Abstract
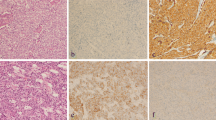
Advances in the understanding of the molecular basis of breast cancer have necessitated a definition of more sensitive and specific indicators of prognosis that are central to the underlying cancer biology and that reflect the complicated and heterogeneous nature of the disease. This study investigates the expression of epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) in breast cancer particularly basal-like phenotype group which remains unclear. EpCAM expression was assessed using immunohistochemistry in a large well-characterised series of breast carcinomas prepared as tissue microarrays. Relationships between EpCAM expression with molecular subtypes, clinicopathological variables and patients’ outcome were examined. EpCAM expression was associated with higher tumour grade (P < 0.001), larger tumour size (P < 0.001) and basal phenotype (P = 0.03). Importantly, within the basal-like tumours those positive for EpCAM showed a significantly shorter DFI (LR = 7.97, P = 0.005) and MFS (LR 4.01, P = 0.045). EpCAM may play a role in breast cancer progression and its expression is associated with poor patient outcome in basal-like breast cancer, independent of other prognostic factors.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-Rehim DM, Ball G, Pinder SE, Rakha E, Paish C, Robertson JF, Macmillan D, Blamey RW, Ellis IO (2005) High-throughput protein expression analysis using tissue microarray technology of a large well-characterised series identifies biologically distinct classes of breast cancer confirming recent cDNA expression analyses. Int J Cancer 116:340–350
Beckmann MW, Niederacher D, Schnurch HG, Gusterson BA, Bender HG (1997) Multistep carcinogenesis of breast cancer and tumour heterogeneity. J Mol Med 75:429–439
Parkin DM, Bray FI, Devesa SS (2001) Cancer burden in the year 2000. The global picture. Eur J Cancer 37(Suppl 8):S4–S66
Baeuerle PA, Gires O (2007) EpCAM (CD326) finding its role in cancer. Br J Cancer 96:417–423
Yanamoto S, Kawasaki G, Yoshitomi I, Iwamoto T, Hirata K, Mizuno A (2007) Clinicopathologic significance of EpCAM expression in squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue and its possibility as a potential target for tongue cancer gene therapy. Oral Oncol 43:869–877
Kimura H, Kato H, Faried A, Sohda M, Nakajima M, Fukai Y, Miyazaki T, Masuda N, Fukuchi M, Kuwano H (2007) Prognostic significance of EpCAM expression in human esophageal cancer. Int J Oncol 30:171–179
Osta WA, Chen Y, Mikhitarian K, Mitas M, Salem M, Hannun YA, Cole DJ, Gillanders WE (2004) EpCAM is overexpressed in breast cancer and is a potential target for breast cancer gene therapy. Cancer Res 64:5818–5824
Cimino A, Halushka M, Illei P, Wu X, Sukumar S, Argani P (2010) Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) is overexpressed in breast cancer metastases. Breast Cancer Res Treat 123(3):701–708
Litvinov SV, Velders MP, Bakker HA, Fleuren GJ, Warnaar SO (1994) Ep-CAM: a human epithelial antigen is a homophilic cell–cell adhesion molecule. J Cell Biol 125:437–446
Munz M, Kieu C, Mack B, Schmitt B, Zeidler R, Gires O (2004) The carcinoma-associated antigen EpCAM upregulates c-myc and induces cell proliferation. Oncogene 23:5748–5758
Momburg F, Moldenhauer G, Hammerling GJ, Moller P (1987) Immunohistochemical study of the expression of a Mr 34,000 human epithelium-specific surface glycoprotein in normal and malignant tissues. Cancer Res 47:2883–2891
Trzpis M, Popa ER, McLaughlin PM, van Goor H, Timmer A, Bosman GW, de Leij LM, Harmsen MC (2007) Spatial and temporal expression patterns of the epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM/EGP-2) in developing and adult kidneys. Nephron Exp Nephrol 107:e119–e131
Packeisen J, Kaup-Franzen C, Knieriem HJ (1999) Detection of surface antigen 17-1A in breast and colorectal cancer. Hybridoma 18:37–40
