Abstract
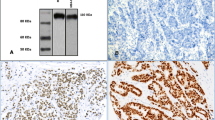
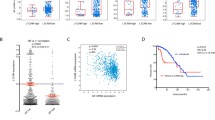
Breast cancer mortality is frequently associated with metastatic disease. Metastasis models have shown adrenoceptor (AR) stimulation induces cell migration which is inhibited by adrenoceptor antagonist drugs. We investigated adrenoceptor protein expression in clinical breast tumours and its association with disease progression and prognosis. Immunohistochemistry on tissue microarrays was used to characterise α1b, α2c and β22 adrenoceptor protein expression in operable breast tumours. Associations with tumour-relevant biological markers and clinical outcome were statistically assessed. Strong α1b expression occurred in large high grade (P < 0.0001), HER2+ (P < 0.0001) or basal-like (CK5/6, P = 0.0005; CK14, P = 0.0001; EGFR, P = 0.003) cancers, showing increased proliferation (Mib1, P = 0.002), decreased apoptosis (Bcl2, P < 0.0001) and poor NPI membership (P = 0.001). α1b expression correlated with poor cancer-specific survival (LR = 7.628, P = 0.022) and tumour recurrence (LR = 6.128, P = 0.047). Strong α2c was over-expressed in high grade (P = 0.007), HER3+ (P = 0.002) and HER4+ (P < 0.0001) cancers with borderline increase in EGFR, p53 and MIB1 proteins, and inverse association with hormonal (PgR, P = 0.002) phenotype. In contrast, strong β2 expression occurred in small-size, luminal-like (ER+, P < 0.001) tumours of low grade (P < 0.001) and lymph node stage (P = 0.027) that showed poor prognosis when hormonal treatment was withheld. Adrenoceptors were not found to be independent predictors of clinical outcome. Alpha1b and α2c AR is over-expressed in basal-like breast tumours of poor prognosis. Strong β2 adrenoceptor expression is seen in patients with a luminal (ER+) tumour phenotype and good prognosis, due to benefits derived from hormonal therapy. These findings suggest a possible role for targeted therapy using adrenoceptor antagonists.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AR:
-
Androgen receptor/adrenoceptor
- BCSS:
-
Breast cancer-specific survival
- CK:
-
Cytokeratin
- DFI:
-
Disease-free interval
- DM:
-
Distant metastasis
- E:
-
Epinephrine
- ER:
-
Oestrogen receptor
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- NE:
-
Norepinephrine
- PGR:
-
Progesterone receptor
References
Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results. http://seer.cancer.gov/publications/
Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Aksien LA et al (2000) Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 406(6797):747–752
Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS et al (2001) Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(19):10869–10874
Johnston SRD (2009) Enhancing the efficacy of hormonal agents with selected targeted agents. Clin Breast Cancer 9:S28–S36
Engel J, Eckel R, Kerr J, Schmidt M, Furstenberger G, Richter R, Sauer H, Senn HJ, Holzel D (2003) The process of metastasisation for breast cancer. Eur J Cancer 39(12):1794–1806
Entschladen F, Drell TL, Lang K, Joseph J, Zaenker KS (2004) Tumour-cell migration, invasion, and metastasis: navigation by neurotransmitters. Lancet Oncol 5(4):254–258
Entschladen F, Drell TL, Lang K, Joseph J, Zaenker KS (2005) Neurotransmitters and chemokines regulate tumor cell migration: potential for a new pharmacological approach to inhibit invasion and metastasis development. Curr Pharm Des 11(3):403–411
Masur K, Niggemann B, Zaenker KS, Entschladen F (2001) Norepinephrine-induced migration of SW 480 colon carcinoma cells is inhibited by beta-blockers. Cancer Res 61(7):2866–2869
Lang K, Drell TL, Lindecke A, Niggemann B, Kaltschmidt C, Zaenker KS, Entschladen F (2004) Induction of a metastatogenic tumor cell type by neurotransmitters and its pharmacological inhibition by established drugs. Int J Cancer 112(2):231–238
Drell TL, Joseph J, Lang K, Niggemann B, Zaenker KS, Entschladen F (2003) Effects of neurotransmitters on the chemokinesis and chemotaxis of MDA-MB-468 human breast carcinoma cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 80(1):63–70
Palm D, Lang K, Niggemann B, Drell TL, Masur K, Zaenker KS, Entschladen F (2006) The norepinephrine-driven metastasis development of PC-3 human prostate cancer cells in BALB/c nude mice is inhibited by beta-blockers. Int J Cancer 118(11):2744–2749
Sood AK, Bhatty R, Kamat AA, Landen CN, Han L, Thaker PH, Li Y, Gershenson DM, Lutgendorf S, Cole SW (2006) Stress hormone-mediated invasion of ovarian cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 12(2):369–375
Dorn GW, Liggett SB (2008) Pharmacogenomics of beta-adrenergic receptors and their accessory signaling proteins in heart failure. CTS Clin Transl Sci 1(3):255–262
Rosini M, Bolognesi ML, Giardina D, Minarini A, Tumiatti V, Melchiorre C (2007) Recent advances in alpha(1)-adrenoreceptor antagonists as pharmacological tools and therapeutic agents. Curr Top Med Chem 7(2):147–162
Harris AM, Warner BW, Wilson JM, Becker A, Rowland RG, Conner W, Lane M, Kimbler K, Durbin EB, Baron AT et al (2007) Effect of alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonist exposure on prostate cancer incidence: an observational cohort study. J Urol 178(5):2176–2180
Algazi M, Plu-Bureau G, Flahault A, Dondon MG, Le MG (2006) Is beta-blocker treatment associated with a decrease in the risk of cancer. Lett Drug Des Discov 3(9):653–661
