Abstract
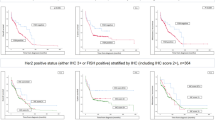
Increased expression and activation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) was reported to be an unfavorable factor in various human cancers, including breast cancer. In order to study FAK gene status as a prognostic factor, we evaluated FAK gene copy number and FAK protein expression in invasive breast cancer. Tumors from 435 patients with invasive breast cancer were evaluated for FAK gene status using fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and immunohistochemistry (IHC) based on tissue array method. Survival analyses were performed using the Kaplan–Meier method in 267 patients. 42 out of 362 evaluable cases (11.6%) showed high polysomy and 22 cases (6.1%) had gene amplification by FISH. 108 out of 393 evaluable cases (27.5%) showed FAK overexpression by IHC. FAK FISH positivity was significantly associated with higher histologic grade, higher T stage, negative estrogen receptor expression, negative progesterone receptor expression and triple-negative phenotype; FAK overexpression with higher histologic grade and triple-negative phenotype. FAK overexpression was noted in 57.8% (37 of 64) of FAK FISH+ cases. The concordance of FISH and IHC results for FAK gene was observed in 74.9% (271 of 362). Survival analyses revealed the patients with FAK FISH+ breast cancer had significantly shorter overall survival and relapse-free survival compared to those with FISH− breast cancer. In node-positive breast cancer patients who received postoperative systemic treatment, the patients with FAK FISH+ showed significantly shorter 5-year survival rates. Despite of high significant concordance between the results of FISH and IHC for FAK gene in invasive breast cancer, only FAK FISH positivity was an unfavorable prognostic factor.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sieg DJ, Hauck CR, Ilic D, Klingbeil CK, Schaefer E, Damsky CH, Schlaepfer DD (2000) FAK integrates growth-factor and integrin signals to promote cell migration. Nat Cell Biol 2:249–256. doi:10.1038/35010517
Mitra SK, Hanson DA, Schlaepfer DD (2005) Focal adhesion kinase: in command and control of cell motility. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:56–68. doi:10.1038/nrm1549
McLean GW, Carragher NO, Avizienyte E, Evans J, Brunton VG, Frame MC (2005) The role of focal-adhesion kinase in cancer—a new therapeutic opportunity. Nat Rev Cancer 5:505–515. doi:10.1038/nrc1647
Weiner TM, Liu ET, Craven RJ, Cance WG (1993) Expression of focal adhesion kinase gene and invasive cancer. Lancet 342:1024–1025
Lark AL, Livasy CA, Calvo B, Caskey L, Moore DT, Yang X, Cance WG (2003) Overexpression of focal adhesion kinase in primary colorectal carcinomas and colorectal liver metastases: immunohistochemistry and real-time PCR analyses. Clin Cancer Res 9:215–222
Owens LV, Xu L, Dent GA, Yang X, Sturge GC, Craven RJ, Cance WG (1996) Focal adhesion kinase as a marker of invasive potential in differentiated human thyroid cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 3:100–105
Judson PL, He X, Cance WG, Van Le L (1999) Overexpression of focal adhesion kinase, a protein tyrosine kinase, in ovarian carcinoma. Cancer 86:1551–1556. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19991015)86:6<1551:AID-CNCR23>3.0.CO;2-P
Oktay MH, Oktay K, Hamele-Bena D, Buyuk A, Koss LG (2003) Focal adhesion kinase as a marker of malignant phenotype in breast and cervical carcinomas. Hum Pathol 34:240–245. doi:10.1053/hupa.2003.40
Kornberg LJ (1998) Focal adhesion kinase and its potential involvement in tumor invasion and metastasis. Head Neck 20:745–752. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0347(199812)20:8<745:AID-HED14>3.0.CO;2-Z
Imaizumi M, Nishimura M, Takeuchi S, Murase M, Hamaguchi M (1997) Role of tyrosine specific phosphorylation of cellular proteins, especially EGF receptor and p125FAK in human lung cancer cells. Lung Cancer 17:69–84
