Abstract
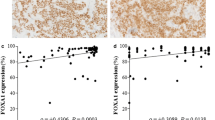
Oestrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer (BC) constitutes a heterogeneous group of tumours with regard to outcome and response to therapy. Accurate stratification of ER-positive BC according to risk of relapse and response to therapy will be achieved through an improved understanding of ER and ER-related biological pathways. Recent studies have identified Forkhead box O3a (FOXO3a) transcription factor as an intracellular mediator of ERα expression and as an important downstream target of the Akt/PI3K pathway indicating a biological and potential clinical role for FOXO3a in ER-positive BC. In this study, we investigated the clinical relevance and biological associations of FOXO3a protein expression, using tissue microarrays and immunohistochemistry, in a large series of patients with invasive breast cancer. FOXO3a protein expression showed both nuclear and/or cytoplasmic staining patterns. FOXO3a predominant nuclear expression was positively associated with biomarkers of good prognosis including PgR, FOXA1 and p27 expression. There was an inverse association with mitotic counts, MIB1 growth fraction, C-MYC and PIK3CA expression. With respect to patient outcome, FOXO3a nuclear localisation was associated with longer BC specific survival (P < 0.001) and longer distant metastasis free interval (P = 0.001), independently of the well-established breast cancer prognostic factors. In conclusion, our results demonstrate the biological and prognostic role of FOXO3a protein expression and its subcellular localisation in ER-positive/luminal-like BC possibly through its involvement in controlling cell proliferation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Murphy LC, Watson P (2002) Steroid receptors in human breast tumorigenesis and breast cancer progression. Biomed Pharmacother 56(2):65–77
Yang J-Y, Hung M-C (2009) A new fork for clinical application: targeting forkhead transcription factors in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 15(3):752–757
Tsai K-L, Sun Y-J, Huang C-Y, Yang J-Y, Hung M-C, Hsiao C-D (2007) Crystal structure of the human FOXO3a-DBD/DNA complex suggests the effects of post-translational modification. Nucleic Acids Res 35(20):6984–6994
Zou Y, Tsai W-B, Cheng C-J, Hsu C, Chung Y, Li P-C, Lin S-H, Hu M (2008) Forkhead box transcription factor FOXO3a suppresses estrogen-dependent breast cancer cell proliferation and tumorigenesis. Breast Cancer Res 10(1):R21
Guo S, Sonenshein GE (2004) Forkhead box transcription factor FOXO3a regulates estrogen receptor alpha expression and is repressed by the Her-2/neu/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol 24(19):8681–8690
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J, Greenberg ME (1999) Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96(6):857–868
Vara JÁF, Casado E, de Castro J, Cejas P, Belda-Iniesta C, González-Barón M (2004) PI3K/Akt signalling pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 30(2):193–204
Huang H, Tindall DJ (2007) Dynamic FoxO transcription factors. J Cell Sci 120(15):2479–2487
Yang J-Y, Zong CS, Xia W, Yamaguchi H, Ding Q, Xie X, Lang J-Y, Lai C-C, Chang C-J, Huang W-C et al (2008) ERK promotes tumorigenesis by inhibiting FOXO3a via MDM2-mediated degradation. Nat Cell Biol 10(2):138–148
Burgering BMT, Medema RH (2003) Decisions on life and death: FOXO Forkhead transcription factors are in command when PKB/Akt is off duty. J Leukoc Biol 73(6):689–701
Burgering BMT, Kops GJPL (2002) Cell cycle and death control: long live Forkheads. Trends Biochem Sci 27(7):352–360
Alvarez B, Martinez-A C, Burgering BMT, Carrera AC (2001) Forkhead transcription factors contribute to execution of the mitotic programme in mammals. Nature 413(6857):744–747
Hu MCT, Lee D-F, Xia W, Golfman LS, Ou-Yang F, Yang J-Y, Zou Y, Bao S, Hanada N, Saso H et al (2004) I[kappa]B kinase promotes tumorigenesis through inhibition of Forkhead FOXO3a. Cell 117(2):225–237
Accili D, Arden KC (2004) FoxOs at the crossroads of cellular metabolism, differentiation, and transformation. Cell 117(4):421–426
Stahl M, Dijkers PF, Kops GJPL, Lens SMA, Coffer PJ, Burgering BMT, Medema RH (2002) The Forkhead transcription factor FoxO regulates transcription of p27Kip1 and Bim in response to IL-2. J Immunol 168(10):5024–5031
Kops GJPL, Dansen TB, Polderman PE, Saarloos I, Wirtz KWA, Coffer PJ, Huang T-T, Bos JL, Medema RH, Burgering BMT (2002) Forkhead transcription factor FOXO3a protects quiescent cells from oxidative stress. Nature 419(6904):316–321
Miyamoto K, Araki KY, Naka K, Arai F, Takubo K, Yamazaki S, Matsuoka S, Miyamoto T, Ito K, Ohmura M et al (2007) Foxo3a is essential for maintenance of the hematopoietic stem cell pool. Cell Stem Cell 1(1):101–112