Pauli C, Munz M, Kieu C, Mack B, Breinl P, Wollenberg B, Lang S, Zeidler R, Gires O (2003) Tumour-specific glycosylation of the carcinoma-associated epithelial cell adhesion molecule EpCAM in head and neck carcinomas. Cancer Lett 193:25–32
Spizzo G, Fong D, Wurm M, Ensinger C, Obrist P, Hofer C, Mazzoleni G, Gastl G, Went P (2011) EpCAM expression in primary tumour tissues and metastases: an immunohistochemical analysis. J Clin Pathol 64(5):415–420
Basak S, Speicher D, Eck S, Wunner W, Maul G, Simmons MS, Herlyn D (1998) Colorectal carcinoma invasion inhibition by CO17–1A/GA733 antigen and its murine homologue. J Natl Cancer Inst 90:691–697
Seligson DB, Pantuck AJ, Liu X, Huang Y, Horvath S, Bui MH, Han KR, Correa AJ, Eeva M, Tze S, Belldegrun AS, Figlin RA (2004) Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (KSA) expression: pathobiology and its role as an independent predictor of survival in renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 10:2659–2669
Spizzo G, Went P, Dirnhofer S, Obrist P, Simon R, Spichtin H, Maurer R, Metzger U, von Castelberg B, Bart R, Stopatschinskaya S, Kochli OR, Haas P, Mross F, Zuber M, Dietrich H, Bischoff S, Mirlacher M, Sauter G, Gastl G (2004) High Ep-CAM expression is associated with poor prognosis in node-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 86:207–213
Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA, Fluge O, Pergamenschikov A, Williams C, Zhu SX, Lonning PE, Borresen-Dale AL, Brown PO, Botstein D (2000) Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 406:747–752
Rakha EA, Putti TC, Abd El-Rehim DM, Paish C, Green AR, Powe DG, Lee AH, Robertson JF, Ellis IO (2006) Morphological and immunophenotypic analysis of breast carcinomas with basal and myoepithelial differentiation. J Pathol 208:495–506
Spizzo G, Obrist P, Ensinger C, Theurl I, Dunser M, Ramoni A, Gunsilius E, Eibl G, Mikuz G, Gastl G (2002) Prognostic significance of Ep-CAM AND Her-2/neu overexpression in invasive breast cancer. Int J Cancer 98:883–888
Tandon AK, Clark GM, Chamness GC, McGuire WL (1990) Association of the 323/A3 surface glycoprotein with tumour characteristics and behaviour in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 50:3317–3321
Ellis IO, Galea M, Broughton N, Locker A, Blamey RW, Elston CW (1992) Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. II. Histological type. Relationship with survival in a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology 20:479–489
Elston CW, Ellis IO (1991) Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological grade in breast cancer: experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology 19:403–410
Galea MH, Blamey RW, Elston CE, Ellis IO (1992) The Nottingham Prognostic Index in primary breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 22:207–219
Madjd Z, Pinder SE, Paish C, Ellis IO, Carmichael J, Durrant LG (2003) Loss of CD59 expression in breast tumours correlates with poor survival. J Pathol 200:633–639
Abd El-Rehim DM, Pinder SE, Paish CE, Bell JA, Rampaul RS, Blamey RW, Robertson JF, Nicholson RI, Ellis IO (2004) Expression and co-expression of the members of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) family in invasive breast carcinoma. Br J Cancer 91:1532–1542
Rakha EA, El-Rehim DA, Paish C, Green AR, Lee AH, Robertson JF, Blamey RW, Macmillan D, Ellis IO (2006) Basal phenotype identifies a poor prognostic subgroup of breast cancer of clinical importance. Eur J Cancer 42:3149–3156
Rakha EA, El-Sayed ME, Green AR, Lee AH, Robertson JF, Ellis IO (2007) Prognostic markers in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer 109:25–32
McShane LM, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W, Taube SE, Gion M, Clark GM (2005) Reporting recommendations for tumour marker prognostic studies. J Clin Oncol 23:9067–9072