Abdel-Fatah TMA, Powe DG, Ball G, Reis JS, Ellis IO (2009) The need for a biological grading system and its relationship to the current Nottingham histological grading system (NGS). EJC Suppl 7(2):264–265
El-Rehim D, Ball G, Pinder S, Rakha E, Paish C, Robertson J, Macmillan D, Blamey R, Ellis I (2005) High throughput protein expression analysis using tissue microarray technology of a large well -characterised series identifies biologically distinct classes of breast cancer confirming recent cDNA expression analyses. Int J Cancer 116(3):340–350
El-Rehim DMA, Ball G, Pinder S, Ellis IO (2004) Molecular classification of breast carcinoma based on the protein expression immunoprofiles. J Pathol 204:3A–4A
Habashy HO, Powe DG, Rakha EA, Ball G, Paish C, Gee J, Nicholson RI, Ellis IO (2008) Forkhead-box A1 (FOXA1) expression in breast cancer and its prognostic significance. Eur J Cancer 44(11):1541–1551
McShane LM, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W, Taube SE, Gion M, Clark GM (2006) REporting recommendations for tumor MARKer prognostic studies (REMARK). Breast Cancer Res Treat 100(2):229–235
Luthy IA, Bruzzone A, Pinero CP, Castillo LF, Chiesa IJ, Vazquez SM, Sarappa MG (2009) Adrenoceptors: non-conventional target for breast cancer? Curr Med Chem 16(15):1850–1862
Badino G, Novelli A, Girardi C, Carlo FD (1996) Evidence for functional beta-adrenoceptor subtypes in CG-5 breast cancer cell. Pharmacol Res 33(4–5):255–260
Marchetti B, Fortier MA, Poyet P, Follea N, Pelletier G, Labrie F (1990) Beta-adrenergic receptors in the rat mammary gland during pregnancy and lactation—characterization, distribution, and coupling to adenylate cyclase. Endocrinology 126(1):565–574
Slotkin TA, Zhang JA, Dancel R, Garcia SJ, Willis C, Seidler FJ (2000) Beta-adrenoceptor signaling and its control of cell replication in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 60(2):153–166
Vandewalle B, Revillion F, Lefebvre J (1990) Functional adrenergic receptors in breast cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 116(3):303–306
Shang ZJ, Liu K, Liang DF (2009) Expression of beta(2)-adrenergic receptor in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med 38(4):371–376
Draoui A, Vandewalle B, Hornez L, Revillion F, Lefebvre J (1991) Beta-adrenergic receptors in human breast cancer—characterization and correlation with progesterone and estradiol receptors. Anticancer Res 11(2):677–680
Schuller HM (2007) Neurotransmitter receptor-mediated signaling pathways as modulators of carcinogenesis. Neuronal Act Tumor Tissue 39:45–63
Lancashire L, Powe D, Reis-Filoh J, Rakha E, Lemetre C, Weigelt B, Abdel-Fatah T, Green A, Mukta R, Blamey R et al (2010) A validated gene expression profile for detecting clinical outcome in breast cancer using artificial neural networks. Breast Cancer Res Treat 120(1):83–93
Al-Wadei HA, Al-Wadei MH, Schuller HM (2009) Prevention of pancreatic cancer by the beta-blocker propranolol. Anti-Cancer Drugs 20(6):477–482
Powe DG, Habashy HO, Voss MH, Zaenker KS, Green AR, Ellis IO, Entschladen F (2010) Beta-blocker drug therapy reduces secondary cancer formation in breast cancer and improves cancer specific survival. Oncotarget 1(7):628–638
Hui HX, Fernando MA, Heaney AP (2008) The alpha(1)-adrenergic receptor antagonist doxazosin inhibits EGFR and NF-kappa B signalling to induce breast cancer cell apoptosis. Eur J Cancer 44(1):160–166
Lowe FC (2004) Role of the newer alpha(1)-adrenergic-receptor antagonists in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia-related lower urinary tract symptoms. Clin Ther 26(11):1701–1713
Chiu G, Connolly PJ, Middleton SA, Li SJ, Pulito V, Liu JC, Baxter EW, Reitz AB (2008) Alpha(1a/1d)-selective adrenergic receptor antagonists for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia/lower urinary tract symptoms. Expert Opin Therap Pat 18(12):1351–1360
Acknowledgments
Members of the Institute of Immunology, Witten/Herdecke University were supported by the Fritz Bender Foundation (Munich, Germany). In addition, the ministry of higher education (Egypt) is thanked for funding HOH.
Conflict interests
The authors have no conflict of interests to declare
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table 1
Supplementary material 1 (DOC 45 kb)
Table 2
Characteristics for patients investigated for α1b adrenoceptor protein expression (DOC 90 kb)
Table 3
Associations between α1b adrenoceptor protein expression and tumour relevant markers (DOC 122 kb)
Table 4
Characteristics for patients investigated for α2c adrenoceptor protein expression (DOC 90 kb)
Table 5
Associations between α2c adrenoceptor protein expression and tumour relevant markers (DOC 121 kb)
Table 6
Characteristics for patients investigated for β2 adrenoceptor protein expression (DOC 90 kb)
Table 7
Associations between β2 adrenoceptor protein expression and tumour relevant markers (DOC 122 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Powe, D.G., Voss, M.J., Habashy, H.O. et al. Alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptor (AR) protein expression is associated with poor clinical outcome in breast cancer: an immunohistochemical study. Breast Cancer Res Treat 130, 457–463 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-011-1371-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-011-1371-z