Itoh S, Maeda T, Shimada M, Aishima S, Shirabe K, Tanaka S, Maehara Y (2004) Role of expression of focal adhesion kinase in progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 10:2812–2817
Miyazaki T, Kato H, Nakajima M, Sohda M, Fukai Y, Masuda N, Manda R, Fukuchi M, Tsukada K, Kuwano H (2003) FAK overexpression is correlated with tumour invasiveness and lymph node metastasis in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer 89:140–145. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6601050
Myllykangas S, Bohling T, Knuutila S (2007) Specificity, selection and significance of gene amplifications in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 17:42–55. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2006.10.005
Agochiya M, Brunton VG, Owens DW, Parkinson EK, Paraskeva C, Keith WN, Frame MC (1999) Increased dosage and amplification of the focal adhesion kinase gene in human cancer cells. Oncogene 18:5646–5653. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202957
Canel M, Secades P, Rodrigo JP, Cabanillas R, Herrero A, Suarez C, Chiara MD (2006) Overexpression of focal adhesion kinase in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma is independent of fak gene copy number. Clin Cancer Res 12:3272–3279. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1583
Cance WG, Harris JE, Iacocca MV, Roche E, Yang X, Chang J, Simkins S, Xu L (2000) Immunohistochemical analyses of focal adhesion kinase expression in benign and malignant human breast and colon tissues: correlation with preinvasive and invasive phenotypes. Clin Cancer Res 6:2417–2423
Pylayeva Y, Gillen KM, Gerald W, Beggs HE, Reichardt LF, Giancotti FG (2009) Ras- and PI3K-dependent breast tumorigenesis in mice and humans requires focal adhesion kinase signaling. J Clin Invest 119:252–266. doi:10.1172/JCI37160
Lahlou H, Sanguin-Gendreau V, Zuo D, Cardiff RD, McLean GW, Frame MC, Muller WJ (2007) Mammary epithelial-specific disruption of the focal adhesion kinase blocks mammary tumor progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:20302–20307. doi:10.1073/pnas.0710091104
Molckovsky A, Siu LL (2008) First-in-class, first-in-human phase I results of targeted agents: highlights of the 2008 American society of clinical oncology meeting. J Hematol Oncol 1:20. doi:10.1186/1756-8722-1-20
Siu LL, Burris HA III, Mileshkin LR, Camidge DR, Eckhardt SG, Lamb, A, Chen EX, Jones SF, Xu H, Fingert H (2008) A phase I clinical, pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) evaluation of PF-00562271 targeting focal adhesion kinase (FAK) in patients (pts) with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol (Meeting Abstracts) 26
Zhao J, Guan JL (2009) Signal transduction by focal adhesion kinase in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 28:35–49. doi:10.1007/s10555-008-9165-4
Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID (2002) AJCC cancer staging manual
Hyun CL, Lee HE, Kim KS, Kim SW, Kim JH, Choe G, Park SY (2008) The effect of chromosome 17 polysomy on HER-2/neu status in breast cancer. J Clin Pathol 61:317–321. doi:10.1136/jcp.2007.050336
Park JY, Cho MO, Leonard S, Calder B, Mian IS, Kim WH, Wijnhoven S, van Steeg H, Mitchell J, van der Horst GT, Hoeijmakers J, Cohen P, Vijg J, Suh Y (2008) Homeostatic imbalance between apoptosis and cell renewal in the liver of premature aging Xpd mice. PLoS One 3:e2346. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002346
De Santis G, Miotti S, Mazzi M, Canevari S, Tomassetti A (2009) E-cadherin directly contributes to PI3 K/AKT activation by engaging the PI3K-p85 regulatory subunit to adherens junctions of ovarian carcinoma cells. Oncogene 28:1206–1217. doi:10.1038/onc.2008.470
