Abstract
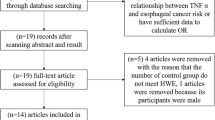
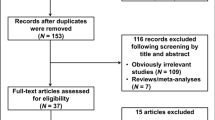
To date, many publications discussed the correlation between ERCC2 Asp312Asn polymorphism and breast cancer risk. However, the results were not unanimous. In order to derive a more precise conclusion, a meta-analysis was performed in this study by searching Medline, PubMed, and ISI Web of Knowledge databases. Finally, 17 studies including 12,019 cases and 10,747 controls were collected for this meta-analysis. The strength of association between ERCC2 Asp312Asn polymorphism and breast cancer risk was assessed by calculating crude ORs with 95% CIs. Overall, no significant associations between ERCC2 Asp312Asn polymorphism and breast cancer susceptibility were found. In the stratified analysis by ethnicity, significant associations were observed for Asn/Asn versus Asp/Asp (OR = 0.55; 95% CI 0.32–0.96) and Asn/Asn versus Asn/Asp + Asp/Asp (OR = 0.53; 95% CI 0.32–0.90) in Asians. In the stratified analysis by study design, significant associations were found for Asn/Asn versus Asp/Asp (OR = 0.79; 95% CI 0.64–0.98) and Asn/Asn versus Asn/Asp + Asp/Asp (OR = 0.82; 95% CI 0.68–0.99) in population-based studies. In conclusion, this meta-analysis provides an evidence that ERCC2 312Asn allele may have a protective effect for breast cancer development in Asians.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ (2009) Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin 59:225–249
Lunn RM, Helzlsouer KJ, Parshad R, Umbach DM, Harris EL, Sanford KK, Bell DA (2000) XPD polymorphisms: effects on DNA repair proficiency. Carcinogenesis 21:551–555
Bernstein C, Bernstein H, Payne CM, Garewal H (2002) DNA repair/pro-apoptotic dual-role proteins in five major DNA repair pathways: fail-safe protection against carcinogenesis. Mutat Res 511:145–178
Wang XW, Vermeulen W, Coursen JD, Gibson M, Lupold SE, Forrester K, Xu G, Elmore L, Yeh H, Hoeijmakers JH, Harris CC (1996) The XPB and XPD DNA helicases are components of the p53-mediated apoptosis pathway. Genes Dev 10:1219–1232
Manuguerra M, Saletta F, Karagas MR, Berwick M, Veglia F, Vineis P, Matullo G (2006) XRCC3 and XPD/ERCC2 single nucleotide polymorphisms and the risk of cancer: a HuGE review. Am J Epidemiol 164:297–302
Wang F, Chang D, Hu FL, Sui H, Han B, Li DD, Zhao YS (2008) DNA repair gene XPD polymorphisms and cancer risk: a meta-analysis based on 56 case-control studies. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 17:507–517
Seker H, Butkiewicz D, Bowman ED, Rusin M, Hedayati M, Grossman L, Harris CC (2001) Functional significance of XPD polymorphic variants: attenuated apoptosis in human lymphoblastoid cells with the XPD 312 Asp/Asp genotype. Cancer Res 61:7430–7434
Tang D, Cho S, Rundle A, Chen S, Phillips D, Zhou J, Hsu Y, Schnabel F, Estabrook A, Perera FP (2002) Polymorphisms in the DNA repair enzyme XPD are associated with increased levels of PAH-DNA adducts in a case-control study of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 75:159–166
Försti A, Angelini S, Festa F, Sanyal S, Zhang Z, Grzybowska E, Pamula J, Pekala W, Zientek H, Hemminki K, Kumar R (2004) Single nucleotide polymorphisms in breast cancer. Oncol Rep 11:917–922
Justenhoven C, Hamann U, Pesch B, Harth V, Rabstein S, Baisch C, Vollmert C, Illig T, Ko YD, Brüning T, Brauch H (2004) ERCC2 genotypes and a corresponding haplotype are linked with breast cancer risk in a German population. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 13:2059–2064
Shi Q, Wang LE, Bondy ML, Brewster A, Singletary SE, Wei Q (2004) Reduced DNA repair of benzo[a]pyrene diol epoxide-induced adducts and common XPD polymorphisms in breast cancer patients. Carcinogenesis 25:1695–1700