McCarty KS Jr, Miller LS, Cox EB, Konrath J, McCarty KS Sr (1985) Oestrogen receptor analyses. Correlation of biochemical and immunohistochemical methods using monoclonal antireceptor antibodies. Arch Pathol Lab Med 109:716–721
Okegawa T, Pong RC, Li Y, Hsieh JT (2004) The role of cell adhesion molecule in cancer progression and its application in cancer therapy. Acta Biochim Pol 51:445–457
Chelius D, Ruf P, Gruber P, Ploscher M, Liedtke R, Gansberger E, Hess J, Wasiliu M, Lindhofer H (2010) Structural and functional characterization of the trifunctional antibody catumaxomab. MAbs 2(3):309–319
Heiss MM, Murawa P, Koralewski P, Kutarska E, Kolesnik OO, Ivanchenko VV, Dudnichenko AS, Aleknaviciene B, Razbadauskas A, Gore M, Ganea-Motan E, Ciuleanu T, Wimberger P, Schmittel A, Schmalfeldt B, Burges A, Bokemeyer C, Lindhofer H, Lahr A, Parsons SL (2010) The trifunctional antibody catumaxomab for the treatment of malignant ascites due to epithelial cancer: Results of a prospective randomized phase II/III trial. Int J Cancer 127(9):2209–2221
Sears HF, Atkinson B, Mattis J, Ernst C, Herlyn D, Steplewski Z, Hayry P, Koprowski H (1982) Phase-I clinical trial of monoclonal antibody in treatment of gastrointestinal tumours. Lancet 1:762–765
Schmidt M, Scheulen ME, Dittrich C, Obrist P, Marschner N, Dirix L, Ruttinger D, Schuler M, Reinhardt C, Awada A (2010) An open-label, randomized phase II study of adecatumumab, a fully human anti-EpCAM antibody, as monotherapy in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol 21(2):275–282
Schmidt DS, Klingbeil P, Schnolzer M, Zoller M (2004) CD44 variant isoforms associate with tetraspanins and EpCAM. Exp Cell Res 297:329–347
Maaser K, Borlak J (2008) A genome-wide expression analysis identifies a network of EpCAM-induced cell cycle regulators. Br J Cancer 99:1635–1643
Hori M, Shimazaki J, Inagawa S, Itabashi M (2002) Overexpression of MDM2 oncoprotein correlates with possession of oestrogen receptor alpha and lack of MDM2 mRNA splice variants in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 71:77–83
Sankpal NV, Willman MW, Fleming TP, Mayfield JD, Gillanders WE (2009) Transcriptional repression of epithelial cell adhesion molecule contributes to p53 control of breast cancer invasion. Cancer Res 69:753–757
Litvinov SV, Balzar M, Winter MJ, Bakker HA, Briaire-de Bruijn IH, Prins F, Fleuren GJ, Warnaar SO (1997) Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (Ep-CAM) modulates cell–cell interactions mediated by classic cadherins. J Cell Biol 139:1337–1348
Kovacs A, Dhillon J, Walker RA (2003) Expression of P-cadherin, but not E-cadherin or N-cadherin, relates to pathological and functional differentiation of breast carcinomas. Mol Pathol 56:318–322
Paredes J, Lopes N, Milanezi F, Schmitt FC (2007) P-cadherin and cytokeratin 5: useful adjunct markers to distinguish basal-like ductal carcinomas in situ. Virchows Arch 450:73–80
Bischoff JR, Plowman GD (1999) The Aurora/Ipl1p kinase family: regulators of chromosome segregation and cytokinesis. Trends Cell Biol 9:454–459
Sorlie T, Perou CM, Fan C, Geisler S, Aas T, Nobel A, Anker G, Akslen LA, Botstein D, Borresen-Dale AL, Lonning PE (2006) Gene expression profiles do not consistently predict the clinical treatment response in locally advanced breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 5:2914–2918
Urruticoechea A, Smith IE, Dowsett M (2005) Proliferation marker Ki-67 in early breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:7212–7220
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Breast Cancer Campaign.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no disclosures or conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agboola, A.J., Paish, E.C., Rakha, E.A. et al. EpCAM expression is an indicator of recurrence in basal-like breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 133, 575–582 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-011-1813-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-011-1813-7