Tothova Z, Kollipara R, Huntly BJ, Lee BH, Castrillon DH, Cullen DE, McDowell EP, Lazo-Kallanian S, Williams IR, Sears C et al (2007) FoxOs are critical mediators of hematopoietic stem cell resistance to physiologic oxidative stress. Cell 128(2):325–339
You H, Yamamoto K, Mak TW (2006) Regulation of transactivation-independent proapoptotic activity of p53 by FOXO3a. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(24):9051–9056
Myatt SS, Lam EWF (2007) The emerging roles of forkhead box (Fox) proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 7(11):847–859
Krol J, Francis RE, Albergaria A, Sunters A, Polychronis A, Coombes RC, Lam EWF (2007) The transcription factor FOXO3a is a crucial cellular target of gefitinib (Iressa) in breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 6(12):3169–3179
Sunters A, Fernandez de Mattos S, Stahl M, Brosens JJ, Zoumpoulidou G, Saunders CA, Coffer PJ, Medema RH, Coombes RC, Lam EWF (2003) FoxO3a transcriptional regulation of Bim controls apoptosis in paclitaxel-treated breast cancer cell lines. J Biol Chem 278(50):49795–49805
Sunters A, Madureira PA, Pomeranz KM, Aubert M, Brosens JJ, Cook SJ, Burgering BMT, Coombes RC, Lam EW-F (2006) Paclitaxel-induced nuclear translocation of FOXO3a in breast cancer cells is mediated by c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase and Akt. Cancer Res 66(1):212–220
El-Rehim DMA, Ball G, Pinder SE, Rakha E, Paish C, Robertson JFR, Macmillan D, RWB I, Ellis aO (2005) High-throughput protein expression analysis using tissue microarray technology of a large well-characterised series identifies biologically distinct classes of breast cancer confirming recent cDNA expression analyses. Int J Cancer 116(3):340–350
Elston CW, Ellis IO (1991) Pathological prognostic factors in breast-cancer. 1. The value of histological grade in breast-cancer—experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology 19(5):403–410
Galea MH, Blamey RW, Elston CE, Ellis IO (1992) The Nottingham prognostic index in primary breast-cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 22(3):207–219
Habashy HO, Powe DG, Rakha EA, Ball G, Paish C, Gee J, Nicholson RI, Ellis IO (2008) Forkhead-box A1 (FOXA1) expression in breast cancer and its prognostic significance. Eur J Cancer 44(11):1541–1551
El-Rehim DMA, Pinder SE, Paish CE, Bell J, Blamey R, Robertson JFR, Nicholson RI, Ellis IO (2004) Expression of luminal and basal cytokeratins in human breast carcinoma. J Pathol 203(2):661–671
Rakha EA, El-Sayed ME, Powe DG, Green AR, Habashy H, Grainge MJ, Robertson JFR, Blamey R, Gee J, Nicholson RI et al (2008) Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast: response to hormonal therapy and outcomes. Eur J Cancer 44(1):73–83
Habashy H, Powe D, Rakha E, Ball G, Macmillan R, Green A, Ellis I (2010) The prognostic significance of PELP1 expression in invasive breast cancer with emphasis on the ER-positive luminal-like subtype. Breast Cancer Res Treat 120:603–612
Aleskandarany M, Rakha E, Ahmed M, Powe D, Paish E, Macmillan R, Ellis I, Green A (2010) PIK3CA expression in invasive breast cancer: a biomarker of poor prognosis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 122(1):45–53
McShane LM, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W, Taube SE, Gion M, Clark GM (2005) Reporting recommendations for tumor marker prognostic studies. J Clin Oncol 23(36):9067–9072
McShane LM, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W, Taube SE, Gion M, Clark GM (2006) REporting recommendations for tumor MARKer prognostic studies (REMARK). Breast Cancer Res Treat 100(2):229–235
Loi S (2008) Molecular analysis of hormone receptor positive (luminal) breast cancers—what have we learnt? Eur J Cancer 44(18):2813–2818
Bardou V-J, Arpino G, Elledge RM, Osborne CK, Clark GM (2003) Progesterone receptor status significantly improves outcome prediction over estrogen receptor status alone for adjuvant endocrine therapy in two large breast cancer databases. J Clin Oncol 21(10):1973–1979
Thorat MA, Marchio C, Morimiya A, Savage K, Nakshatri H, Reis-Filho JS, Badve S (2007) FOXA1 expression in breast cancer is associated with luminal subtype and good prognosis. J Clin Pathol 61:327–332
Delpuech O, Griffiths B, East P, Essafi A, Lam EWF, Burgering B, Downward J, Schulze A (2007) Induction of Mxi1-SR{alpha} by FOXO3a contributes to repression of Myc-dependent gene expression. Mol Cell Biol 27(13):4917–4930
Acknowledgments
We thank the Ministry of Higher Education (Egypt) for funding H. O. Habashy, M. Ahmed, M. Aleskandarany and E. Rakha.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Habashy, H.O., Rakha, E.A., Aleskandarany, M. et al. FOXO3a nuclear localisation is associated with good prognosis in luminal-like breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 129, 11–21 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-010-1161-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-010-1161-z