Kuschel B, Chenevix-Trench G, Spurdle AB, Chen X, Hopper JL, Giles GG, McCredie M, Chang-Claude J, Gregory CS, Day NE, Easton DF, Ponder BA, Dunning AM, Pharoah PD (2005) Common polymorphisms in ERCC2 (Xeroderma pigmentosum D) are not associated with breast cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 14:1828–1831
Lee SA, Lee KM, Park WY, Kim B, Nam J, Yoo KY, Noh DY, Ahn SH, Hirvonen A, Kang D (2005) Obesity and genetic polymorphism of ERCC2 and ERCC4 as modifiers of risk of breast cancer. Exp Mol Med 37:86–90
Zhang L, Zhang Z, Yan W (2005) Single nucleotide polymorphisms for DNA repair genes in breast cancer patients. Clin Chim Acta 359:150–155
Debniak T, Scott RJ, Huzarski T, Byrski T, Masojć B, van de Wetering T, Serrano-Fernandez P, Górski B, Cybulski C, Gronwald J, Debniak B, Maleszka R, Kładny J, Bieniek A, Nagay L, Haus O, Grzybowska E, Wandzel P, Niepsuj S, Narod SA, Lubinski J (2006) XPD common variants and their association with melanoma and breast cancer risk. Breast Cancer Res Treat 98:209–215
Mechanic LE, Millikan RC, Player J, de Cotret AR, Winkel S, Worley K, Heard K, Heard K, Tse CK, Keku T (2006) Polymorphisms in nucleotide excision repair genes, smoking and breast cancer in African Americans and whites: a population-based case-control study. Carcinogenesis 27:1377–1385
Shen J, Desai M, Agrawal M, Kennedy DO, Senie RT, Santella RM, Terry MB (2006) Polymorphisms in nucleotide excision repair genes and DNA repair capacity phenotype in sisters discordant for breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 15:1614–1619
Crew KD, Gammon MD, Terry MB, Zhang FF, Zablotska LB, Agrawal M, Shen J, Long CM, Eng SM, Sagiv SK, Teitelbaum SL, Neugut AI, Santella RM (2007) Polymorphisms in nucleotide excision repair genes, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-DNA adducts, and breast cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 16:2033–2041
Jorgensen TJ, Visvanathan K, Ruczinski I, Thuita L, Hoffman S, Helzlsouer KJ (2007) Breast cancer risk is not associated with polymorphic forms of xeroderma pigmentosum genes in a cohort of women from Washington County, Maryland. Breast Cancer Res Treat 101:65–71
Bernard-Gallon D, Bosviel R, Delort L, Fontana L, Chamoux A, Rabiau N, Kwiatkowski F, Chalabi N, Satih S, Bignon YJ (2008) DNA repair gene ERCC2 polymorphisms and associations with breast and ovarian cancer risk. Mol Cancer 7:36
Smith TR, Levine EA, Freimanis RI, Akman SA, Allen GO, Hoang KN, Liu-Mares W, Hu JJ (2008) Polygenic model of DNA repair genetic polymorphisms in human breast cancer risk. Carcinogenesis 29:2132–2138
Jakubowska A, Gronwald J, Menkiszak J, Górski B, Huzarski T, Byrski T, Tołoczko-Grabarek A, Gilbert M, Edler L, Zapatka M, Eils R, Lubiński J, Scott RJ, Hamann U (2010) BRCA1-associated breast and ovarian cancer risks in Poland: no association with commonly studied polymorphisms. Breast Cancer Res Treat 119:201–211
Cochran WG (1954) The combination of estimates from different experiments. Biometrics 10:101–129
Mantel N, Haenszel W (1959) Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J Natl Cancer Inst 22:719–748
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7:177–188
Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315:629–634
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National 973 Programs of China Grants 2004CB518605, the National 863 Project of China Grants 2006AA020501, and the National Key Sci-Tech Special Project of China Grants 2008ZX10002-020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Lei Yao and Li-Xin Qiu contributed equally to this work and should be considered as co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, L., Qiu, LX., Yu, L. et al. The association between ERCC2 Asp312Asn polymorphism and breast cancer risk: a meta-analysis involving 22,766 subjects. Breast Cancer Res Treat 123, 227–231 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-010-0754-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-010-0754-x