Marinari B, Moretti F, Botti E, Giustizieri ML, Descargues P, Giunta A, Stolfi C, Ballaro C, Papoutsaki M, Alema S, Monteleone G, Chimenti S, Karin M, Costanzo A (2008) The tumor suppressor activity of IKKalpha in stratified epithelia is exerted in part via the TGF-beta antiproliferative pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:17091–17096. doi:10.1073/pnas.0809288105
Cappuzzo F, Hirsch FR, Rossi E, Bartolini S, Ceresoli GL, Bemis L, Haney J, Witta S, Danenberg K, Domenichini I, Ludovini V, Magrini E, Gregorc V, Doglioni C, Sidoni A, Tonato M, Franklin WA, Crino L, Bunn PA Jr, Varella-Garcia M (2005) Epidermal growth factor receptor gene and protein and gefitinib sensitivity in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 97:643–655. doi:10.1093/jnci/dji112
Lark AL, Livasy CA, Dressler L, Moore DT, Millikan RC, Geradts J, Iacocca M, Cowan D, Little D, Craven RJ, Cance W (2005) High focal adhesion kinase expression in invasive breast carcinomas is associated with an aggressive phenotype. Mod Pathol 18:1289–1294. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800424
Schmitz KJ, Grabellus F, Callies R, Otterbach F, Wohlschlaeger J, Levkau B, Kimmig R, Schmid KW, Baba HA (2005) High expression of focal adhesion kinase (p125FAK) in node-negative breast cancer is related to overexpression of HER-2/neu and activated Akt kinase but does not predict outcome. Breast Cancer Res 7:R194–R203. doi:10.1186/bcr977
Turner CE, Schaller MD, Parsons JT (1993) Tyrosine phosphorylation of the focal adhesion kinase pp125FAK during development: relation to paxillin. J Cell Sci 105(Pt 3):637–645
Choschzick M, Lassen P, Lebeau A, Marx AH, Terracciano L, Heilenkotter U, Jaenicke F, Bokemeyer C, Izbicki J, Sauter G, Simon R (2010) Amplification of 8q21 in breast cancer is independent of MYC and associated with poor patient outcome. Mod Pathol. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2010.5
Roberts WG, Ung E, Whalen P, Cooper B, Hulford C, Autry C, Richter D, Emerson E, Lin J, Kath J, Coleman K, Yao L, Martinez-Alsina L, Lorenzen M, Berliner M, Luzzio M, Patel N, Schmitt E, LaGreca S, Jani J, Wessel M, Marr E, Griffor M, Vajdos F (2008) Antitumor activity and pharmacology of a selective focal adhesion kinase inhibitor, PF-562, 271. Cancer Res 68:1935–1944. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5155
Bagi CM, Roberts GW, Andresen CJ (2008) Dual focal adhesion kinase/Pyk2 inhibitor has positive effects on bone tumors: implications for bone metastases. Cancer 112:2313–2321. doi:10.1002/cncr.23429
Watanabe N, Takaoka M, Sakurama K, Tomono Y, Hatakeyama S, Ohmori O, Motoki T, Shirakawa Y, Yamatsuji T, Haisa M, Matsuoka J, Beer DG, Nagatsuka H, Tanaka N, Naomoto Y (2008) Dual tyrosine kinase inhibitor for focal adhesion kinase and insulin-like growth factor-I receptor exhibits anticancer effect in esophageal adenocarcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res 14:4631–4639. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-4755
Parsons JT, Slack-Davis J, Tilghman R, Roberts WG (2008) Focal adhesion kinase: targeting adhesion signaling pathways for therapeutic intervention. Clin Cancer Res 14:627–632. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-2220
Golubovskaya VM, Conway-Dorsey K, Edmiston SN, Tse CK, Lark AA, Livasy CA, Moore D, Millikan RC, Cance WG (2009) FAK overexpression and p53 mutations are highly correlated in human breast cancer. Int J Cancer 125:1735–1738. doi:10.1002/ijc.24486
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Korea Breast Cancer Foundation (2009). We thank Hye Jung Lee, Sat Pyul Kim, and Seung Hee Jung for their contributions to tissue array construction, FISH, and immunohistochemical studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yom, C.K., Noh, DY., Kim, W.H. et al. Clinical significance of high focal adhesion kinase gene copy number and overexpression in invasive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 128, 647–655 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-010-1150-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-010-1150-2