathways and cardiomyopathy: implications for trastuzumab cardiotoxicity. Semin Oncol 27:9–14 (discussion 92–100)
Crone SA, Zhao YY, Fan L, Gu Y, Minamisawa S, Liu Y, Peterson KL, Chen J, Kahn R, Condorelli G, Ross J Jr, Chien KR, Lee KF (2002) ErbB2 is essential in the prevention of dilated cardiomyopathy. Nat Med 8:459–465. doi:10.1038/nm0502-459
Force T, Krause DS, Van Etten RA (2007) Molecular mechanisms of cardiotoxicity of tyrosine kinase inhibition. Nat Rev Cancer 7:332–344. doi:10.1038/nrc2106
Agus DB, Gordon MS, Taylor C, Natale RB, Karlan B, Mendelson DS, Press MF, Allison DE, Sliwkowski MX, Lieberman G, Kelsey SM, Fyfe G (2005) Phase I clinical study of pertuzumab, a novel HER dimerization inhibitor, in patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:2534–2543. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.03.184
Burris HA 3rd, Hurwitz HI, Dees EC, Dowlati A, Blackwell KL, O’Neil B, Marcom PK, Ellis MJ, Overmoyer B, Jones SF, Harris JL, Smith DA, Koch KM, Stead A, Mangum S, Spector NL (2005) Phase I safety, pharmacokinetics, and clinical activity study of lapatinib (GW572016), a reversible dual inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases, in heavily pretreated patients with metastatic carcinomas. J Clin Oncol 23:5305–5313. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.16.584
Perez EA, Koehler M, Byrne J, Preston AJ, Rappold E, Ewer MS (2008) Cardiac safety of lapatinib: pooled analysis of 3689 patients enrolled in clinical trials. Mayo Clinic Proc 83:679–686
Fedele C, Riccio G, Coppola C, Barbieri A, Monti MG, Arra C, Tocchetti CG, D’Alessio G, Maurea N, De Lorenzo C (2011) Comparison of preclinical cardiotoxic effects of different ErbB2 inhibitors. Breast Cancer Res Treat. doi:10.1007/s10549-011-1783-9
De Lorenzo C, Palmer DB, Piccoli R, Ritter MA, D’Alessio G (2002) A new human antitumor immunoreagent specific for ErbB2. Clin Cancer Res 8:1710–1719
De Lorenzo C, Tedesco A, Terrazzano G, Cozzolino R, Laccetti P, Piccoli R, D’Alessio G (2004) A human, compact, fully functional anti-ErbB2 antibody as a novel antitumour agent. Br J Cancer 91:1200–1204. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6602110
De Lorenzo C, Cozzolino R, Carpentieri A, Pucci P, Laccetti P, D’Alessio G (2005) Biological properties of a human compact anti-ErbB2 antibody. Carcinogenesis 26:1890–1895. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgi146
De Lorenzo C, Troise F, Cafaro V, D’Alessio G (2007) Combinatorial experimental protocols for erbicin-derived immunoagents and herceptin. Br J Cancer 97:1354–1360. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6604022
Troise F, Monti M, Merlino A, Cozzolino F, Fedele C, Russo Krauss I, Sica F, Pucci P, D’Alessio G, De Lorenzo C (2011) A novel ErbB2 epitope targeted by human antitumor immunoagents. FEBS J 278:1156–1166. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08041.x
Riccio G, Esposito G, Leoncini E, Contu R, Condorelli G, Chiariello M, Laccetti P, Hrelia S, D’Alessio G, De Lorenzo C (2009) Cardiotoxic effects, or lack thereof, of anti-ErbB2 immunoagents. FASEB J 23:3171–3178. doi:10.1096/fj.09-131383
Daly JM, Jannot CB, Beerli RR, Graus-Porta D, Maurer FG, Hynes NE (1997) Neu differentiation factor induces ErbB2 down-regulation and apoptosis of ErbB2-overexpressing breast tumor cells. Cancer Res 57:3804–3811
Fendly BM, Winget M, Hudziak RM, Lipari MT, Napier MA, Ullrich A (1990) Characterization of murine monoclonal antibodies reactive to either the human epidermal growth factor receptor or HER2/Neu gene product. Cancer Res 50:1550–1558
Kuramochi Y, Guo X, Sawyer DB (2006) Neuregulin activates erbB2-dependent src/FAK signaling and cytoskeletal remodeling in isolated adult rat cardiac myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 41:228–235
Gassmann M, Casagranda F, Orioli D, Simon H, Lai C, Klein R, Lemke G (1995) Aberrant neural and cardiac development in mice lacking the ErbB4 neuregulin receptor. Nature 378:390–394
Lee KF, Simon H, Chen H, Bates B, Hung MC, Hauser C (1995) Requirement for neuregulin receptor erbB2 in neural and cardiac development. Nature 378:394–398
Meyer D, Birchmeier C (1995) Multiple essential functions of neuregulin in development. Nature 378:386–390
Zhao YY, Sawyer DR, Baliga RR, Opel DJ, Han X, Marchionni MA, Kelly RA (1998) Neuregulins promote survival and growth of cardiac myocytes. Persistence of ErbB2 and ErbB4 expression in neonatal and adult ventricular myocytes. J Biol Chem 273:10261–10269
Pinkas-Kramarski R, Soussan L, Waterman H, Levkowitz G, Alroy I, Klapper L, Lavi S, Seger R, Ratzkin BJ, Sela M, Yarden Y (1996) Diversification of Neu differentiation factor and epidermal growth factor signaling by combinatorial receptor interactions. EMBO J 15:2452–2467
Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX (2001) Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:127–137
Fuller SJ, Sivarajah K, Sugden PH (2008) ErbB receptors, their ligands, and the consequences of their activation and inhibition in the myocardium. J Mol Cell Cardiol 44:831–854
Bersell K, Arab S, Haring B, Kuhn B (2009) Neuregulin1/ErbB4 signaling induces cardiomyocyte proliferation and repair of heart injury. Cell 138:257–270
De Keulenaer GW, Doggen K, Lemmens K (2010) The vulnerability of the heart as a pluricellular paracrine organ: lessons from unexpected triggers of heart failure in targeted ErbB2 anticancer therapy. Circ Res 106:35–46
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Dr. Philip Cunnah (Biotecnol, S.A., Portugal) for kindly providing the anti-ErbB2 compact antibody Erb-hcAb produced by PER.C6® cells. This study was supported by AIRC (Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Carmine Fedele and Gennaro Riccio contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fedele, C., Riccio, G., Malara, A.E. et al. Mechanisms of cardiotoxicity associated with ErbB2 inhibitors. Breast Cancer Res Treat 134, 595–602 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2103-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2103-8